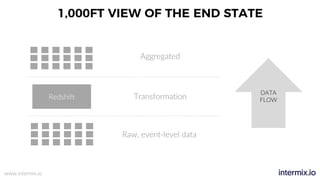
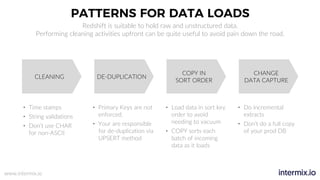
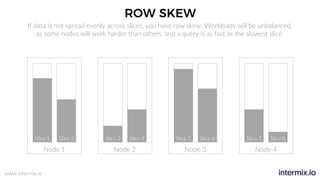
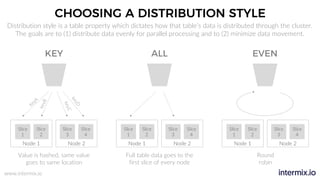
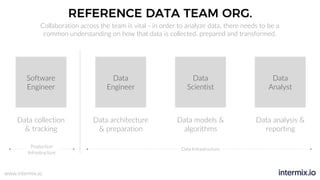
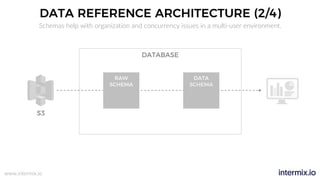
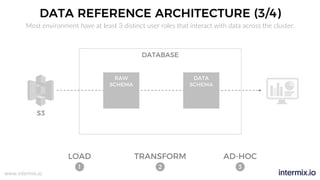
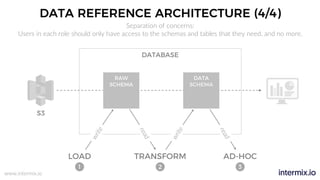
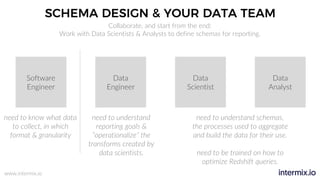
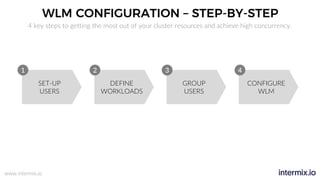
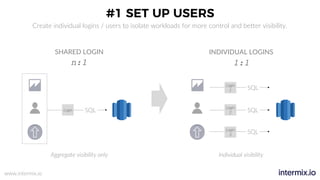
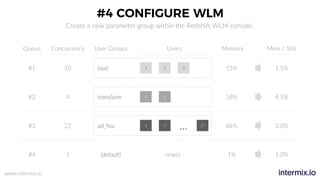
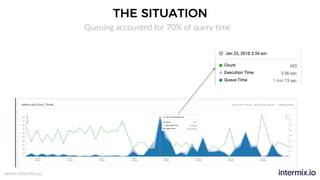
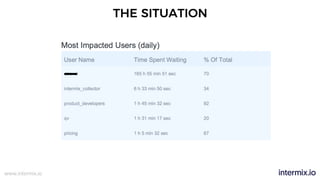
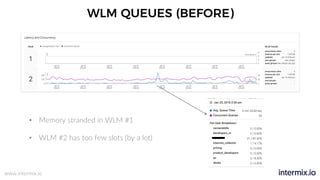
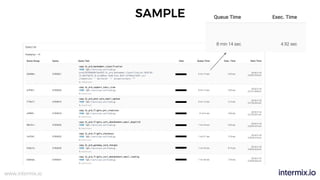
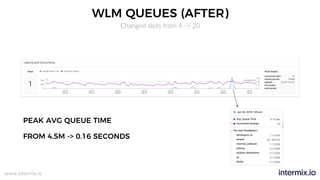
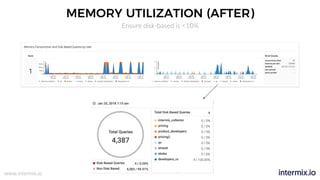
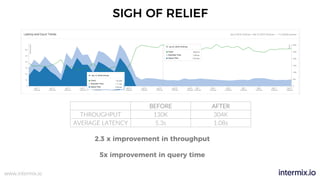
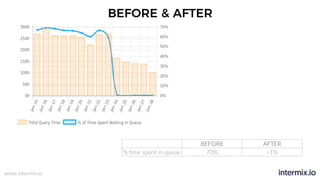
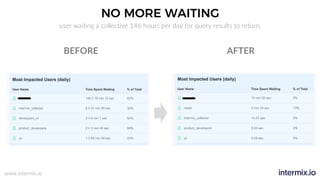
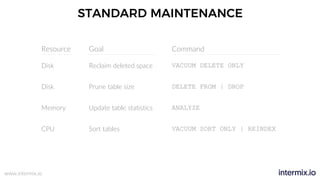
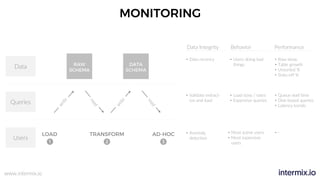
The document provides a comprehensive guide on optimizing Amazon Redshift for data engineering, covering key concepts in data pipelines, query optimization, and performance management. It discusses best practices for building reliable data systems, including considerations for data loading, schema design, and workload management. The training emphasizes collaboration among data teams to enhance data analysis and reporting capabilities while proactively managing and fine-tuning Redshift clusters.