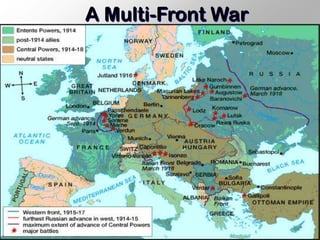
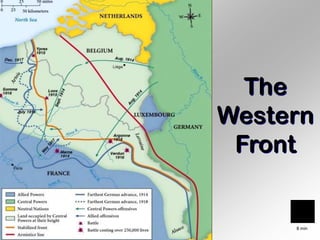
1. Section 4 discusses the various battlefronts of World War 1, including support for the war initially in European nations, Germany's Schlieffen Plan to quickly defeat France, and key battles like Verdun and the Somme on the Western Front.
2. The Eastern Front saw more mobile warfare between Germany/Austria-Hungary against Russia, resulting in enormous casualties for Russia in 1915.
3. Colonial fronts in Africa involved clashes between European colonial powers like Britain, France, and Germany competing for territory and trade routes.
4. The war had impacts on the home front as governments took control of economies and propaganda to mobilize populations while new roles for women helped transform views of women's place
















![Fighting in Africa
Black Soldiers in the
German
Schutztruppen
[German E. Africa]
British Sikh
Mountain Gunners](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wwi-battlefronts4-120212075147-phpapp01/85/Wwi-battle-fronts4-21-320.jpg)