Important diagrams in biology.ppt
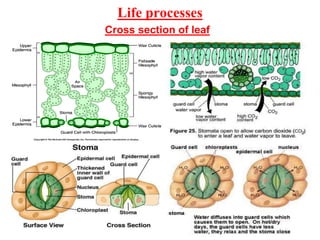
- 1. Life processes Cross section of leaf
- 2. Nutrition in animals :- a) Nutrition in amoeba :- Amoeba is a unicellular animal living in water. It takes in food by forming finger like projections called pseudopodia and forms a food vacuole. Inside the food vacuole the food is digested and absorbed. The undigested food is then sent out through the surface of the cell.
- 4. Breakdown of glucose by various pathways :- presence of oxygen CO2 + H2O + Energy (in mitochondria) presence absence of oxygen of oxygen Glucose Pyruvate Lactic acid + Energy in cytoplasm + (in muscle Energy cells) absence of oxygen Ethanol + CO2 + Energy (in yeast)
- 6. Mechanism of breathing :- When we breathe in air, the muscles of the diaphragm contracts and moves downward and the chest cavity expands and air enters into the lungs. When we breathe out air, the muscles of the diaphragm relaxes and moves upward and the chest cavity contracts and air goes out of the lungs.
- 7. Working of the heart (Circulation of blood) :-
- 8. Human excretory system Structure of Nephron
- 9. Control and coordination Nerve endings ( ) Nerve cell
- 10. HUMAN BRAIN
- 11. Reflex arc :- The pathway of a reflex action is called reflex arc. In a reflex arc the stimulus is received by the receptors (sense organs) and it passes through the sensory nerves to the spinal cord. From the spinal cord the information passes through the motor nerves to the effectors (muscles/glands) for the response. Stimulus Response Receptors (Sense organ) Effectors (Muscles/Glands) Sensory nerves Motor nerves Spinal cord
- 12. REFLEX ARC
- 13. ENDOCRINE GLANDS IN HUMAN BEINGS
- 14. How do organisms reproduce Fission :- is an asexual reproduction by which a unicellular organism divides and forms two or more new individuals. Fission is of two types. They are binary fission and multiple fission. i) Binary fission :- In this method an organism divides and forms two individuals. First the nucleus divides and forms two nuclei. Then the cytoplasm divides and forms two daughter cells. Eg:- Amoeba, Paramaecium etc. ii) Multiple fission :- In this method one organism divides into many daughter cells. Eg.Plasmodium (Malarial parasite).
- 15. Budding :- In this method a bud like projection is formed on the body of the organism. The bud then develops into a new individual. It then separates from the parent and forms an independent individual. Eg:- Hydra, Yeast etc.
- 16. Regeneration :- In this method a part of the body if the organism if cut or broken can develop into a new individual. Eg :- Hydra, Planaria, Star fish etc.
- 17. Fragmentation :- In this method the body of a simple multicellular organism breaks up into smaller pieces on maturation and each fragment develops into new individuals. Eg :- Spirogyra.
- 18. Spore formation :- In this method structures called sporangia produce tiny cells called spores. When the spores come in contact with a moist surface, it develops into new individuals. Eg :- Rhizopus , Mucor, Penicillium etc.
- 19. Sexual reproduction in flowering plants :- a) Reproductive parts of a flower :- The stamen and pistil are the reproductive parts of the flower. Stamen is the male reproductive part. It produces pollen grains in the anther which contains the male germ cell (male gamete). Pistil is the female reproductive part. It produces ovules in the ovary which contain the female germ cell (female gamete).
- 20. b) Pollination :- The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. It takes place by wind, water or insects. If the pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower it is self pollination and if it is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower it is cross pollination. Pollination takes place by insects, wind, water etc. Self pollination Cross pollination
- 21. c) Fertilisation :- After the pollen grain is transferred to the stigma it produces a pollen tube which passes through the style and enters the ovary and ovule. In the ovule the male germ cell (male gamete) fuses with the female germ cell (female gamete) to form a zygote. This process is called fertilisation. After fertilisation the zygote divides several times and forms the embryo which then develops into the seed and the ovary develops into the fruit.
- 24. Heridity and evolution a) When plants having one pair of character (Eg :- tall and short plant) was crossed (Monohybrid cross) :- Mendel selected pea plants having one pair of character – a tall pea plant and a short pea plant. He selected pure tall (TT) and pure short (tt) pea plants and cross pollinated them. He obtained all tall plants (Tt) in the first generation (F1 ). When the first generation plants were self pollinated, he obtained tall and dwarf plants in the ratio 3:1 in the second generation. (F2) The ratio of pure tall (TT), hybrid tall (Tt) and pure dwarf (tt) was in the ratio 1:2:1 The trait that is expressed in the F1 generation is called the dominant trait and the trait that is supressed in the F1 is called the recessive trait.
- 25. b) When plants having two pairs of characters (Eg:- shape and colour of seeds) were crossed (Dihybrid cross) :- Mendel selected pea plants having two pairs of characters – shape and colour of seed. He selected plants having round yellow seeds (RRYY) and wrinkled green seeds (rryy) and cross pollinated them. He obtained all plants with round yellow seeds (RrYy) in the F1 generation. When these plants were self pollinated in the F2 generation out of 16 plants, 9 had round yellow (RrYy), 3 had round green (Rryy), 3 had wrinkled yellow (rrYy) and 1 had wrinkled green (rryy) seed. In the ratio 9:3:3:1.
- 26. Sex determination in human beings :- Human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell. Out of this two chromosomes are sex chromosomes X and Y. The female has two X chromosomes (XX) and male has one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The sperms and eggs have one set of sex chromosomes. Some sperms have X chromosome and some have Y chromosome. All eggs have X chromosome. If a sperm having X chromosome fuses with an egg having X chromosome the child will be a girl. If a sperm having Y chromosome fuses with an egg having X chromosome the child will be a boy.
- 27. Homologous organs :- are organs which are similar in structure but different in functions. Eg :- The fore limbs of amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals have similar structures but different functions. Frog (amphibian) uses its fore limb to raise the front of the body. Lizard (reptile) uses its fore limb for walking and running. Birds fore limbs are modified as wings for flying. Mammals use the fore limbs for grasping, walking, running, swimming, flying etc. This shows evolutionary relationship.
- 28. Analogous organs :- are organs which are different in structures but similar in functions. Eg :- The wings of butterfly, bird and bat have different structures but similar functions. This shows evolutionary relationship.
- 29. c) Fossils :- are the remains of organisms which lived long ago. From the study of fossils we can know their structures and the time period in which they lived. The fossils of complex and recent organisms are found closer to the surface of the earth and the fossils of simpler organisms are found deeper inside the earth. The age of fossils can be determined by Radio Carbon Dating. The study of fossils show evolution of simpler forms into complex forms and their evolutionary relationship. Tree trunk fossil Fish fossil (Knightia)
- 30. Evolution by stages :- Complex organisms and its organs developed from simpler organisms gradually over generations. i) Evolution of eyes :- The eyes of planaria are just eye spots to detect light. It developed gradually into a complex organ in higher animals. ii) Evolution of feathers :- Feathers were first developed in dinosaurs and used for protection from cold. Later birds used them for flying. iii) Evolution by artificial selection :- Humans cultivated wild cabbage for over 2000 years and produced different vegetables from it by artificial selection. Eg :- Cabbage – by selecting short distance between the leaves. Cauliflower – by selecting sterile flowers. Kale – by selecting large leaves Kholrabi – by selecting the swollen stem Broccoli – by arresting flower growth
- 31. Our environment A food chain :- is the flow of food energy from one organism to the next and to the next and so on. They usually start with a producer (plants) and end with a carnivore. In a food chain an organism gets food from one group of organisms. eaten by eaten by Eg:- Grass Deer Lion (producer) (primary consumer) (secondary consumer) eaten by eaten by eaten by Grass Insects Frog Snake (producer) (primary consumer) (secondary consumer) (tertiary consumer) eaten by eaten by eaten by eaten by Grass Moth Frog Snake Hawk (producer) (primary consumer) (secondary consumer) (tertiary consumer) (quarternary consumer)
- 32. b) Food web :- Food web is a group of several interconnected food chains. In a food web an organism gets food from more than one group of organisms.
- 33. Trophic levels :- Each step in a food chain where transfer of food energy takes place is called trophic level. The first trophic level consists of producers. The second trophic level consists of primary consumers. The third trophic level consists of secondary consumers. The fourth trophic level consists of tertiary consumers. Since the transfer of food energy decreases at every trophic level, the number of trophic levels are limited and do not exceed four or five.
- 34. Energy flow in trophic levels:- Green plants (producers) absorb about 1% of solar energy falling on the leaves and stores it as food energy during photosynthesis. During the transfer of food energy from one trophic level to the next, 90% of the energy is lost to the environment and only 10% is transferred to the next trophic level. So there is a decrease in the amount of food energy transferred at every trophic level by 10%. This is known as the 10% law.
- 35. Biological magnification (Biomagnification):- Harmful chemicals like insecticides and pesticides which are used to protect crops from insects and pests are absorbed by plants and enter the food chain. Since these chemicals are non biodegradable, they get accumulated at every trophic level and their concentration increases. Since human beings occupy the highest trophic level, the concentration of these harmful chemicals is maximum in our bodies. The increase in concentration of harmful chemicals in the bodies of organisms at higher trophic levels is called biological magnification.
