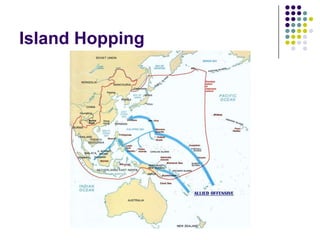
The document summarizes Japan's imperial expansion in Asia and the Pacific prior to World War 2, driven by its goals of acquiring territory, resources, and living space. It describes Japan's invasion of Manchuria in 1931 and increasing aggression in China from 1937. As relations soured with the United States due to its occupation of China, Japan launched a surprise attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941. This brought the US into the war and led to years of fighting across the Pacific as the US retook lost territories in a strategy of island hopping until atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945 led Japan to surrender.