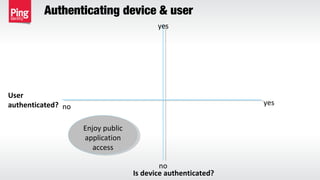
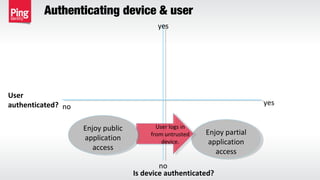
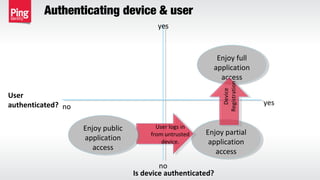
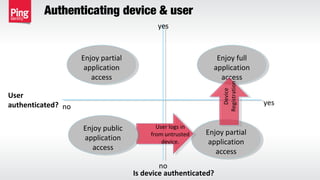
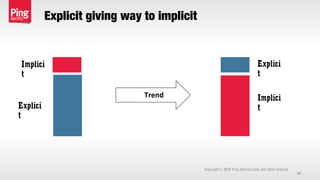
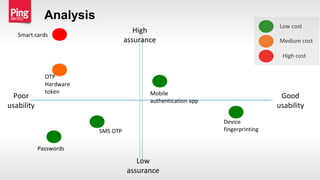
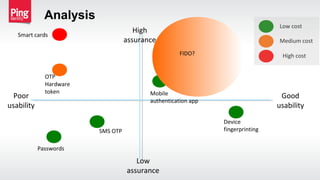
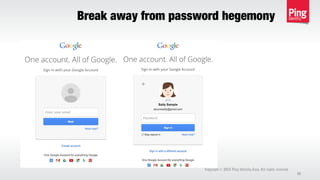
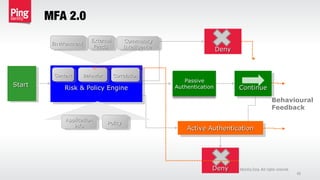
The document discusses the importance of multi-factor authentication (MFA) in enhancing enterprise security by mitigating vulnerabilities associated with single-factor authentication. It explores various authentication factors, trends, and contextual verification to dynamically assess risk and optimize security, usability, and cost. Key recommendations include adopting risk-based MFA that evaluates the potential harm and likelihood of authentication mistakes while providing flexible options for different user scenarios.