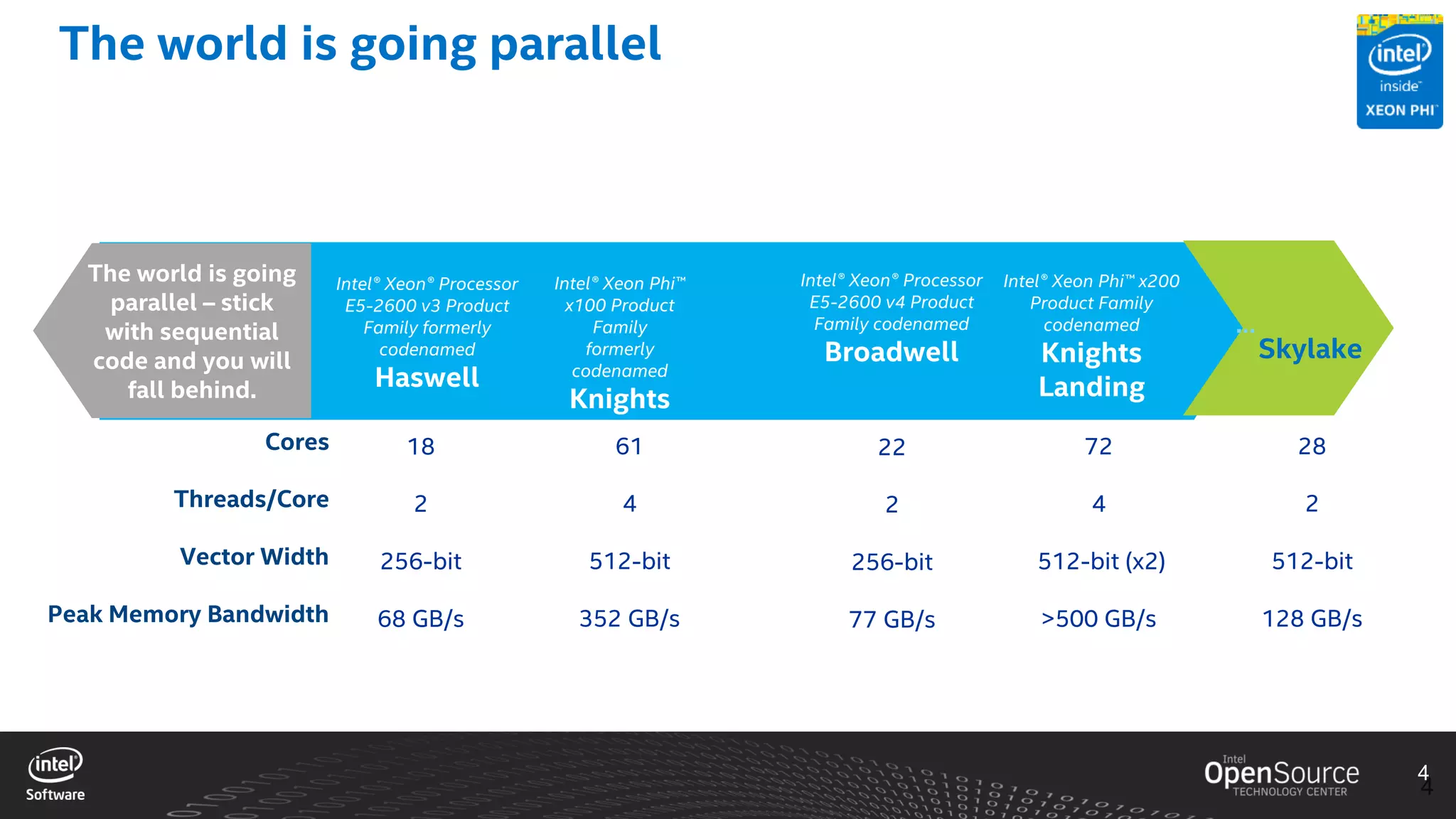
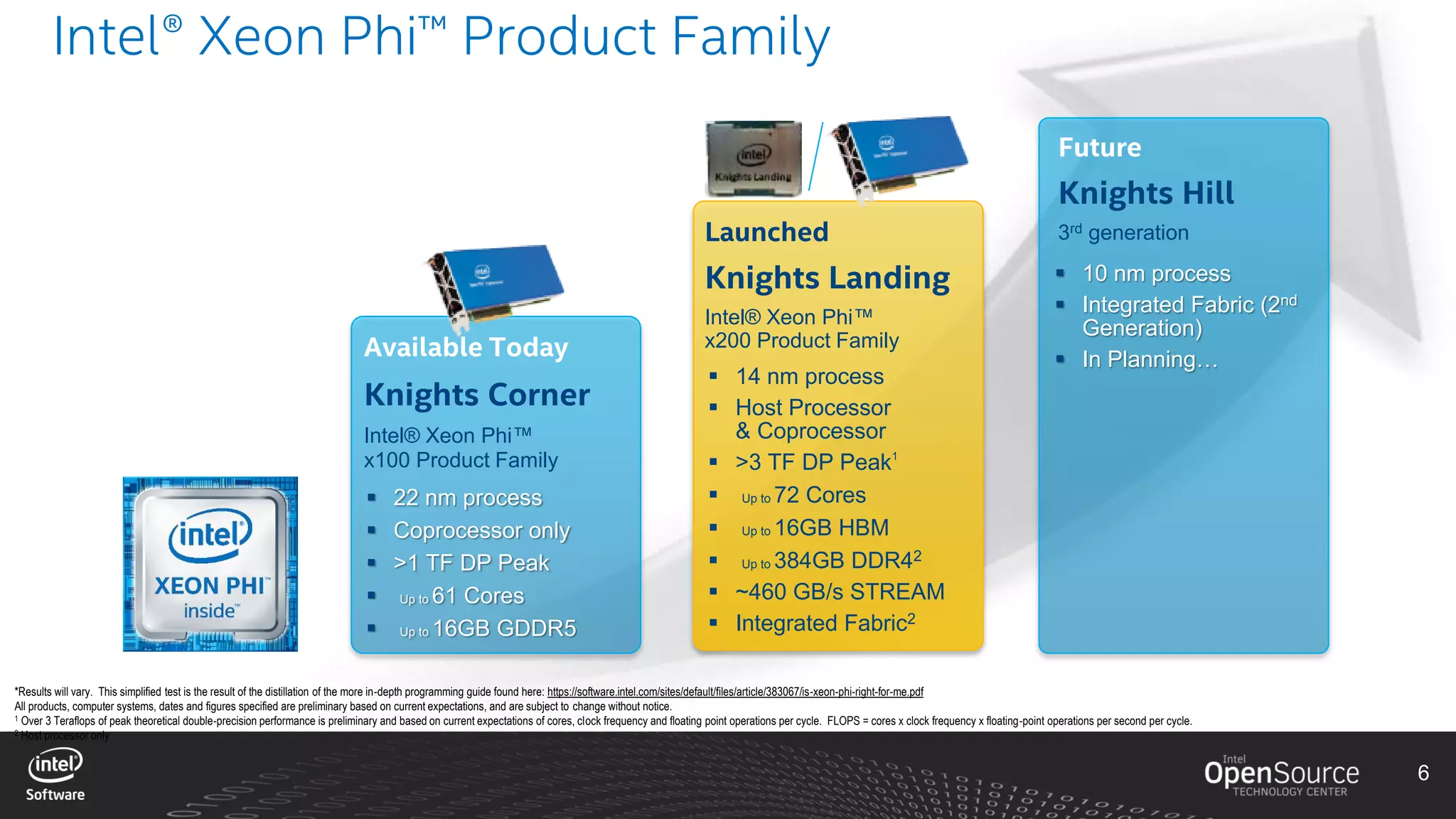
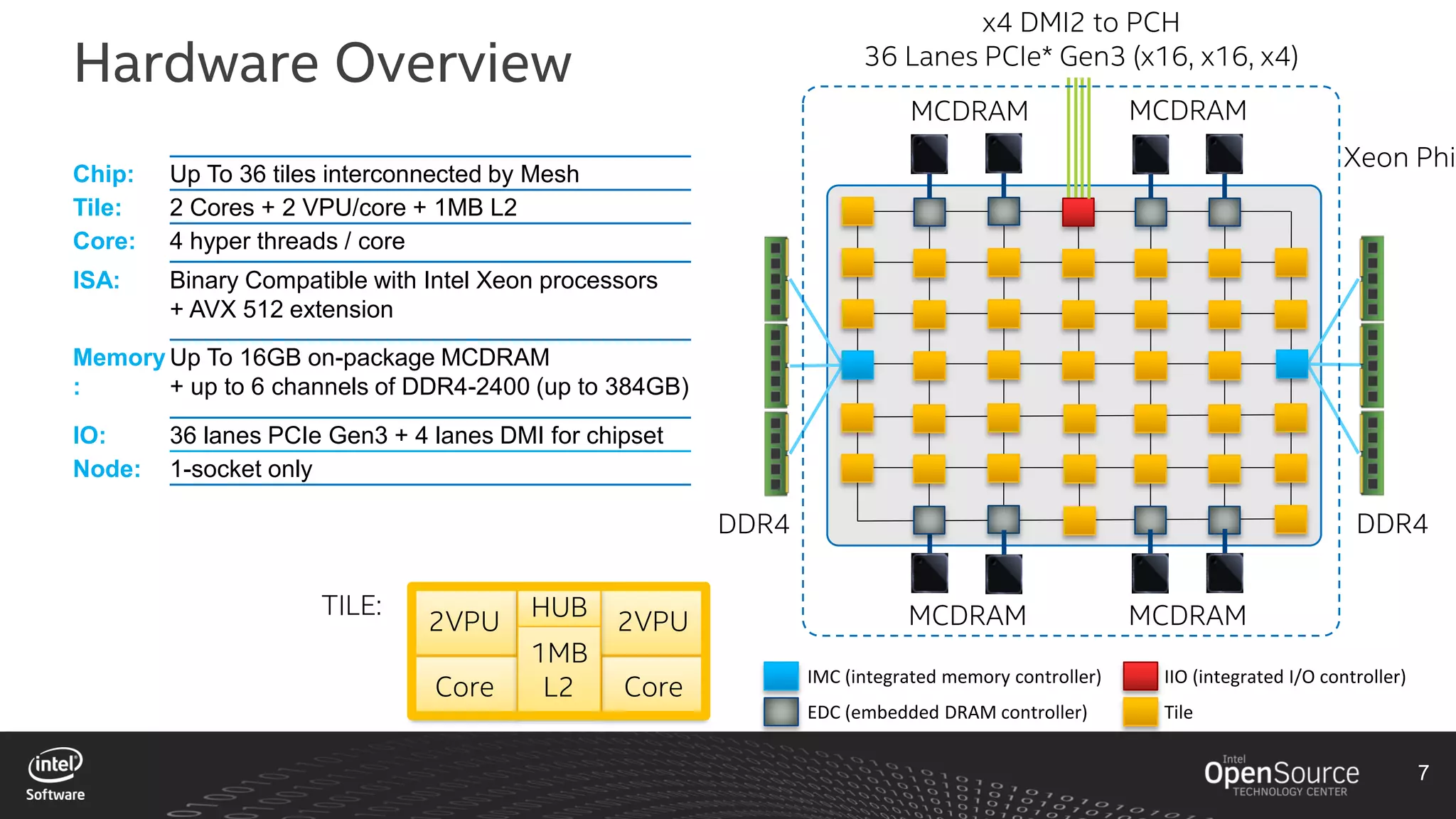
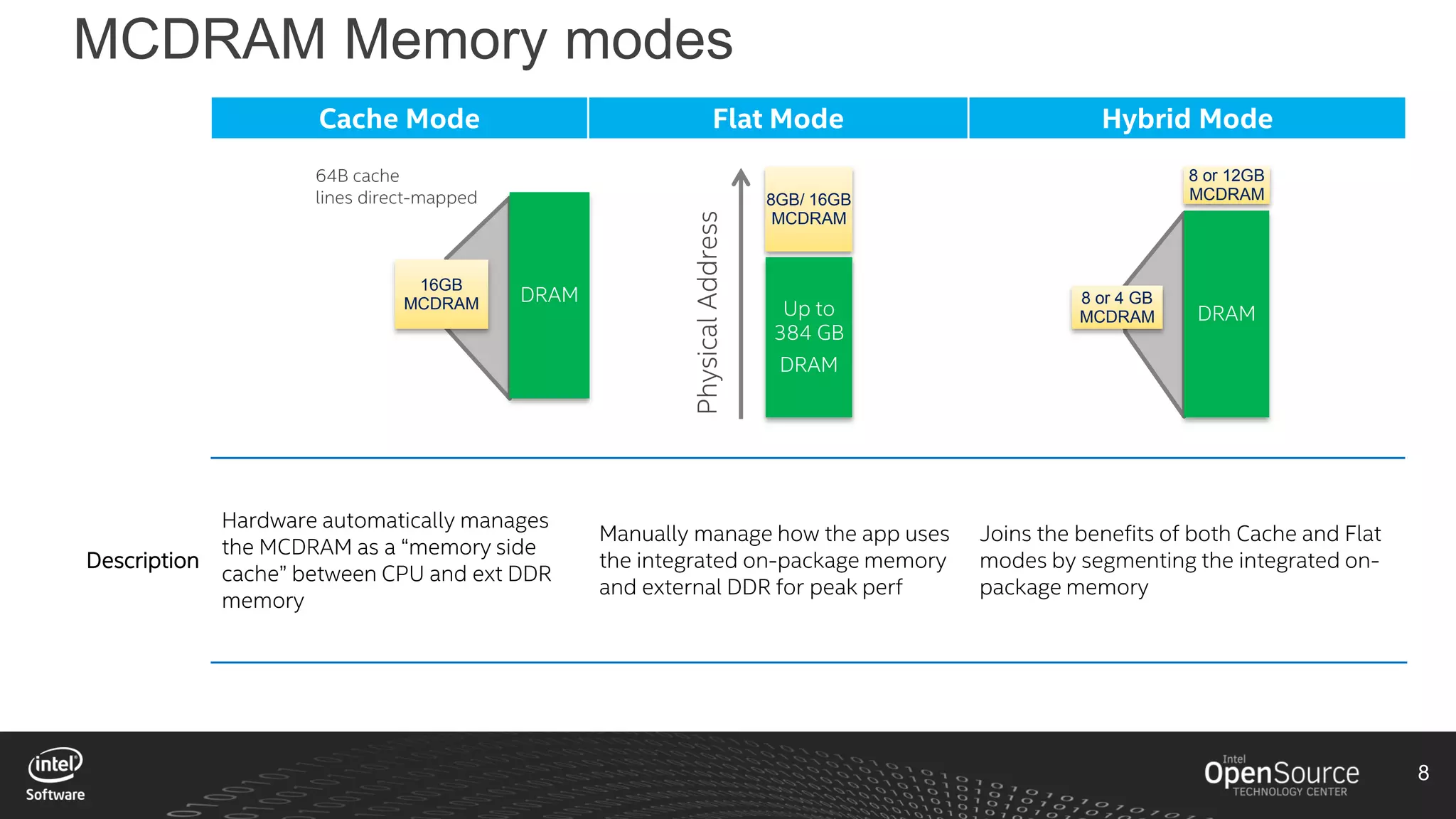
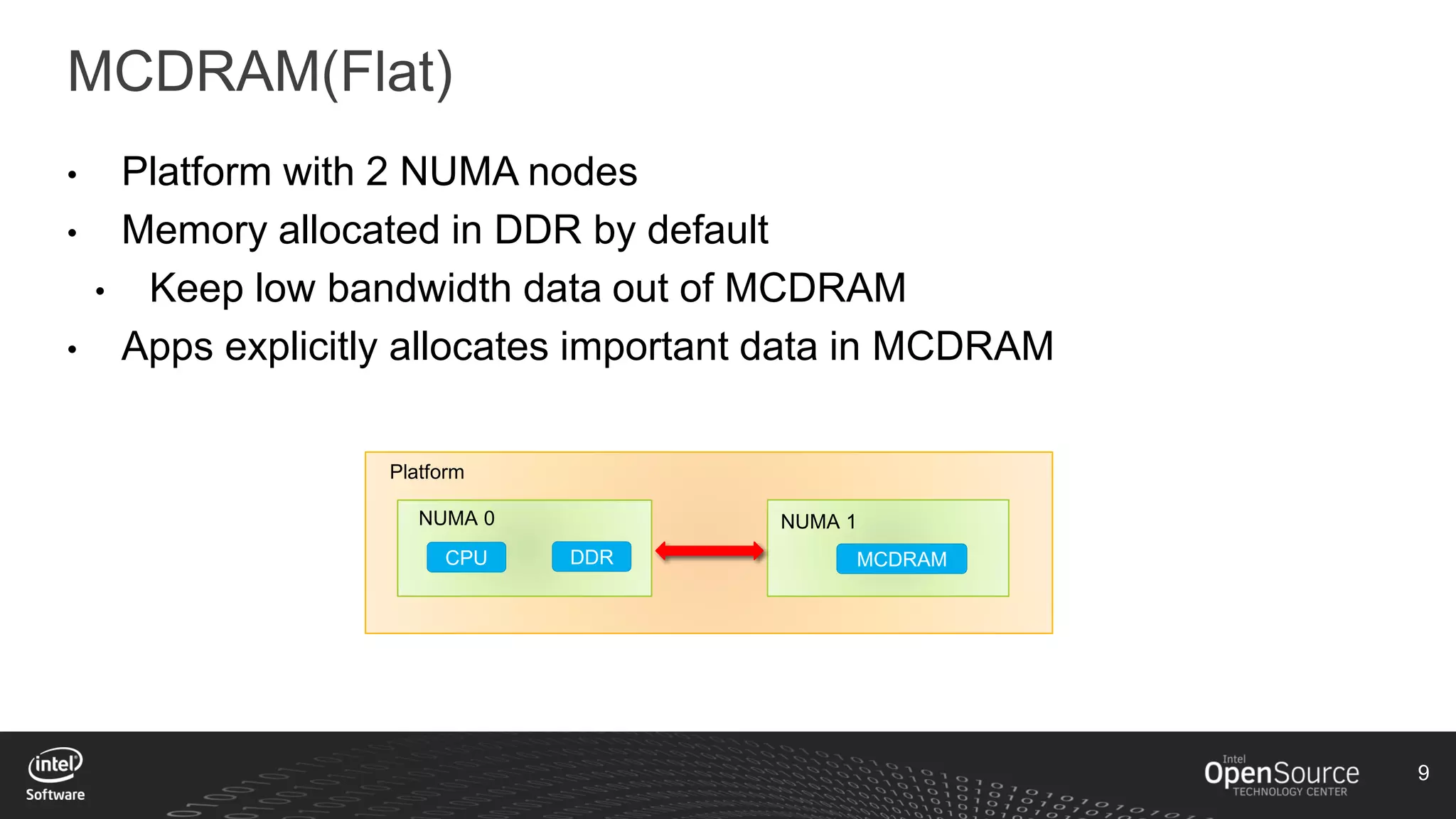
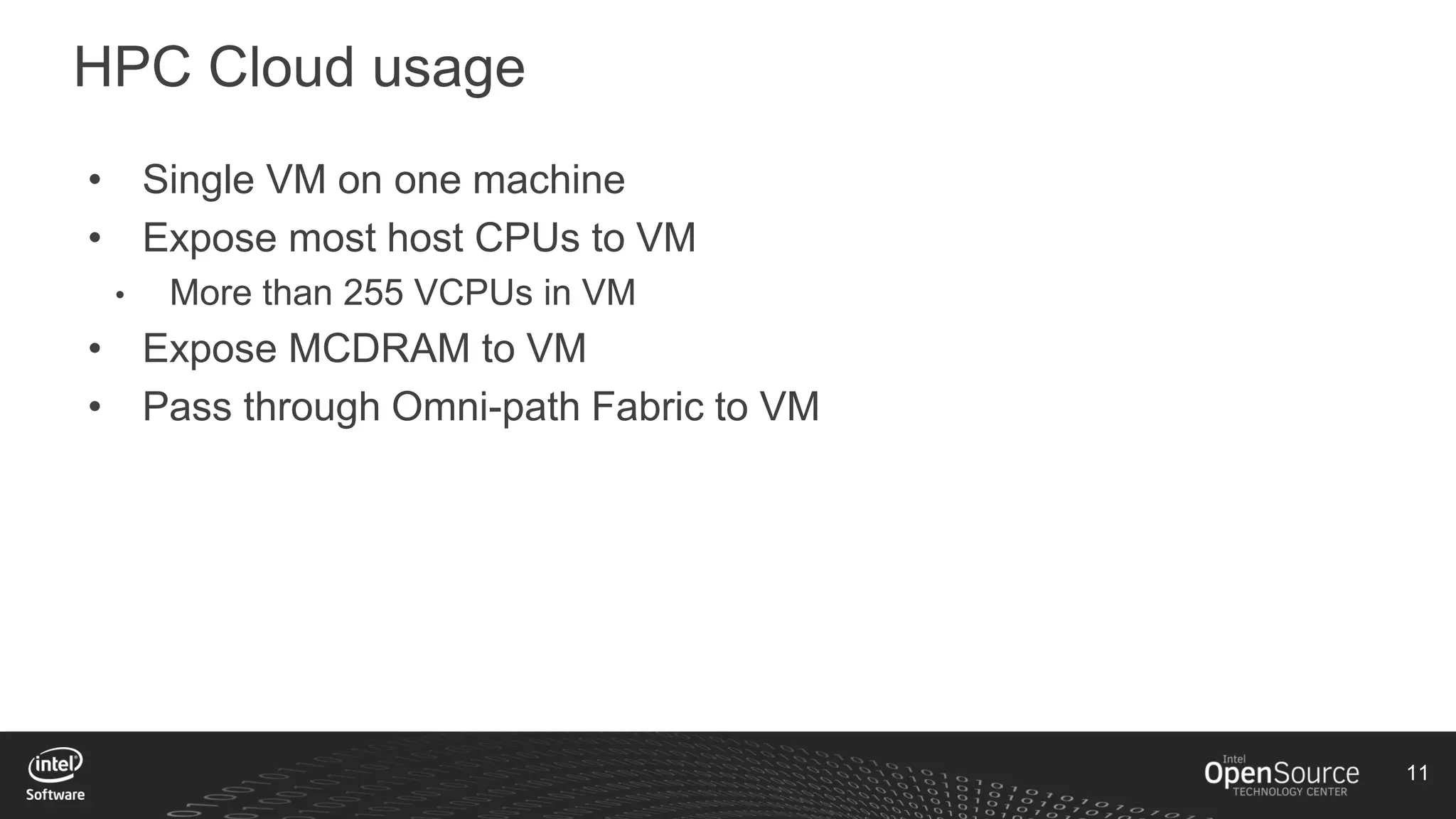
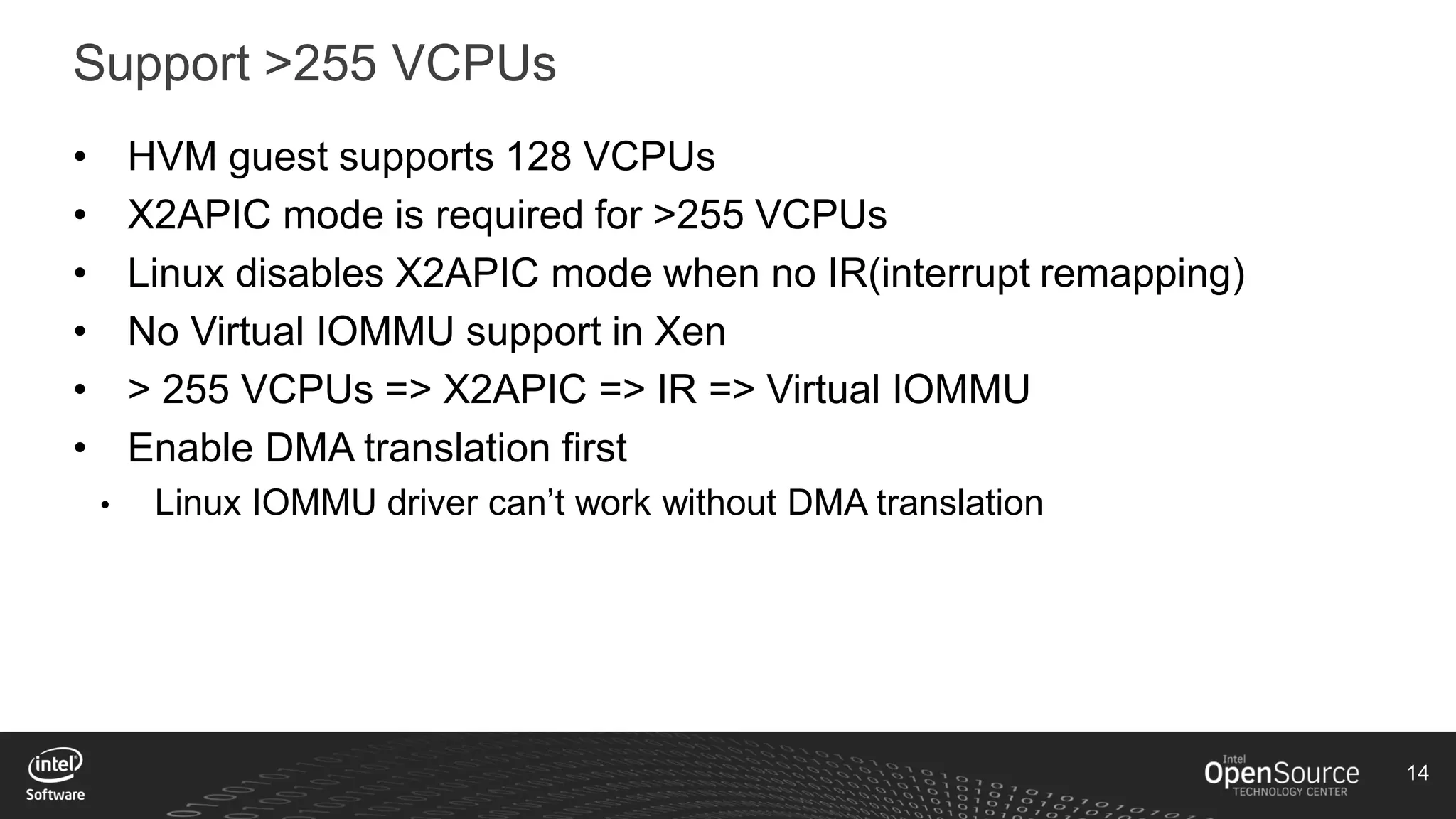
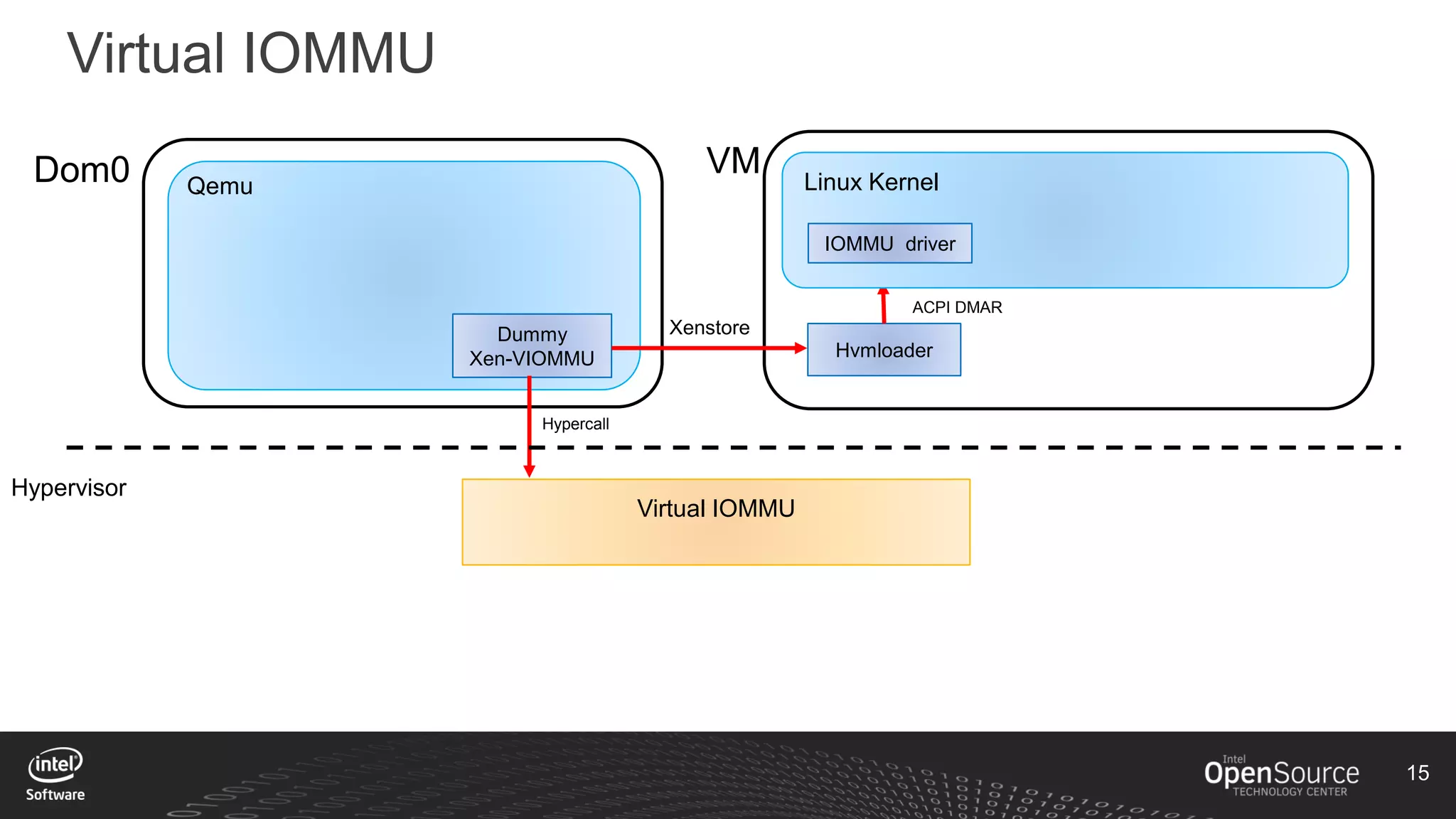
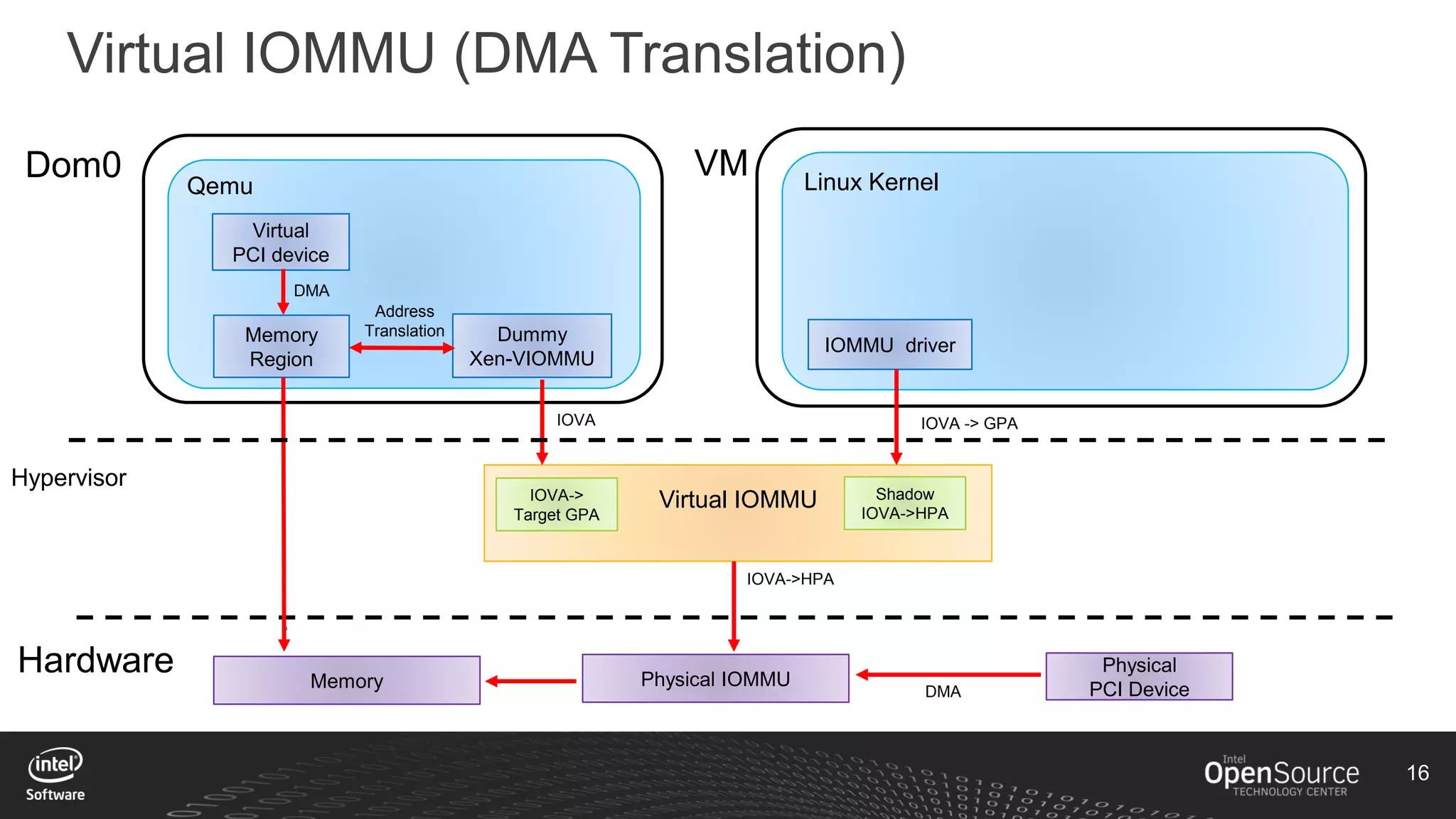
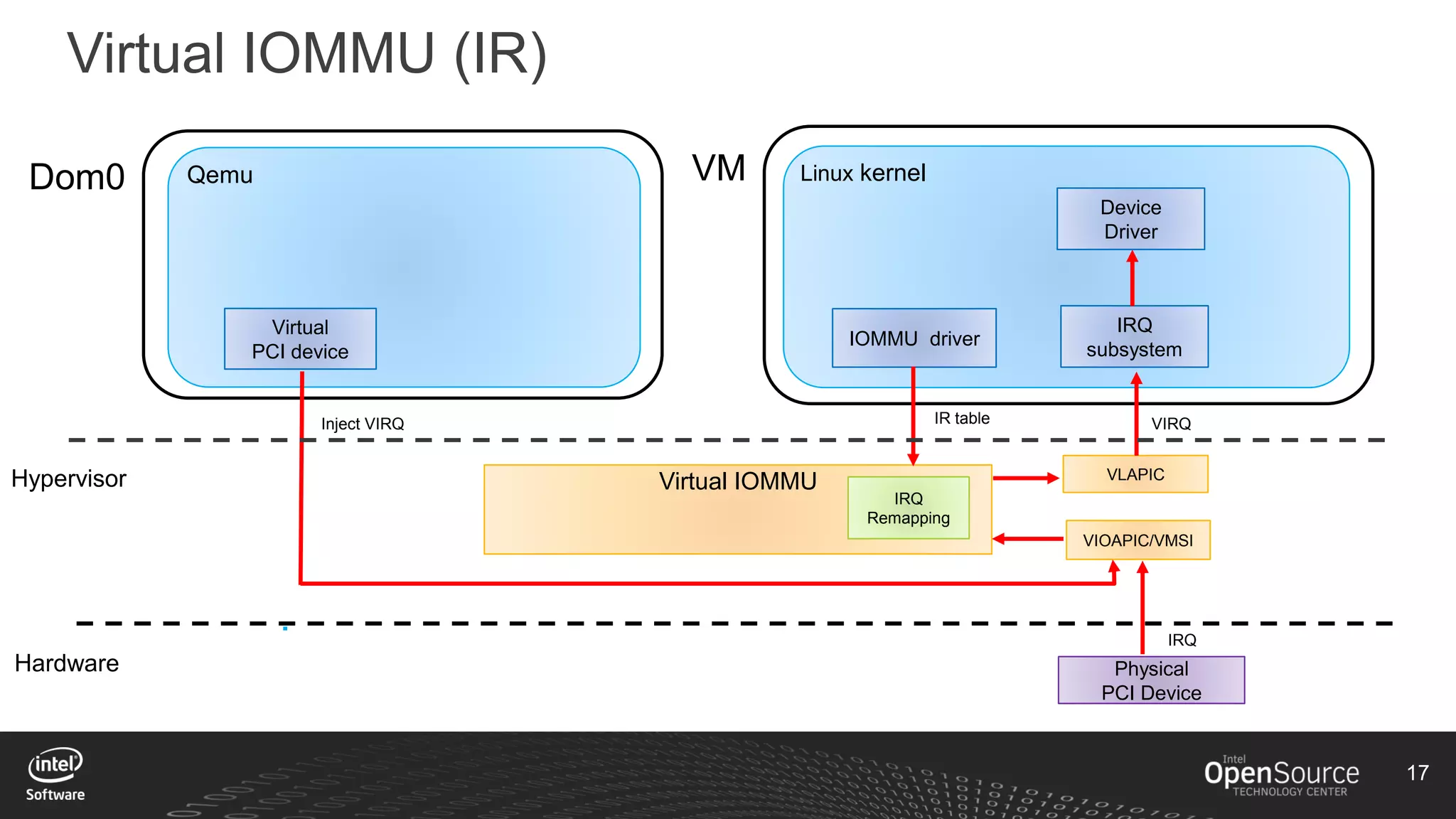
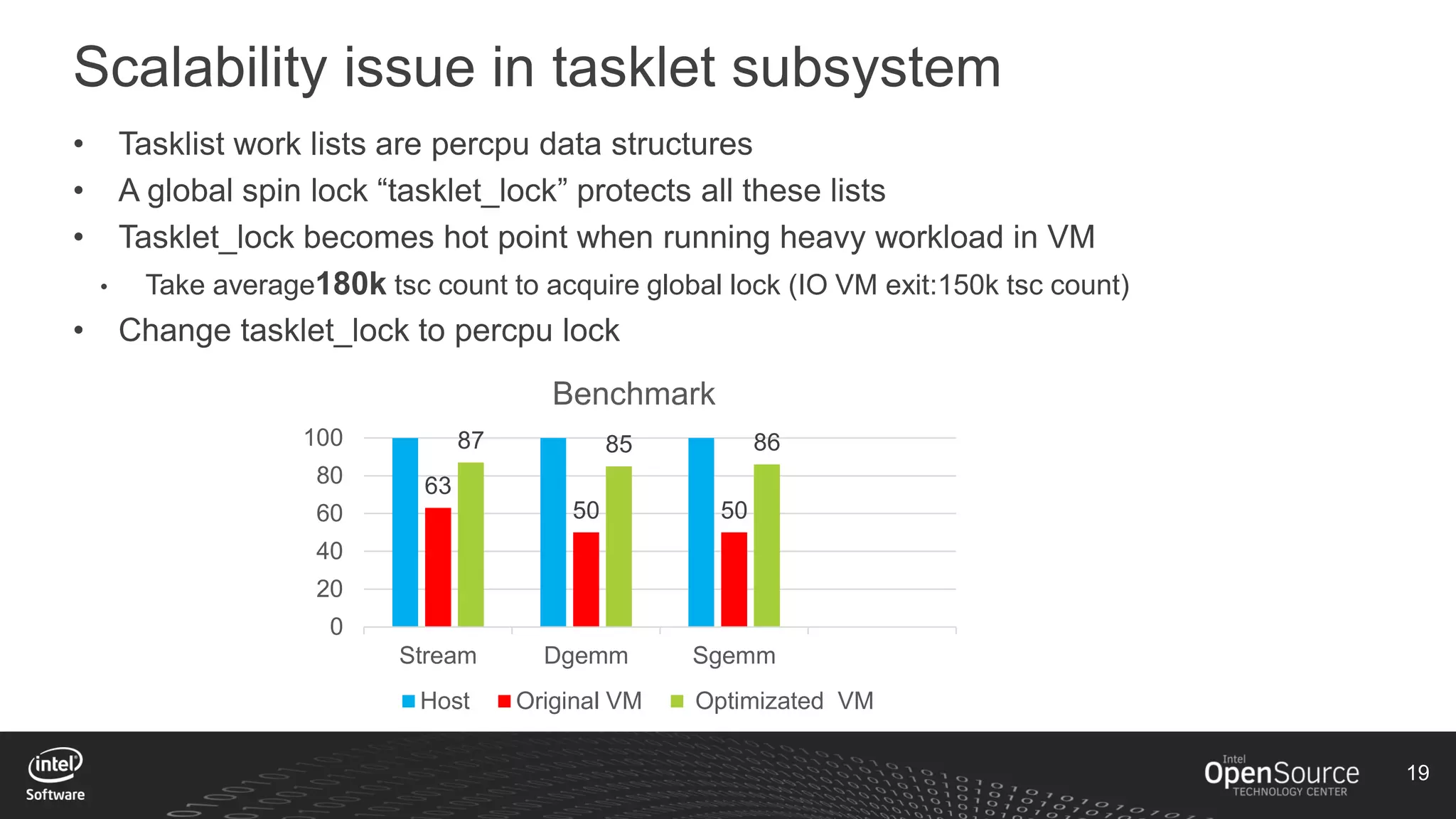
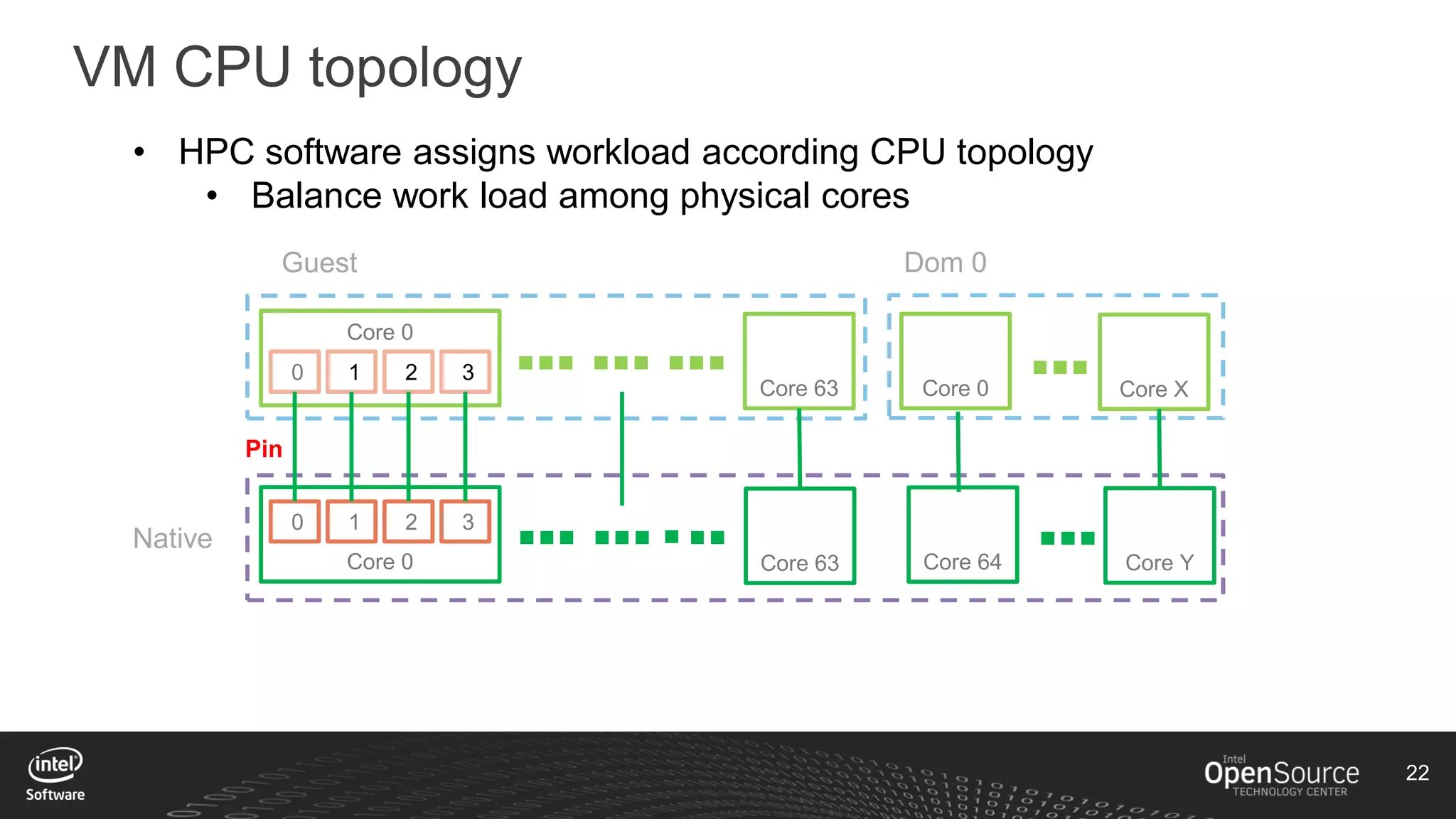
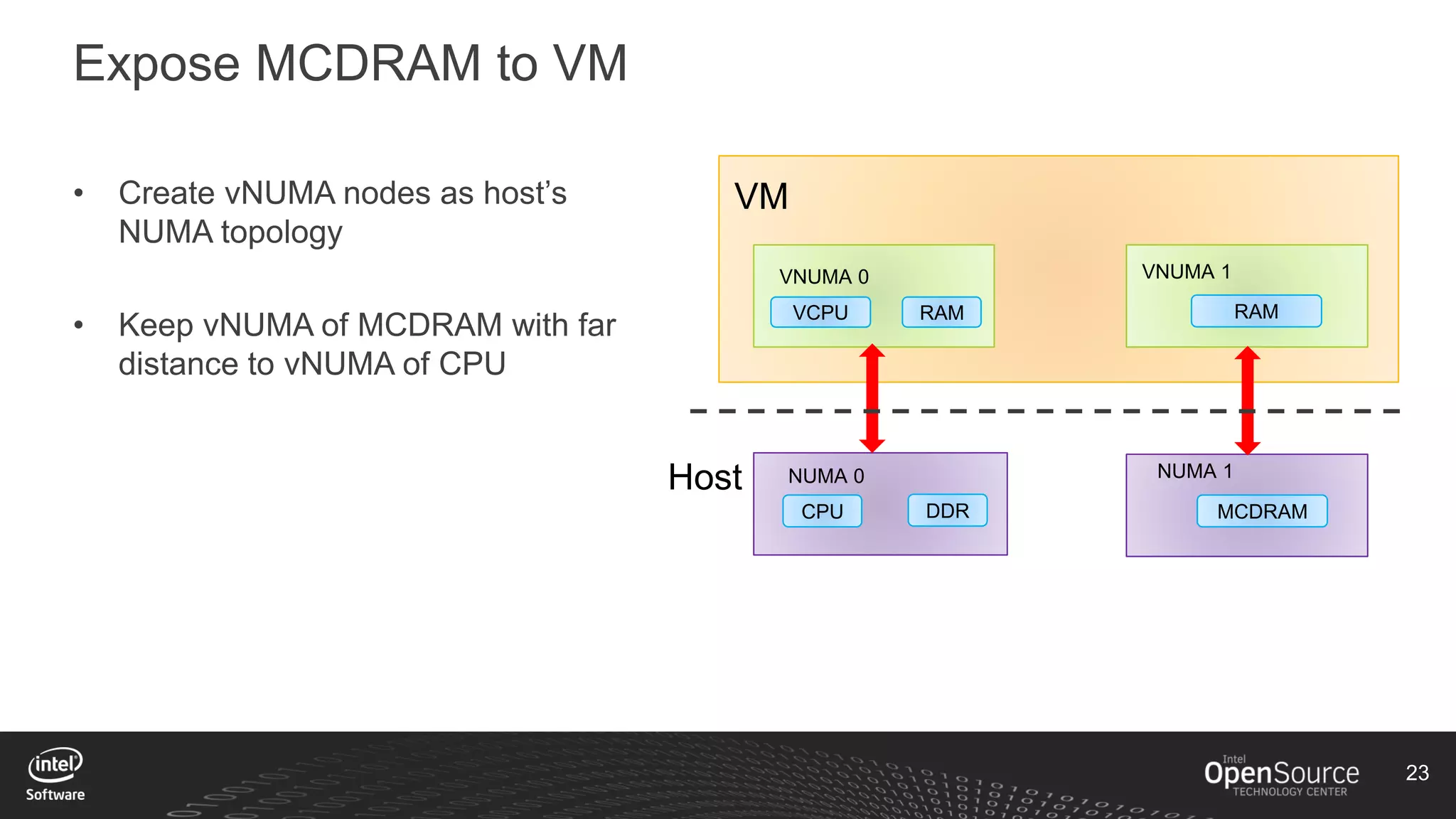
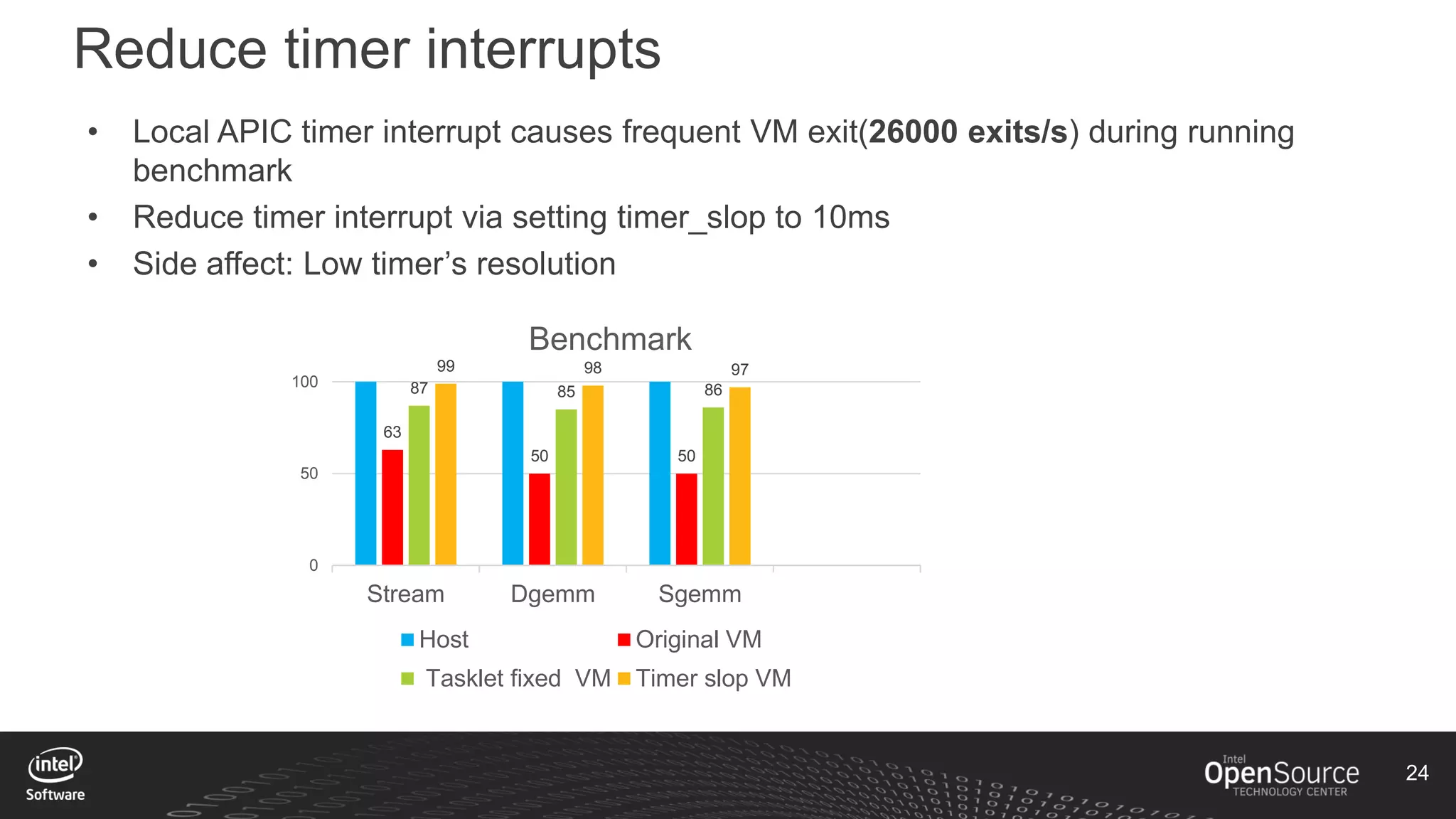
The document discusses high-performance virtualization for HPC (High-Performance Computing) on Xen, focusing on the Intel® Xeon Phi™ product family designed for cloud usage. It outlines challenges faced by Xen, such as support for more than 255 virtual CPUs and the need for virtual IOMMU support, as well as strategies to achieve high performance through optimizing compute resources. A call for action emphasizes the necessity of making changes in Xen to improve virtualization capabilities and performance.