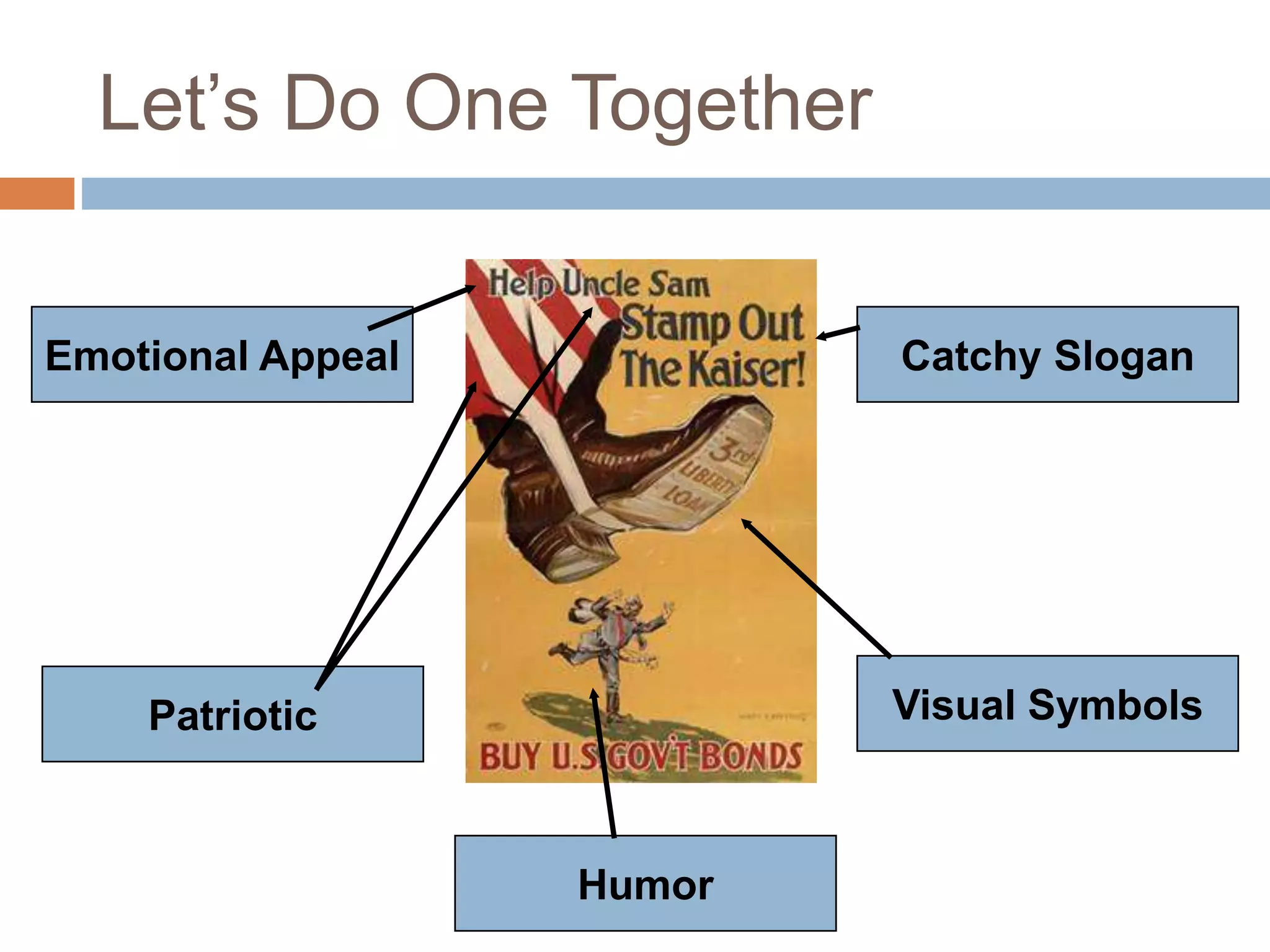
Here is an analysis of one of the propaganda posters as an example:
Emotional Appeal: Playing on patriotism and duty to defend the homeland by joining the army. Portrays a young man hesitating while his family encourages him to enlist.
Visual Symbols: American flag in the background, the family representing the homeland. Uniform on the chair suggests what he could become by joining.
Catchy Slogan: "I Want You for U.S. Army" - Directly addresses the viewer and makes them feel personally responsible.
Patriotic: Explicit use of American flag and appeal to defend the country.
Humor: None - uses a serious tone to encourage enlistment rather than