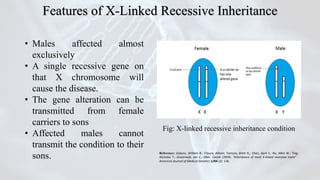
This document discusses X-linked recessive disorders. Key points include:
- X-linked recessive disorders are passed down through families on the X chromosome.
- Males are usually affected because they only have one X chromosome, so only one abnormal gene is needed to cause the disease.
- Females can be carriers and pass the abnormal gene to their sons but usually do not show symptoms themselves because they have a second normal X chromosome.


![Fig: X-linked recessive, carrier mother Fig: X-linked recessive, affected father
Reference: Wattendorf DJ, Hadley DW Am Fam Physician, Family history: the three-
generation pedigree. 2005 Aug 1; 72(3):441-8.[PubMed]
Reference: Wattendorf DJ, Hadley DW Am Fam Physician, Family history: the three-
generation pedigree. 2005 Aug 1; 72(3):441-8.[PubMed]
X-Linked Recessive – In Case of
Carrier Mother And Affected Father](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x-linkedrecessivedisorder-151228132208/85/X-linked-recessive-disorder-4-320.jpg)
![• Most types are caused by a gene
located on the X chromosome
• Red green colorblindness is the
most common type
Fig: Ishihara Test
Reference: Troscianko T, Benton CP, Lovell PG, Tolhurst DJ, Pizlo ZPhilos Trans R Soc
Lond B Biol Sci. on visual perception. 2009 Feb 27; 364(1516):449-61.[PubMed]
Example 1 - Colorblindness](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x-linkedrecessivedisorder-151228132208/85/X-linked-recessive-disorder-5-320.jpg)

