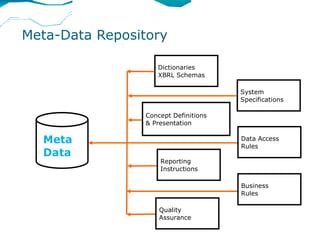
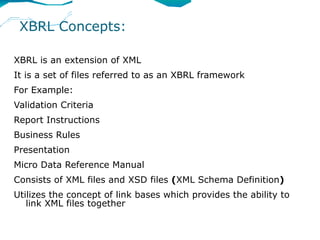
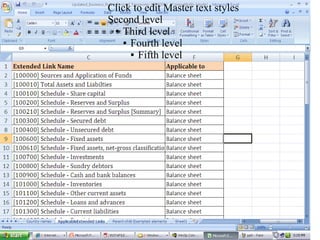
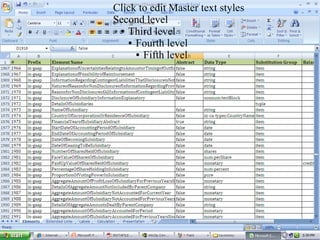
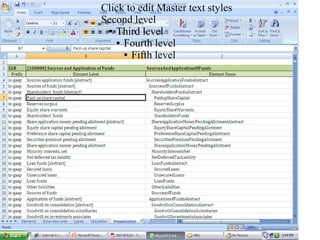
XBRL is a worldwide standard for exchanging business and financial reporting information. It provides a structured format for financial reports using XML tags. This allows computers to read, analyze, and exchange financial data more easily. The document discusses XBRL concepts and taxonomies, which define the elements used for tagging financial information. It also covers the MCA mandate in India for public companies to file financial statements in XBRL format.