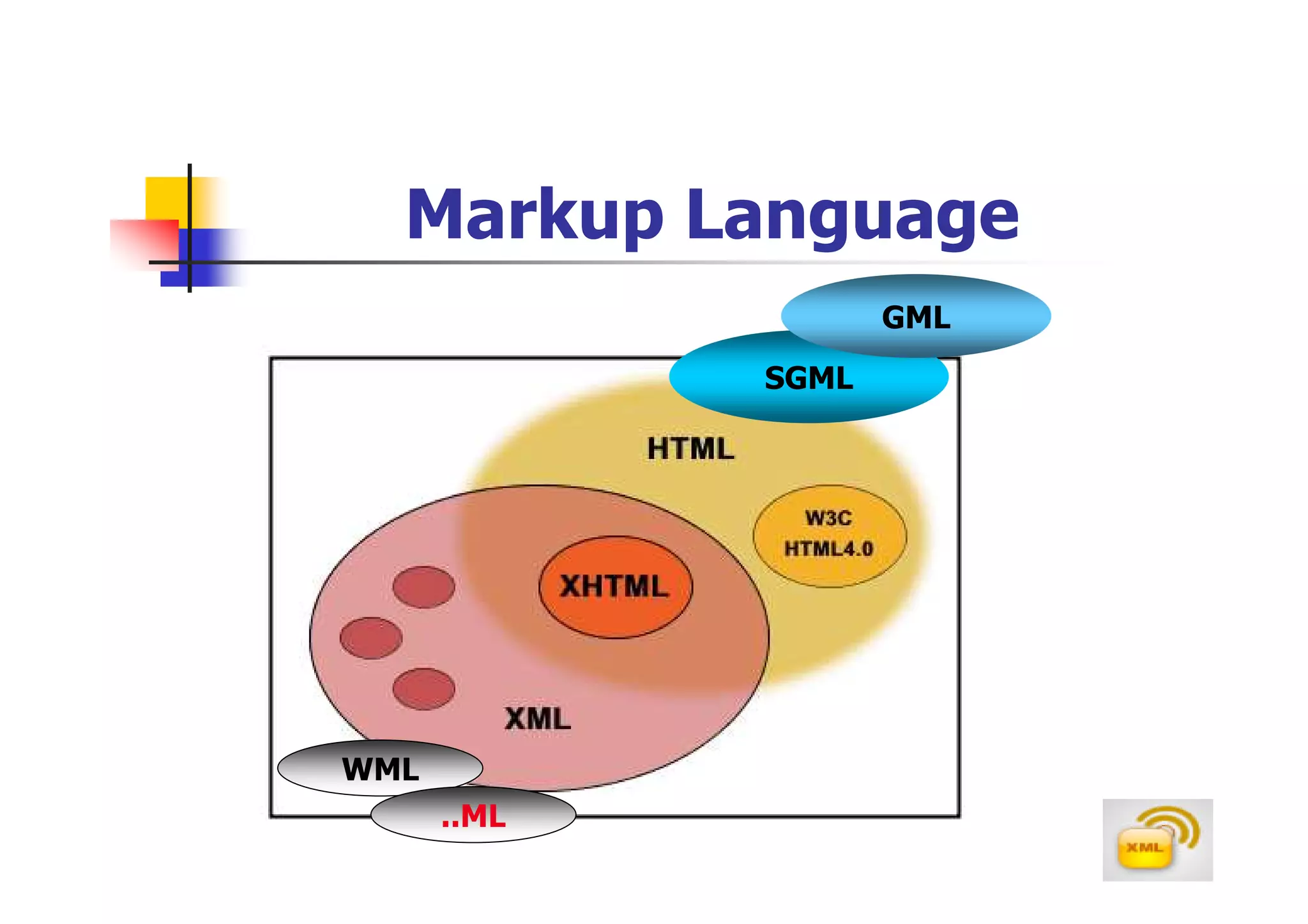
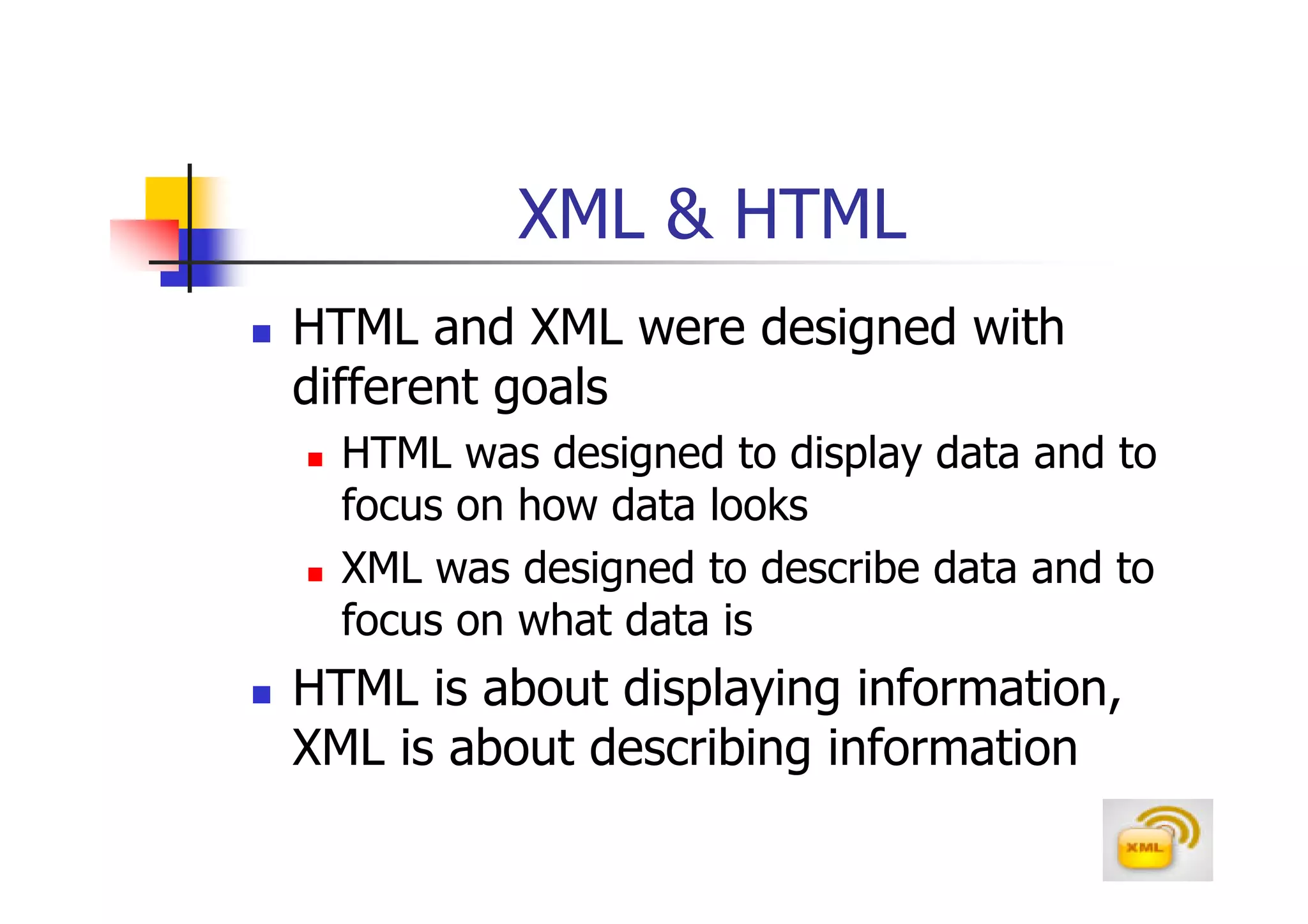
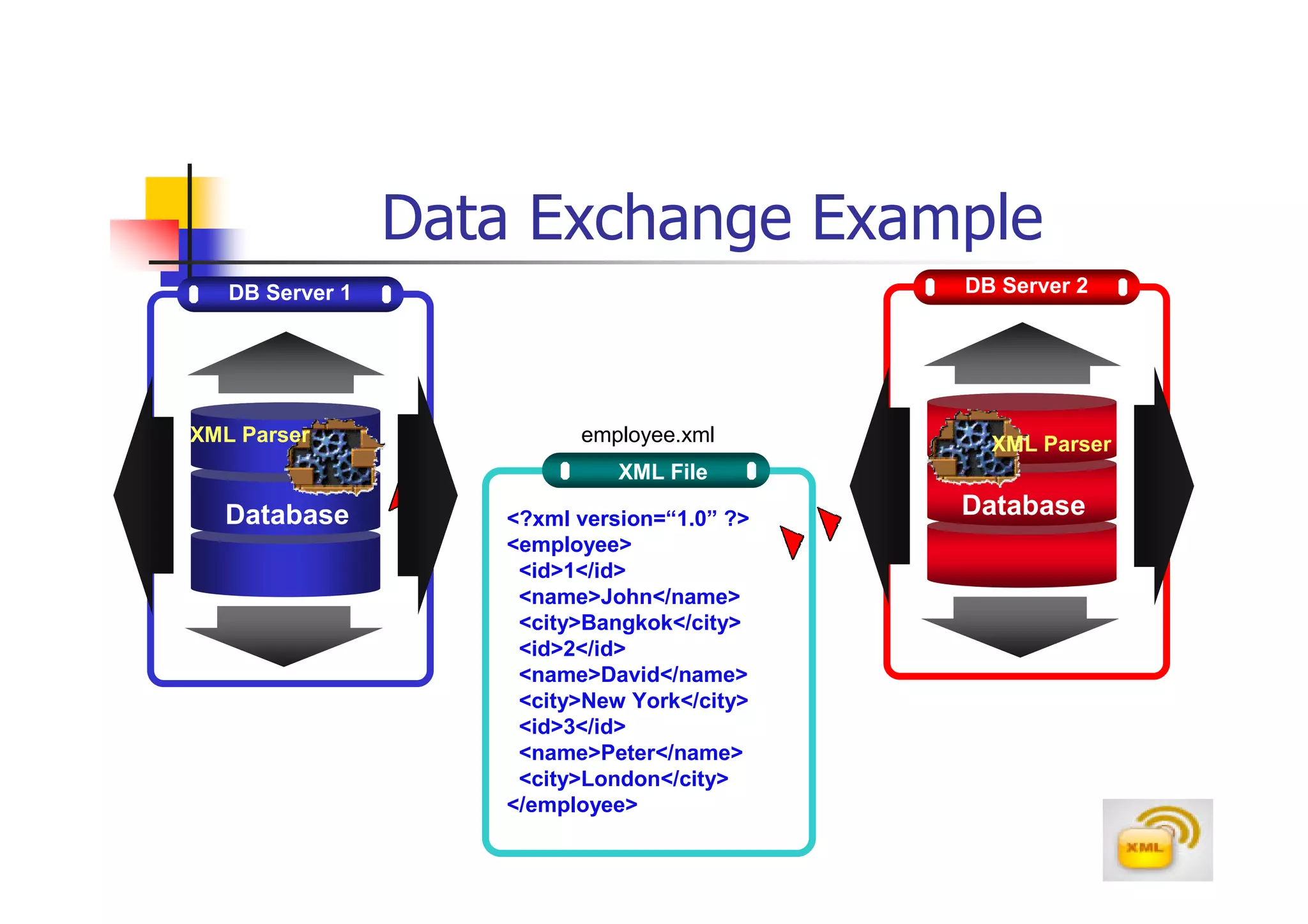
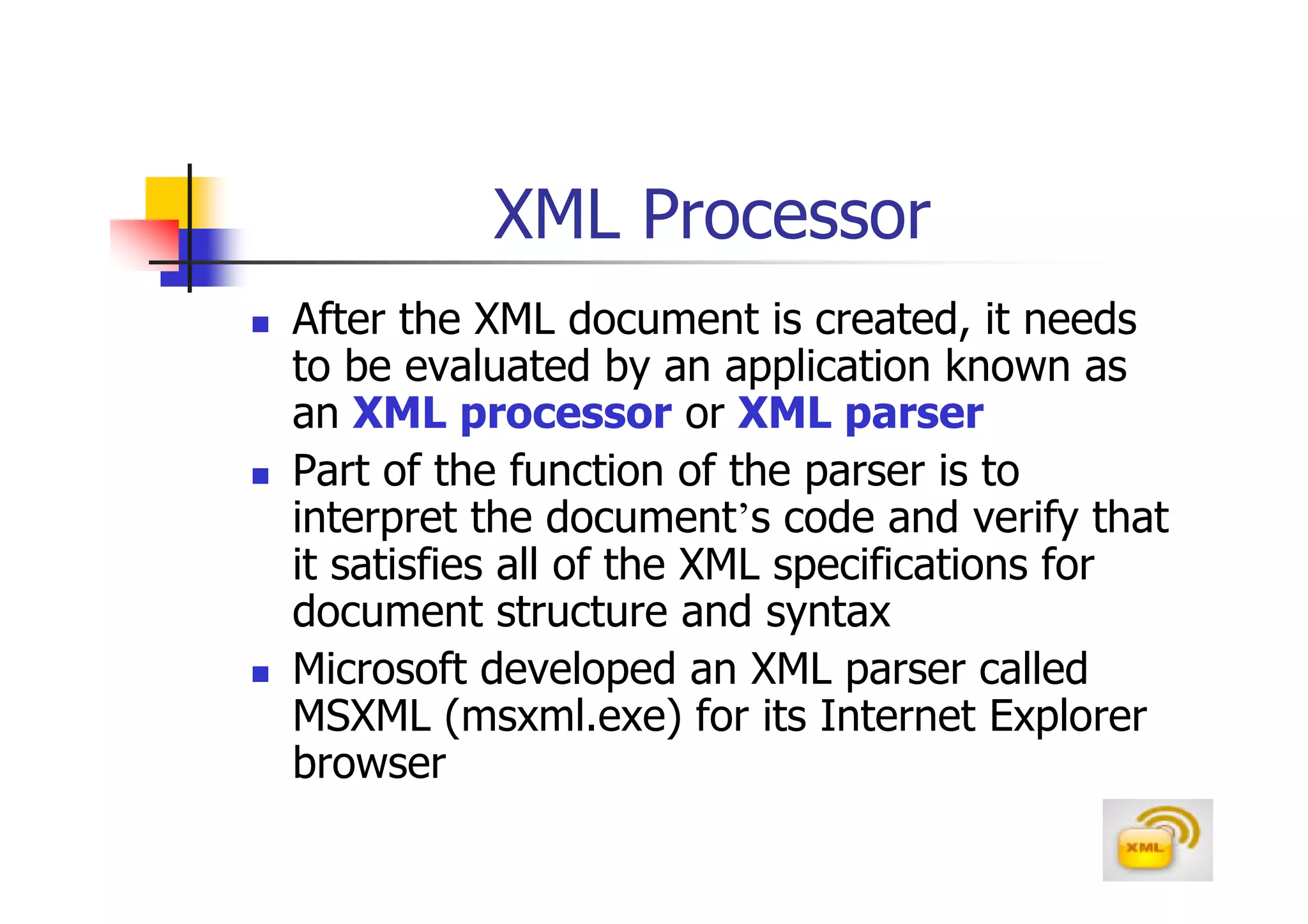
1. XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a markup language much like HTML that was developed by the W3C to describe data.
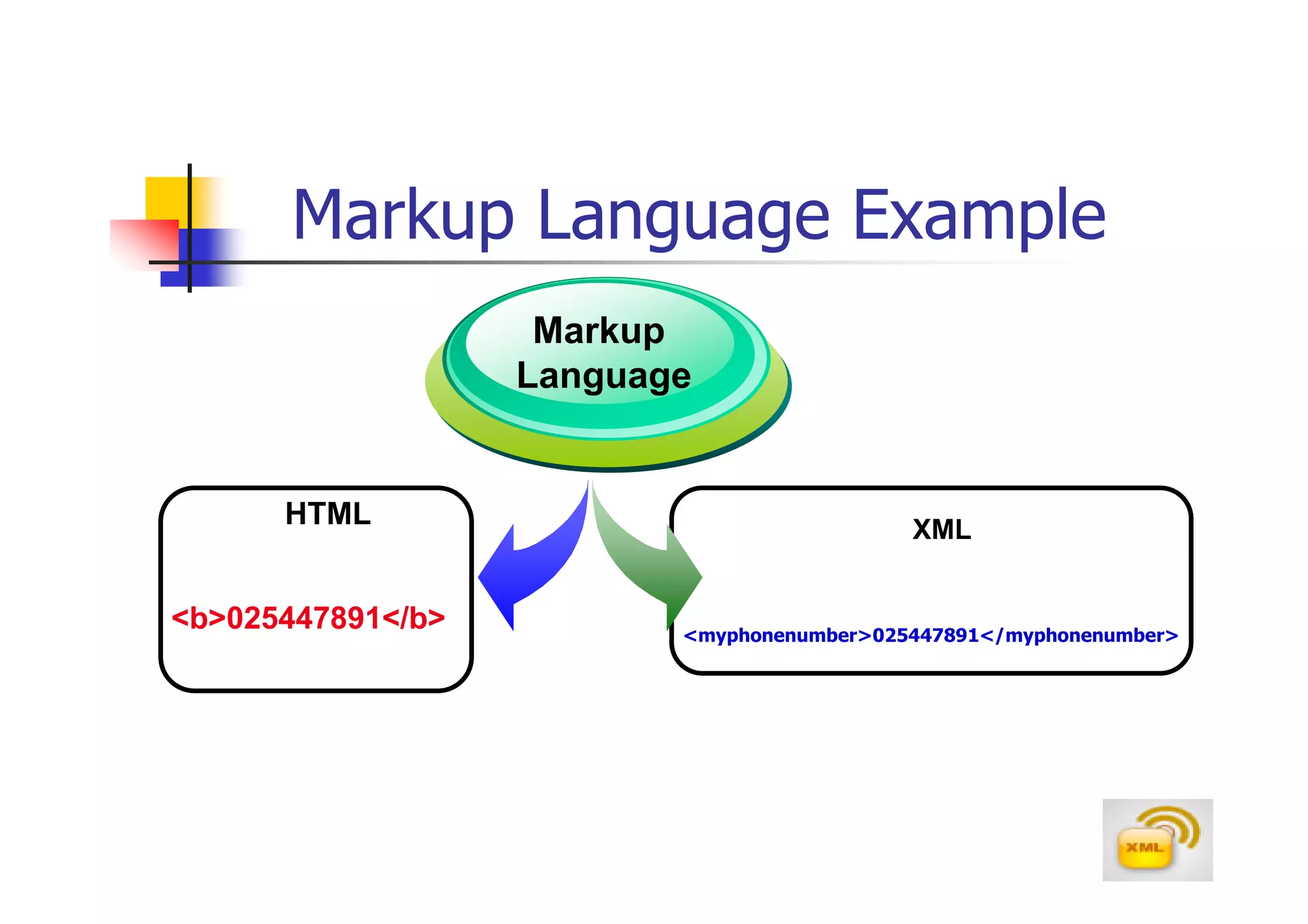
2. XML allows users to define their own tags, while HTML uses predefined tags. XML focuses on describing what the data is, rather than how it looks like.
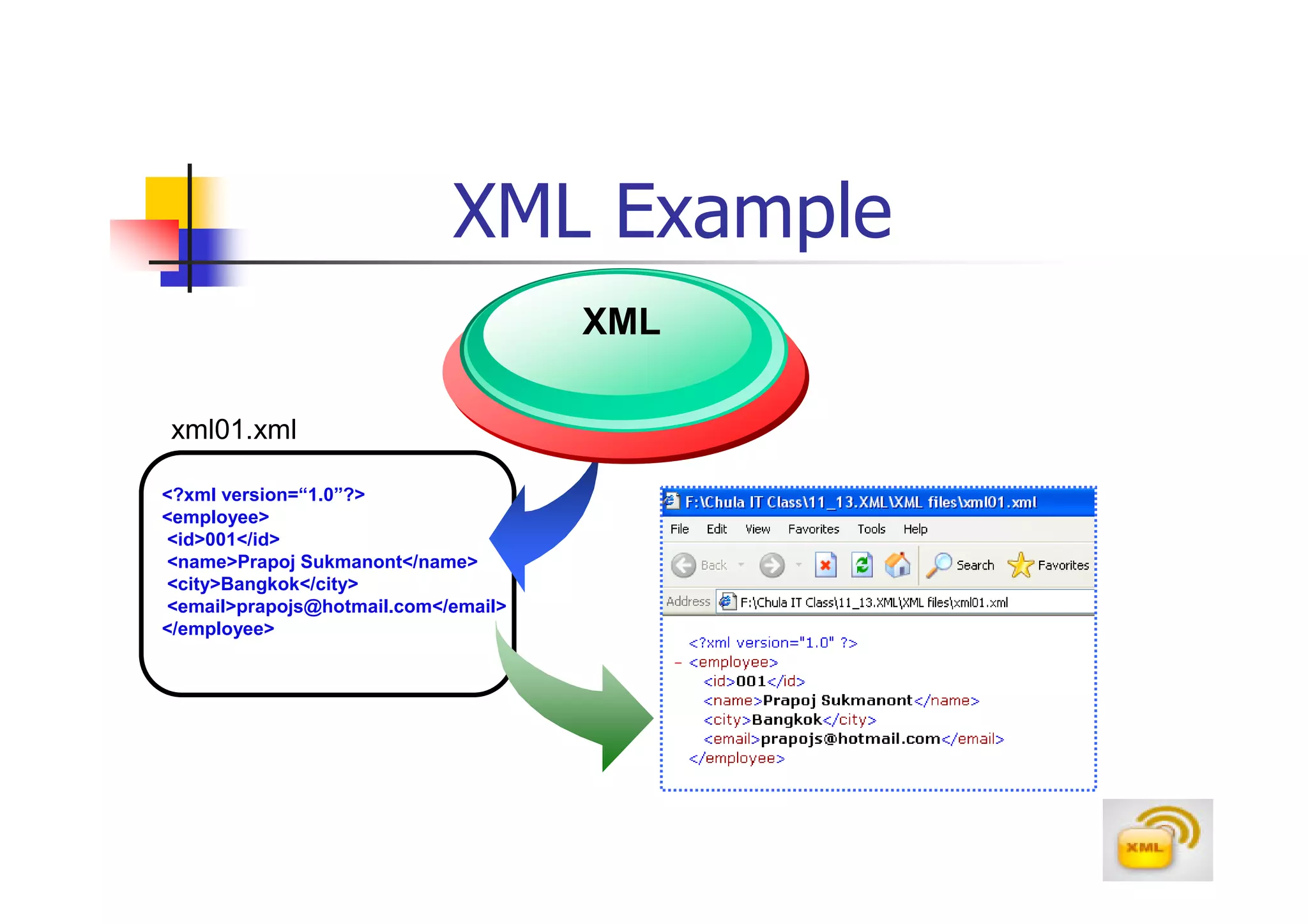
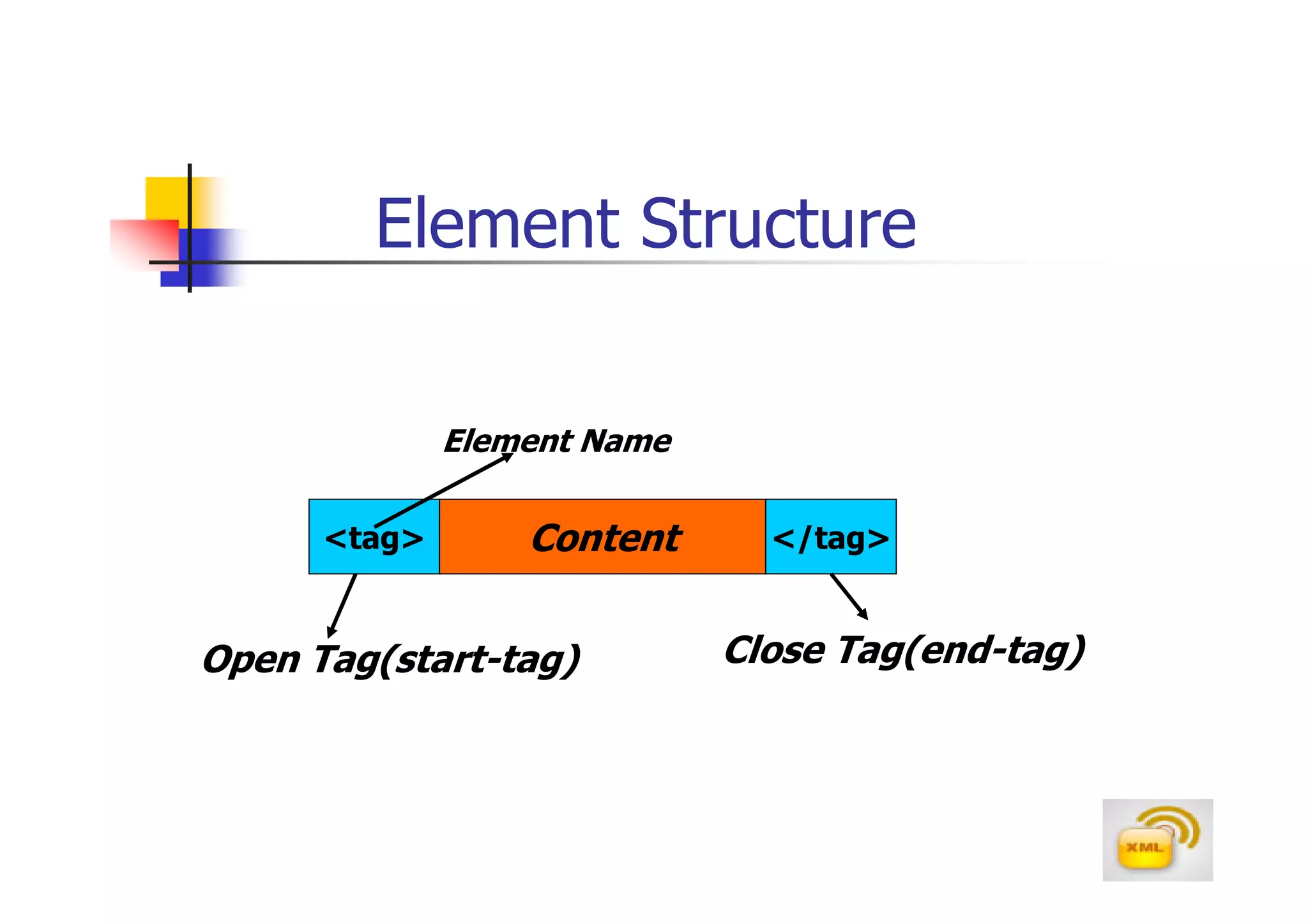
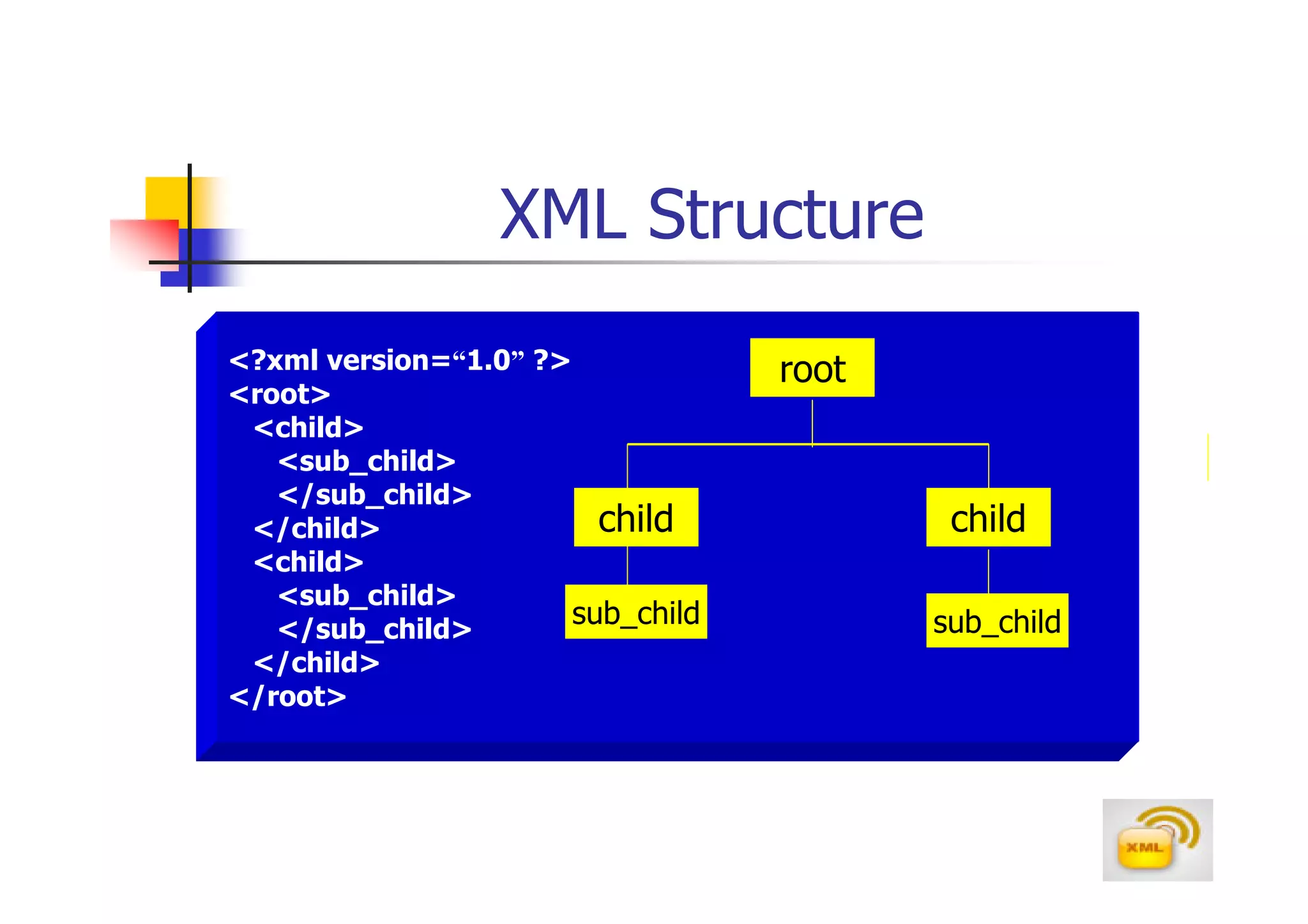
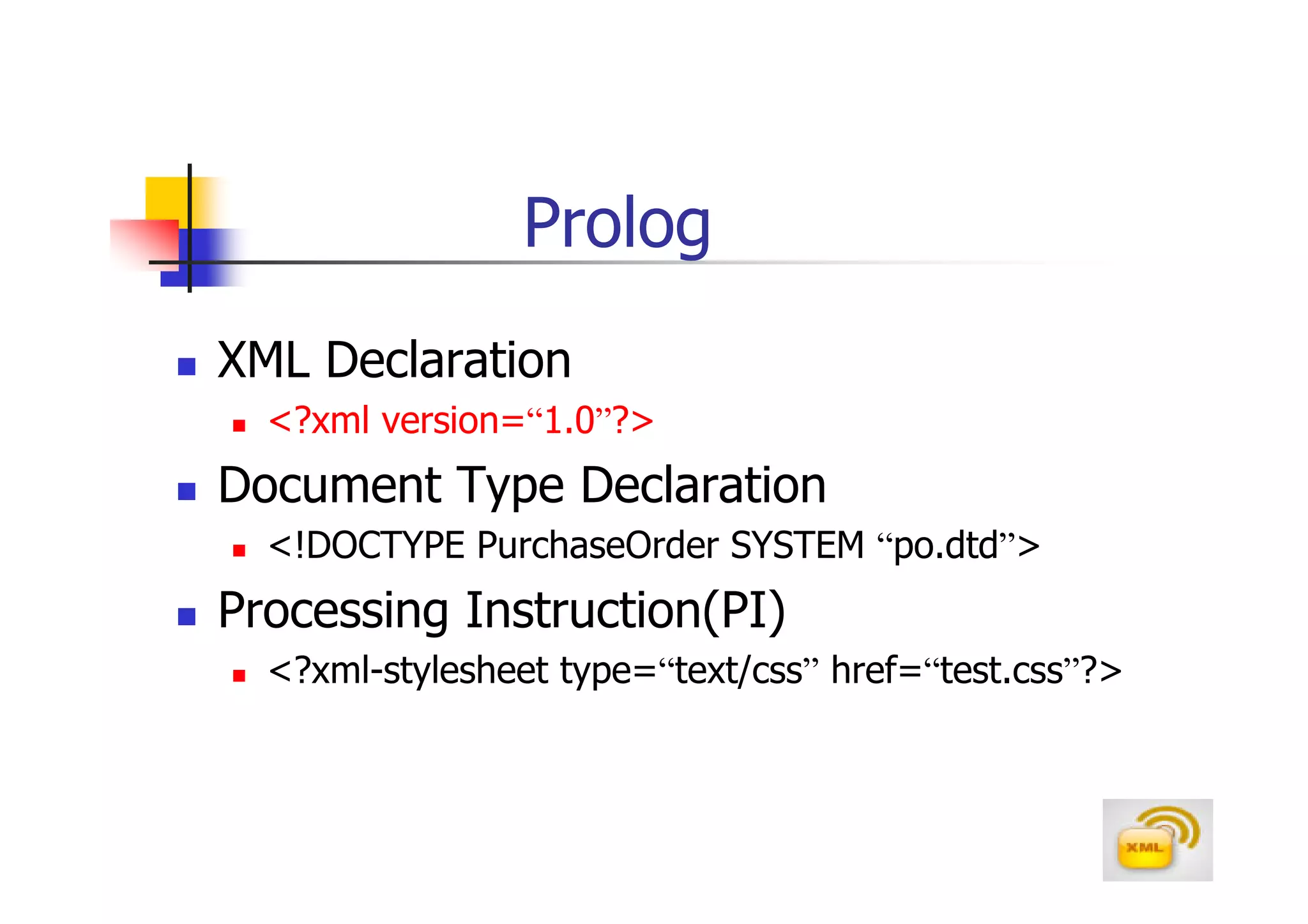
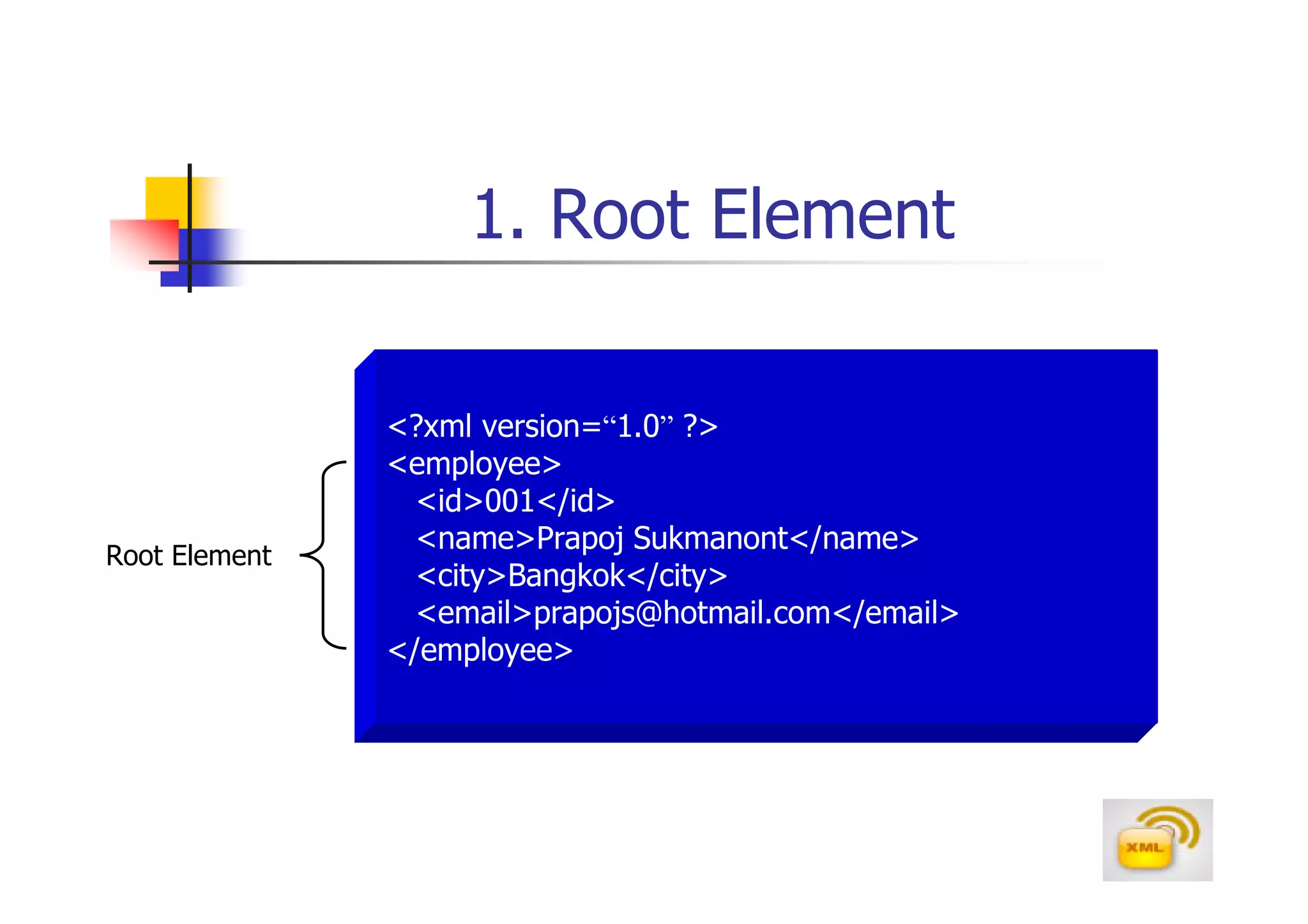
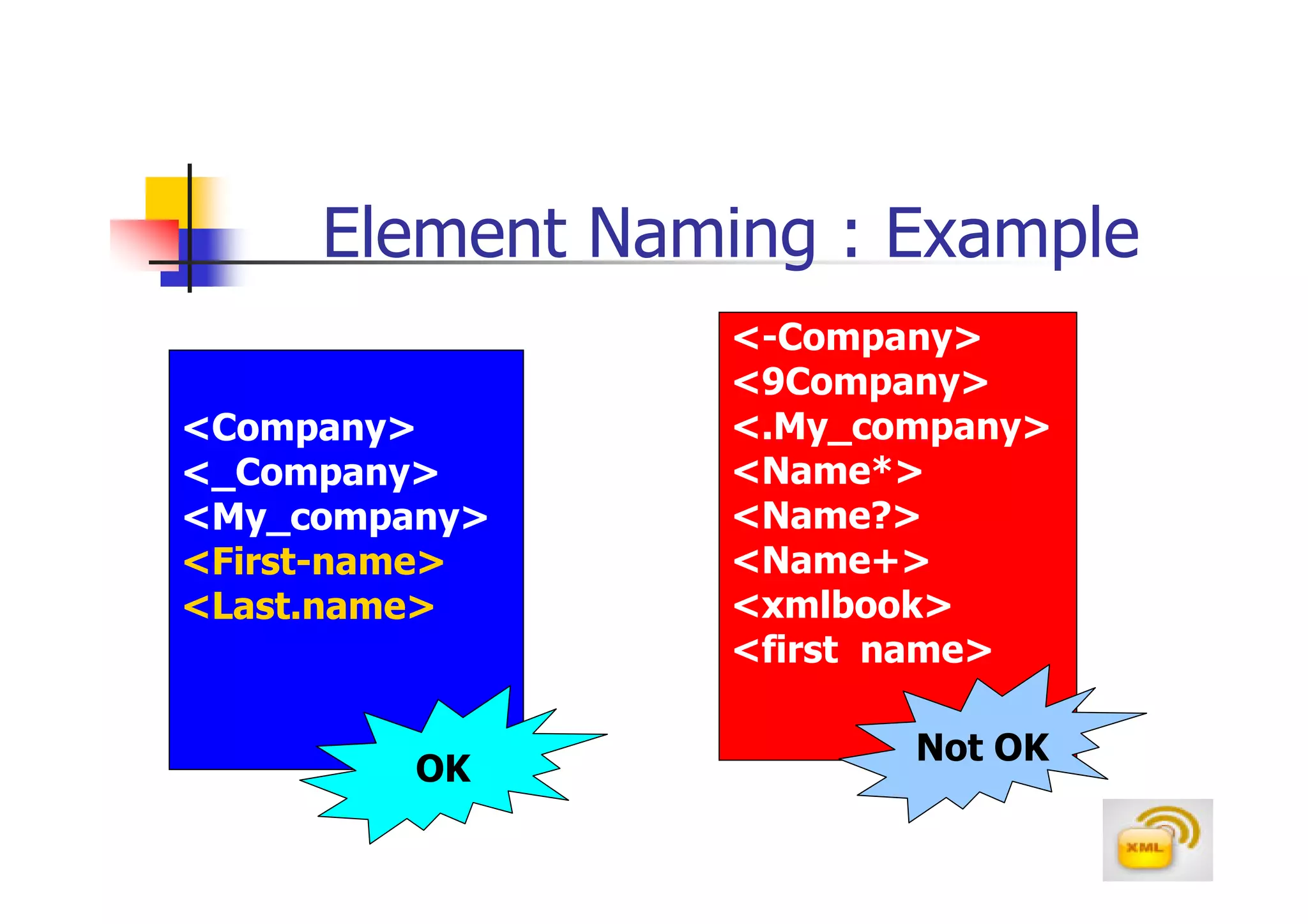
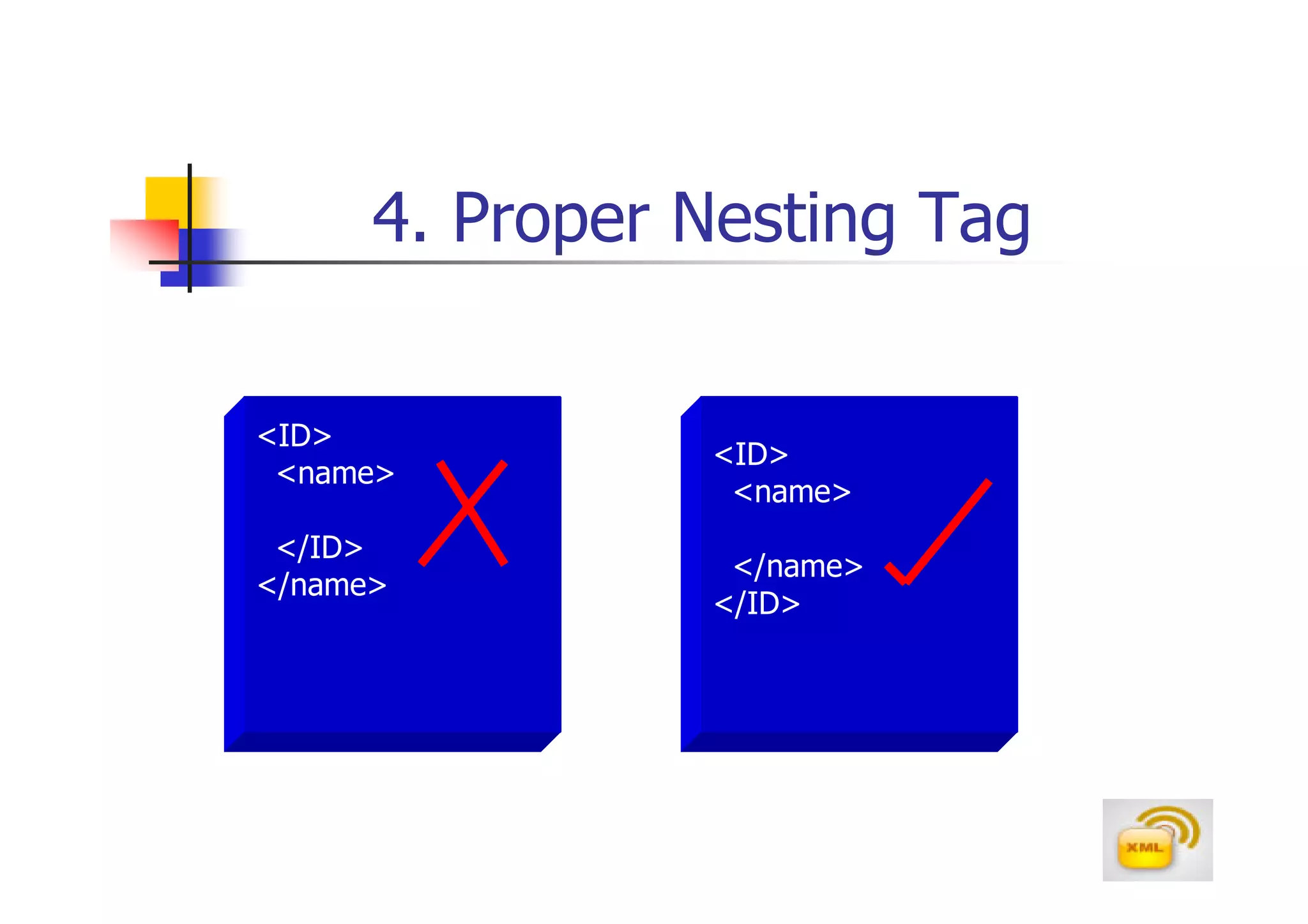
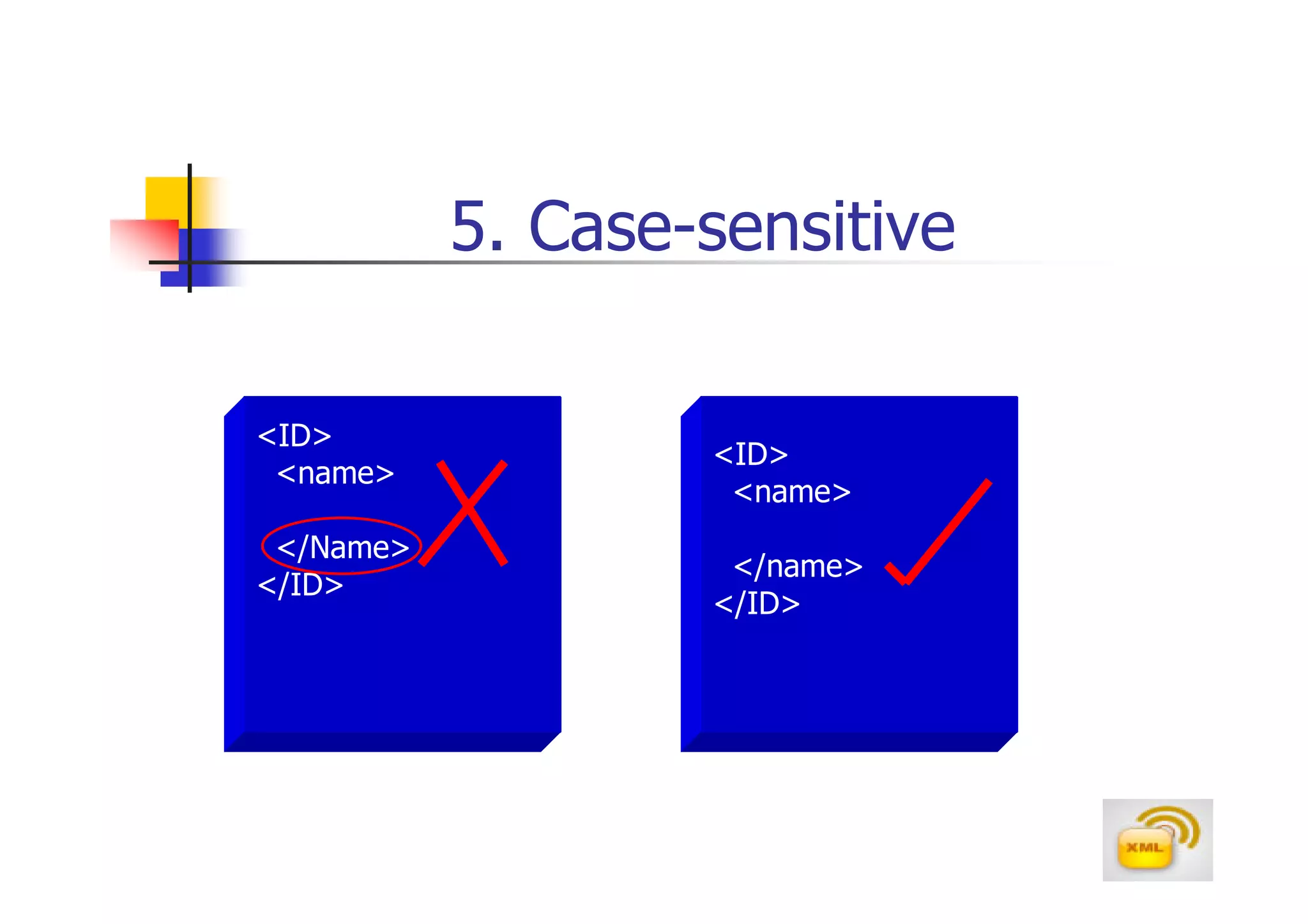
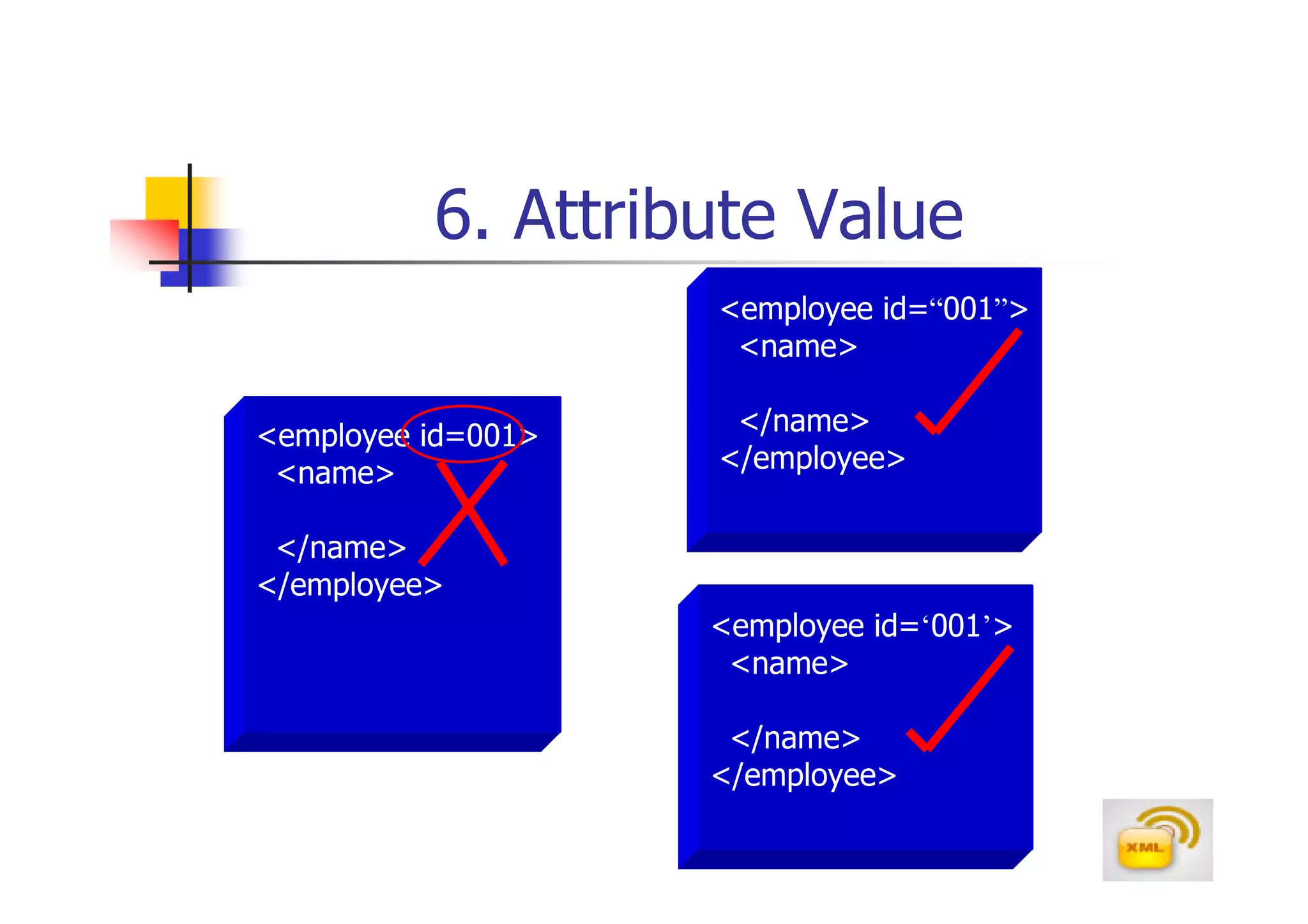
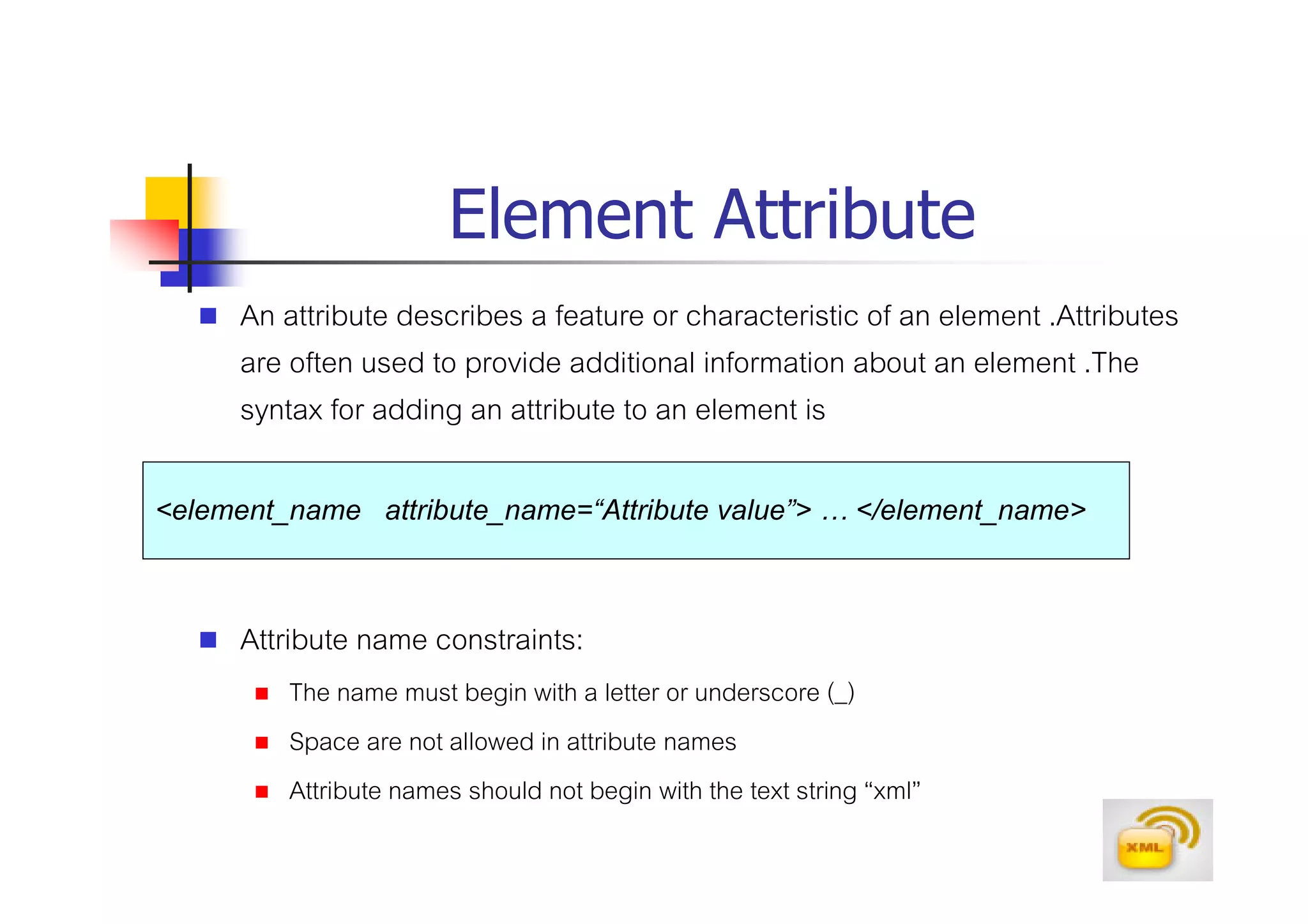
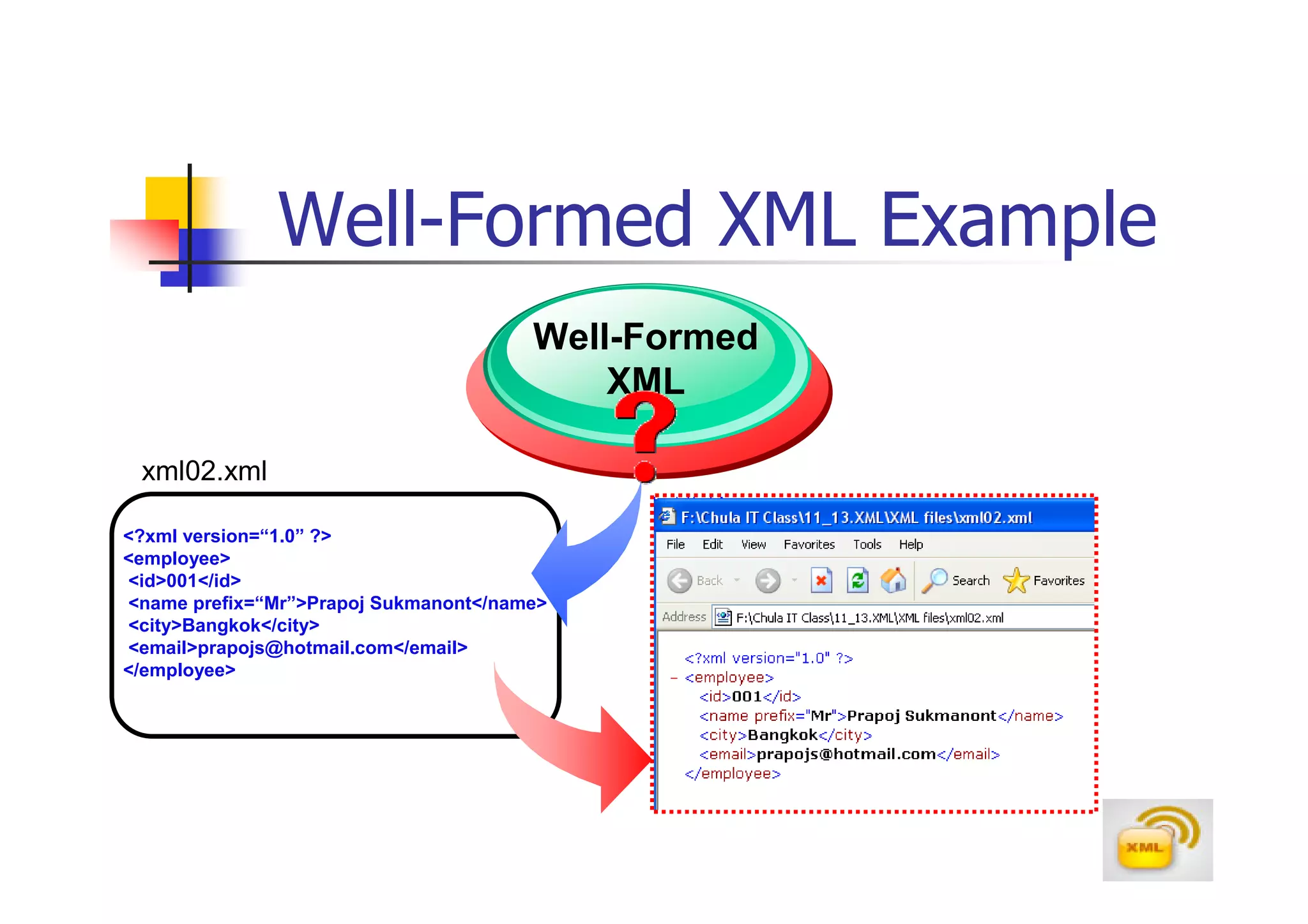
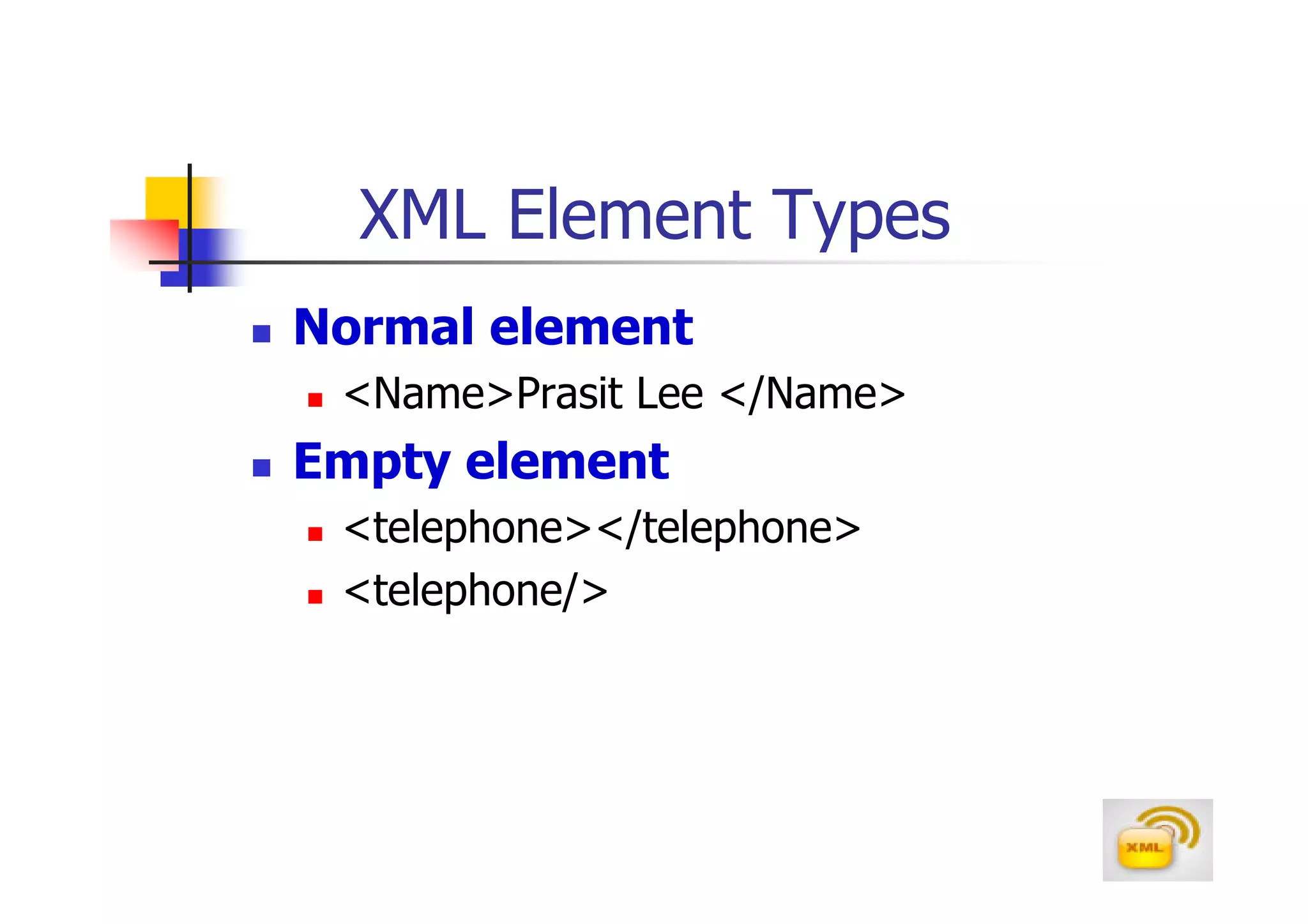
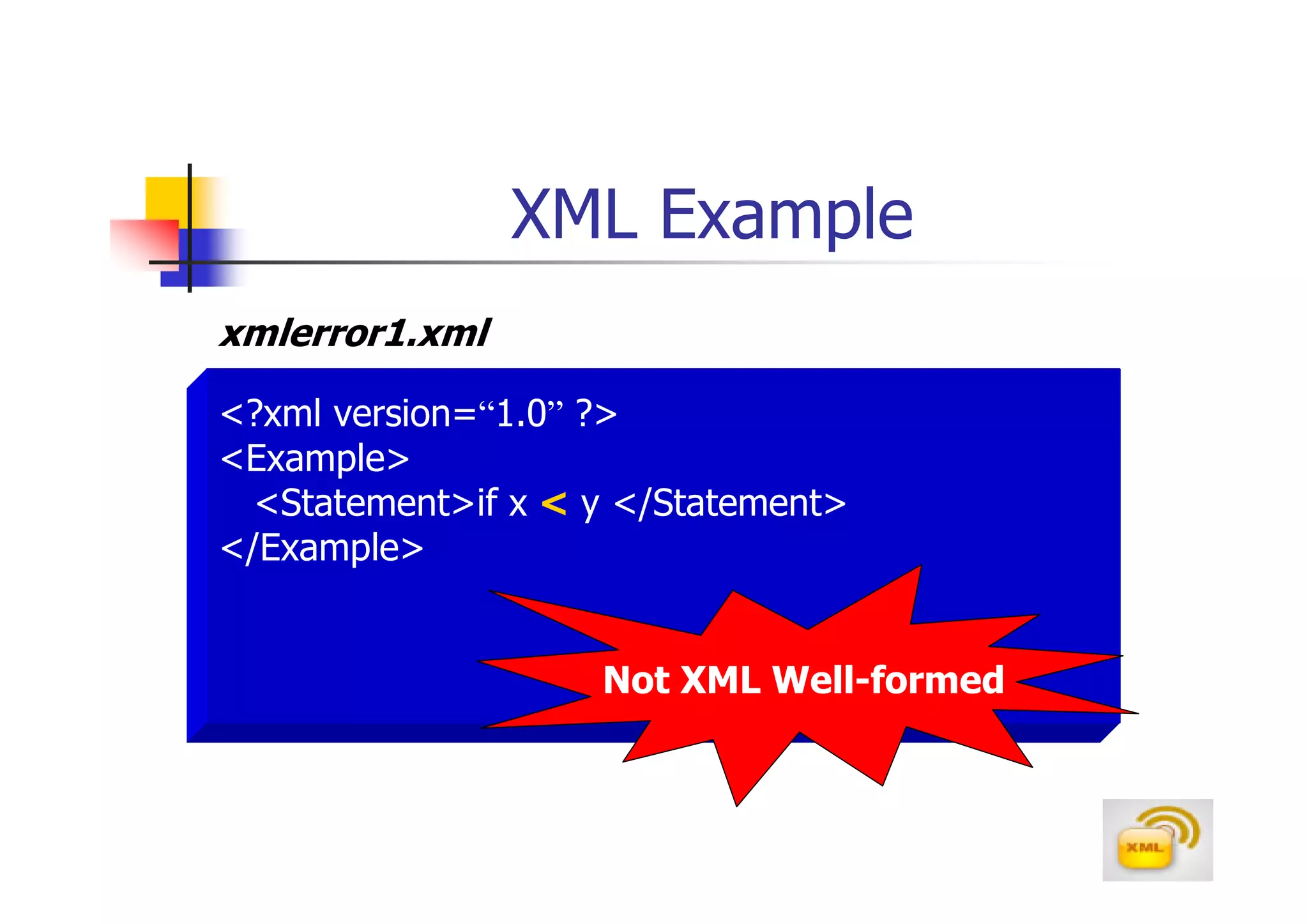
3. An XML document must have a root element, properly closed tags, elements in the correct nesting order, and follow other syntax rules in order to be considered well-formed. Attributes can be added to elements to provide additional information.













![4. CDATA Section
xml04.xml
<?xml version=“1.0”?>
<Example>
<Statement>
<![CDATA[
if x > y and a < b
]]>
</Statement>
</Example>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xmloverview-130130204624-phpapp02/75/Xml-overview-39-2048.jpg)
![CDATA
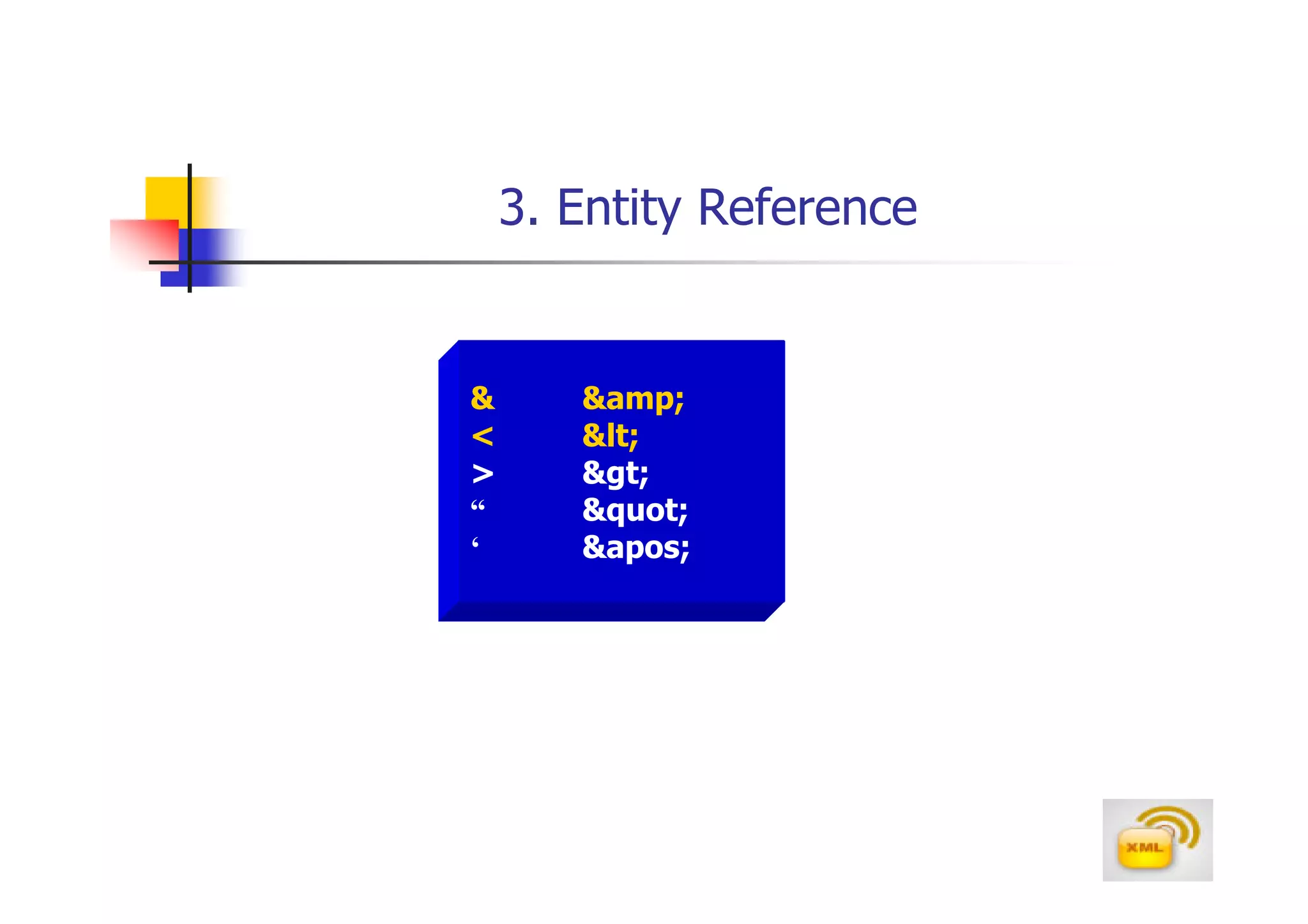
Sometimes, an XML document needs to store large
blocks of text containing the < and > symbols. In
that case, it would be cumbersome to replace all of
the < and > symbols with < and > character
reference, the code itself will be difficult to read
Instead of using character references, you can place
large blocks of text into a CDATA section
A CDATA section is a large block text that the XML
processor interprets only a text
<![CDATA[
Text block
]]>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xmloverview-130130204624-phpapp02/75/Xml-overview-40-2048.jpg)
