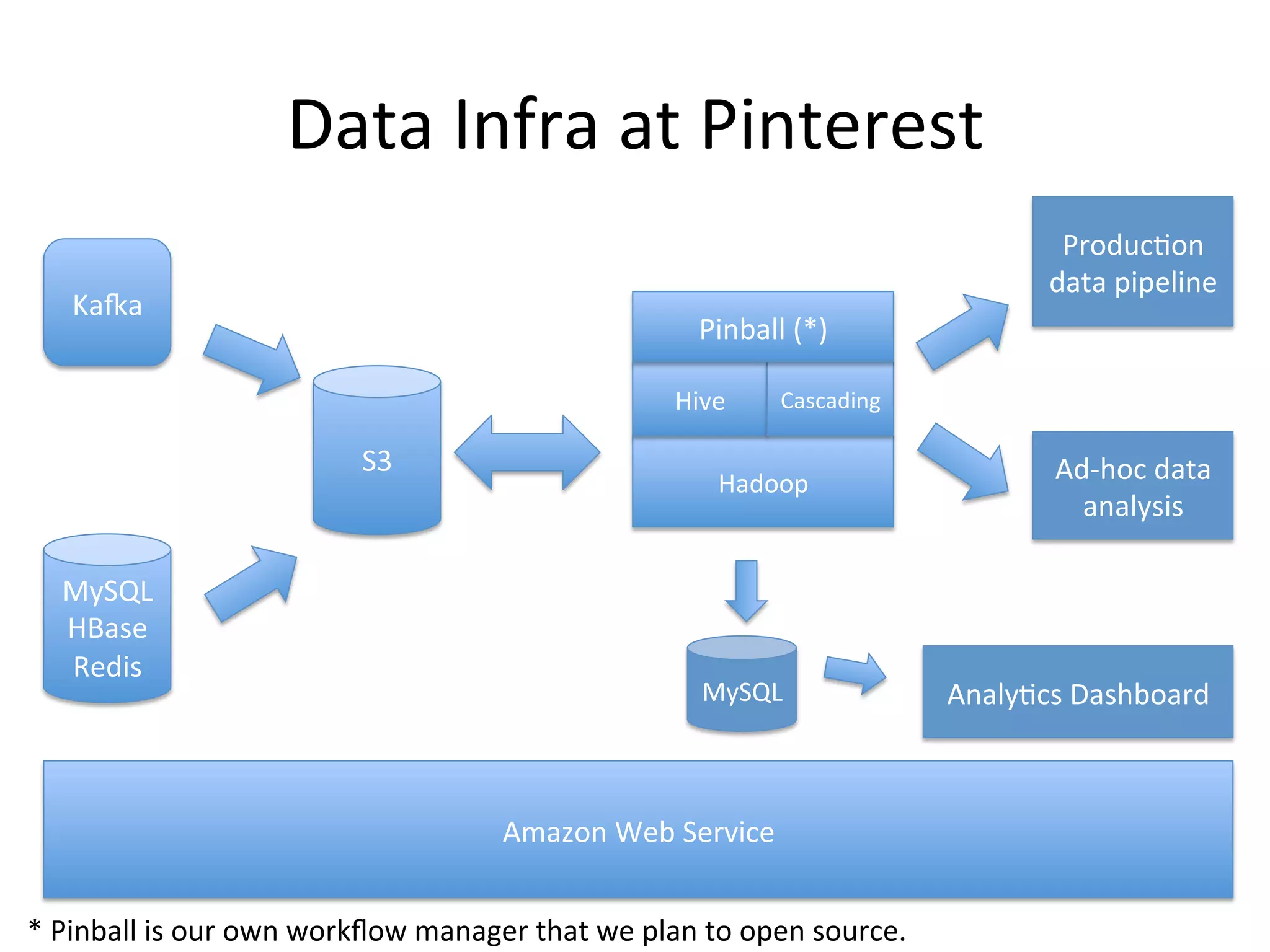
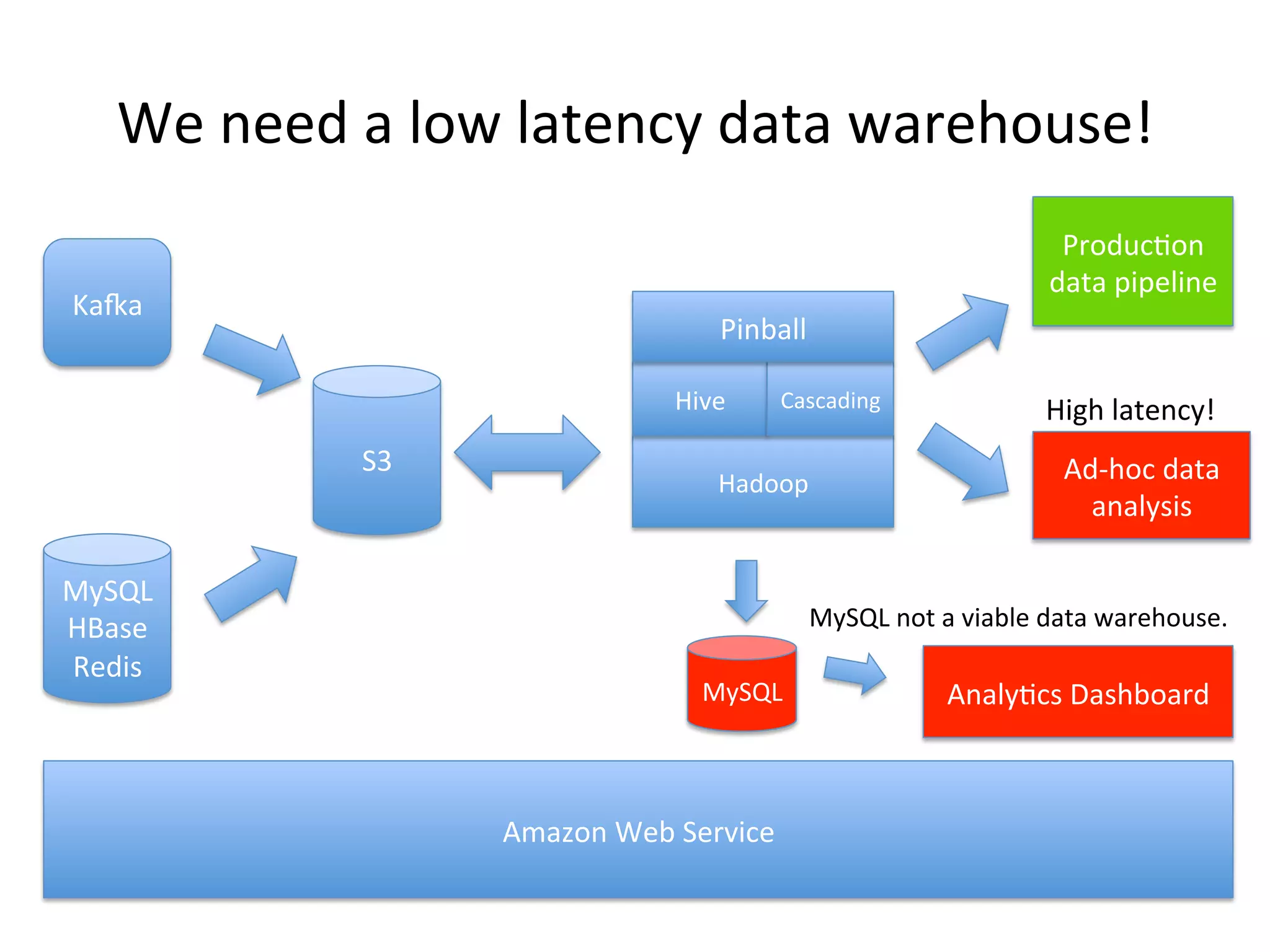
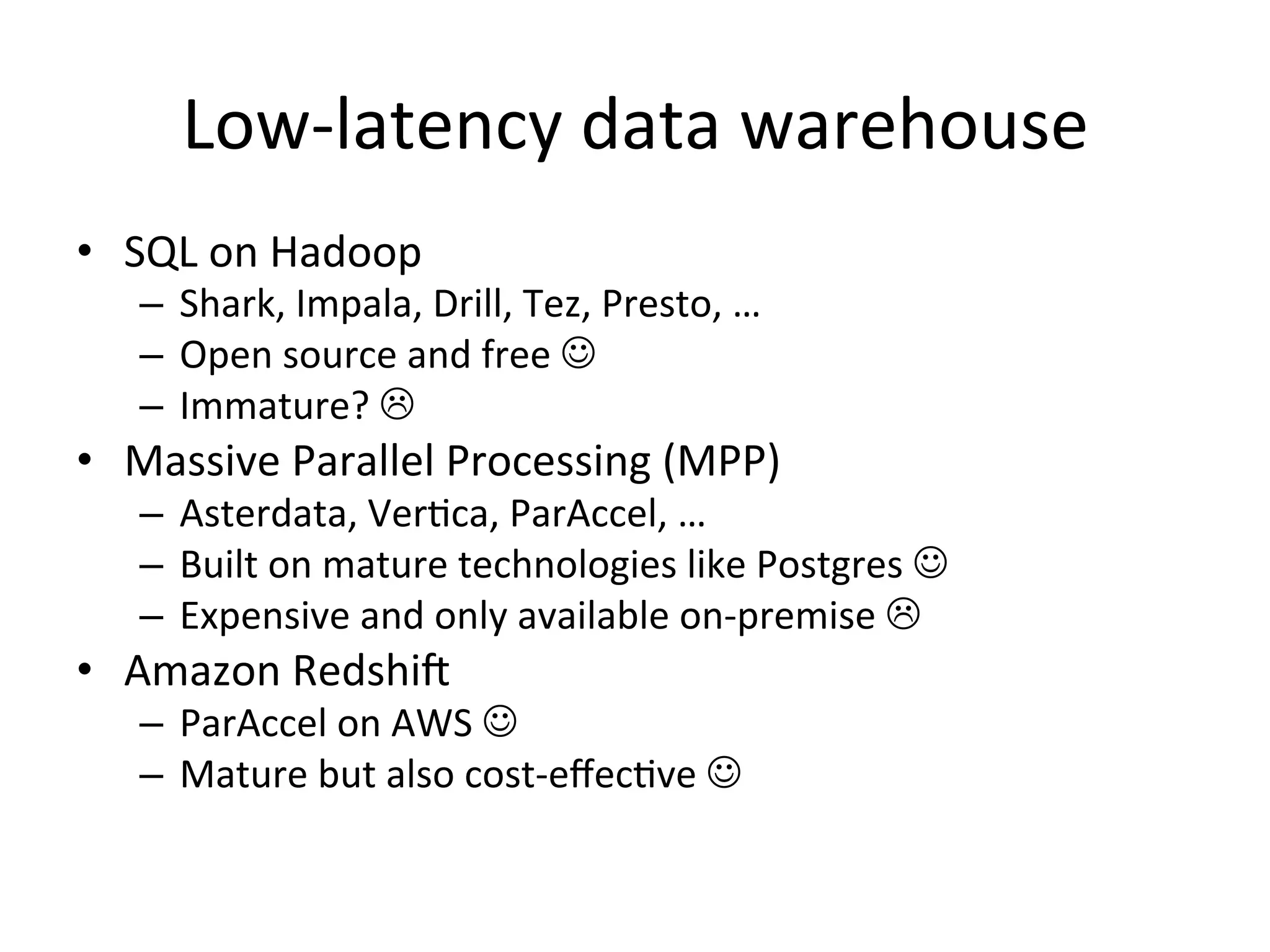
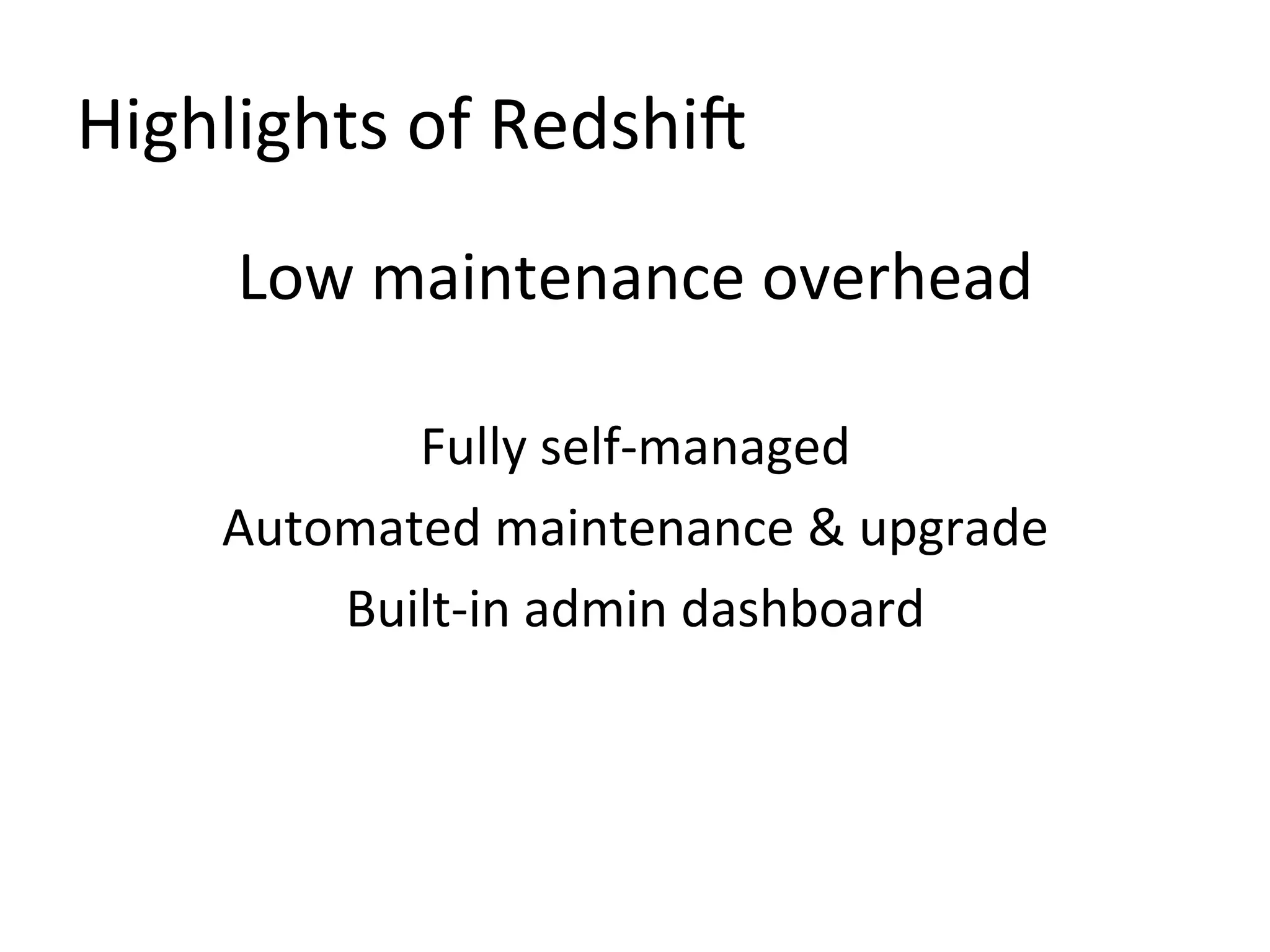
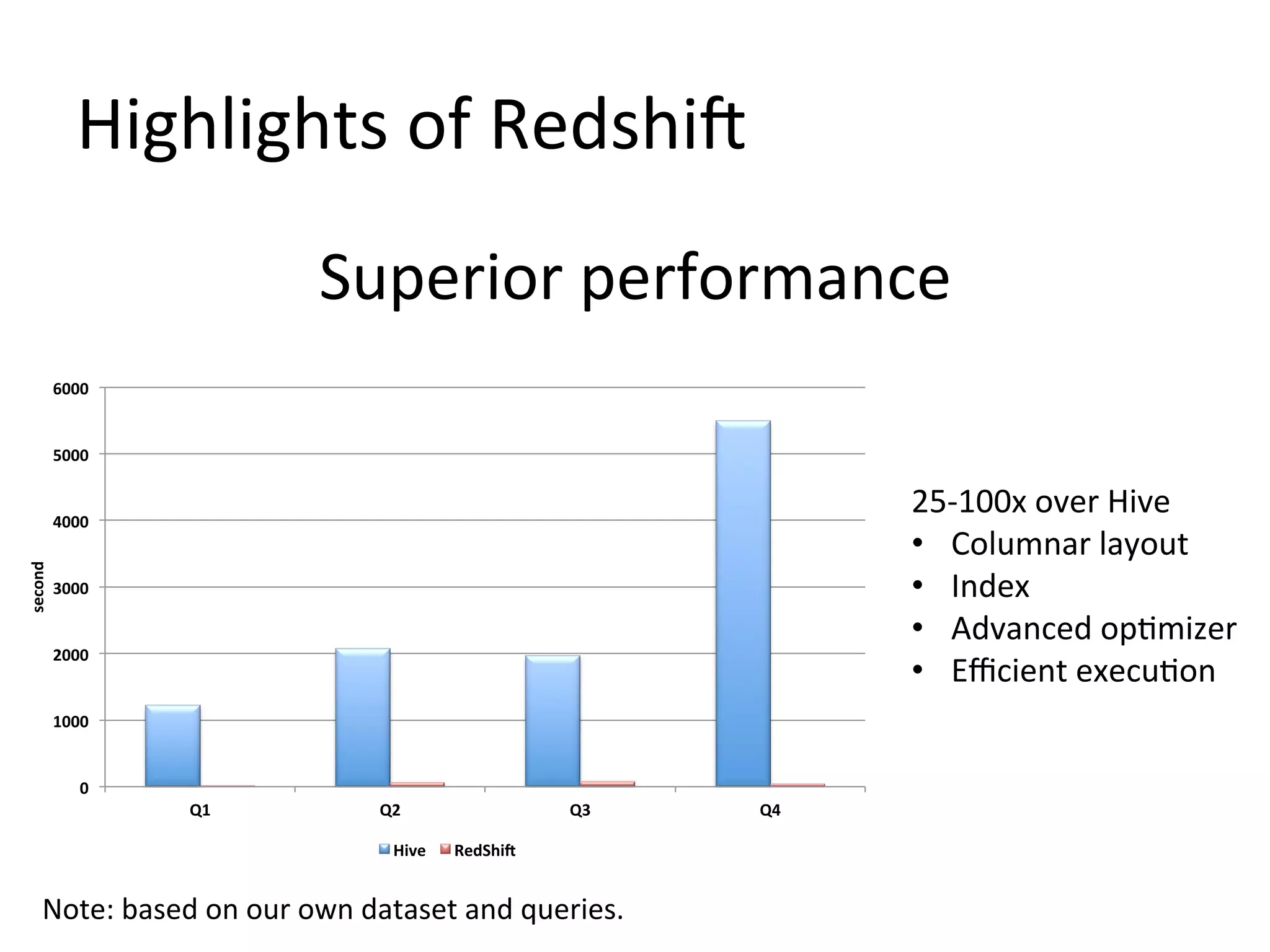
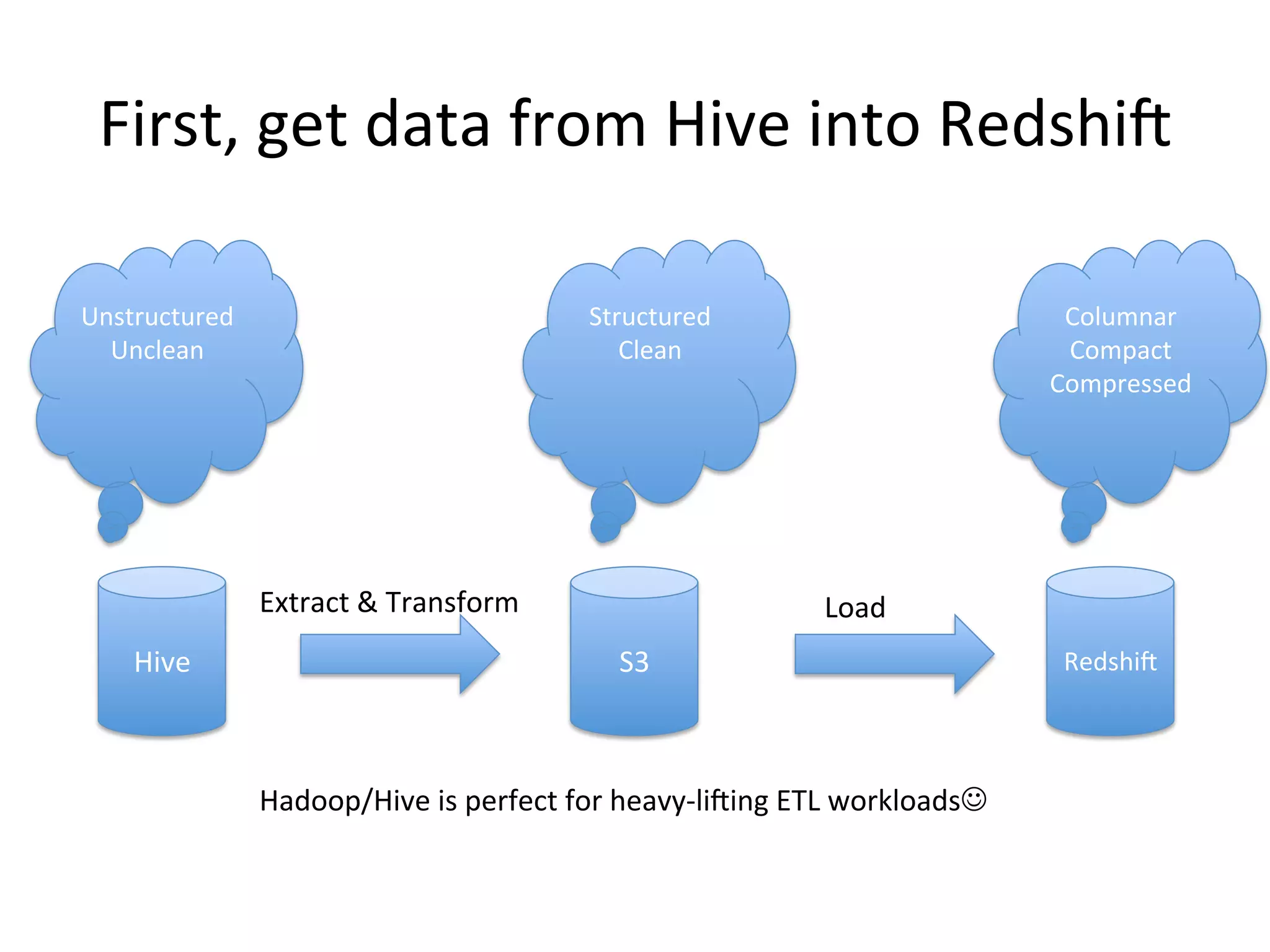
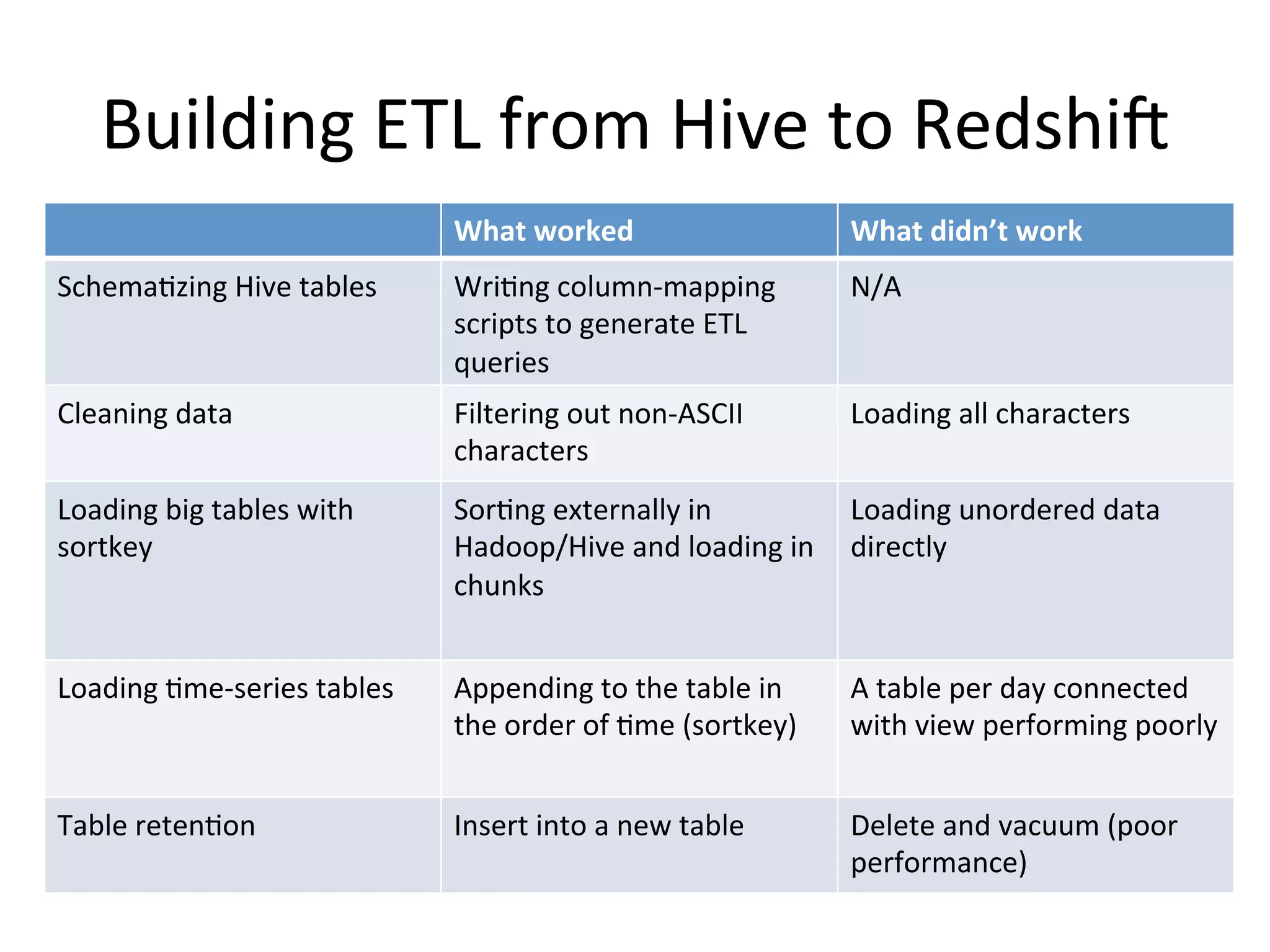
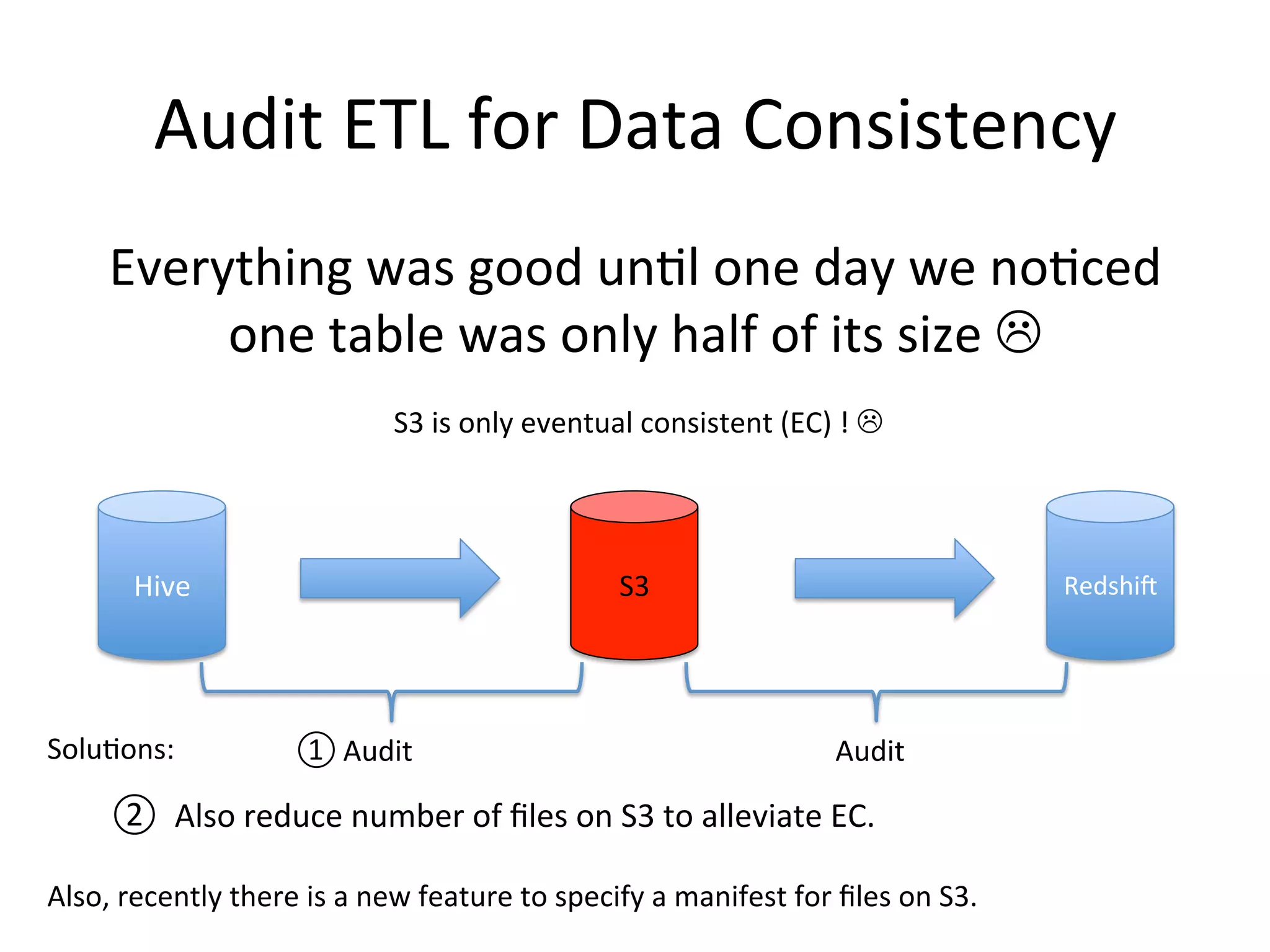
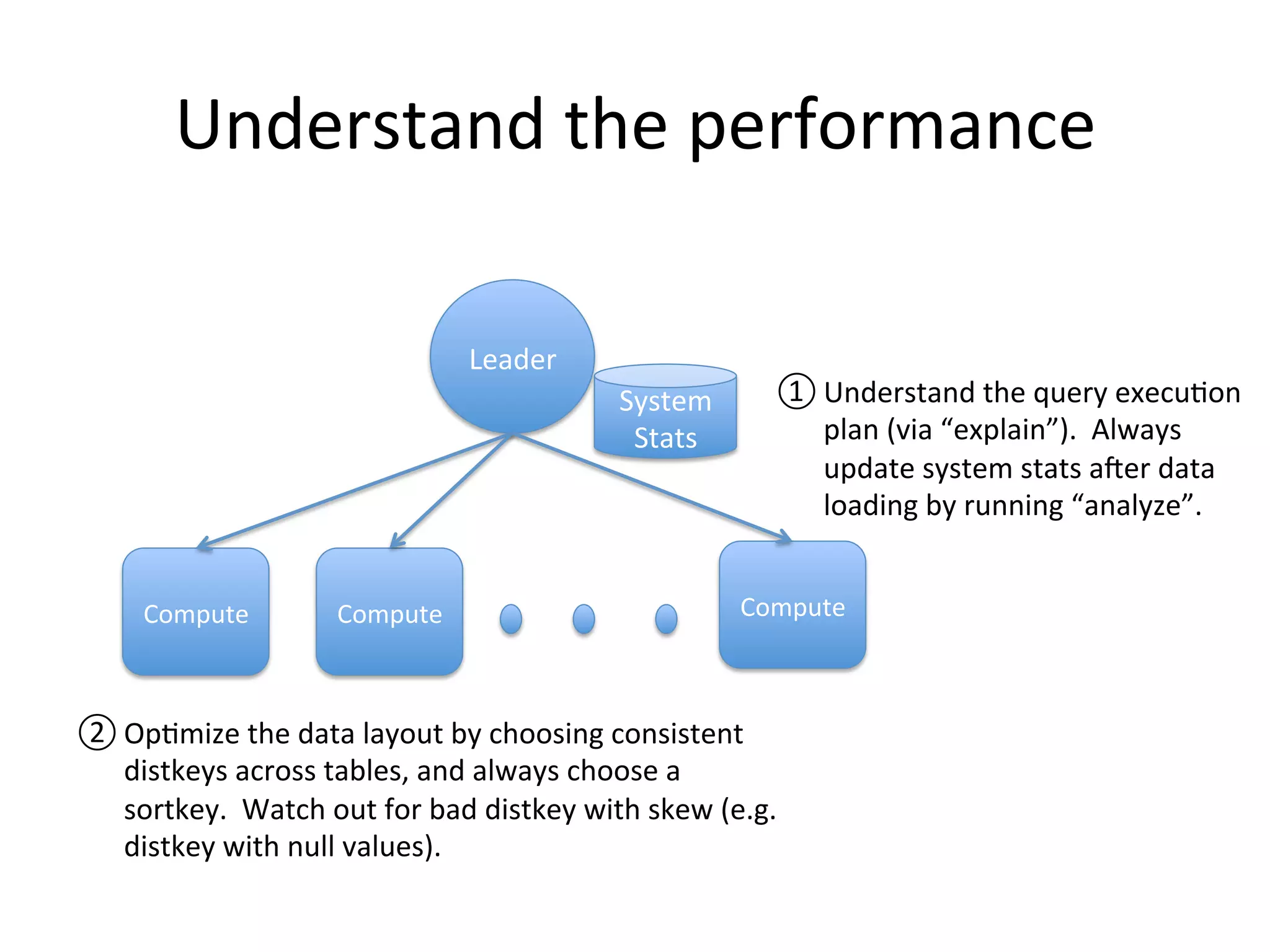
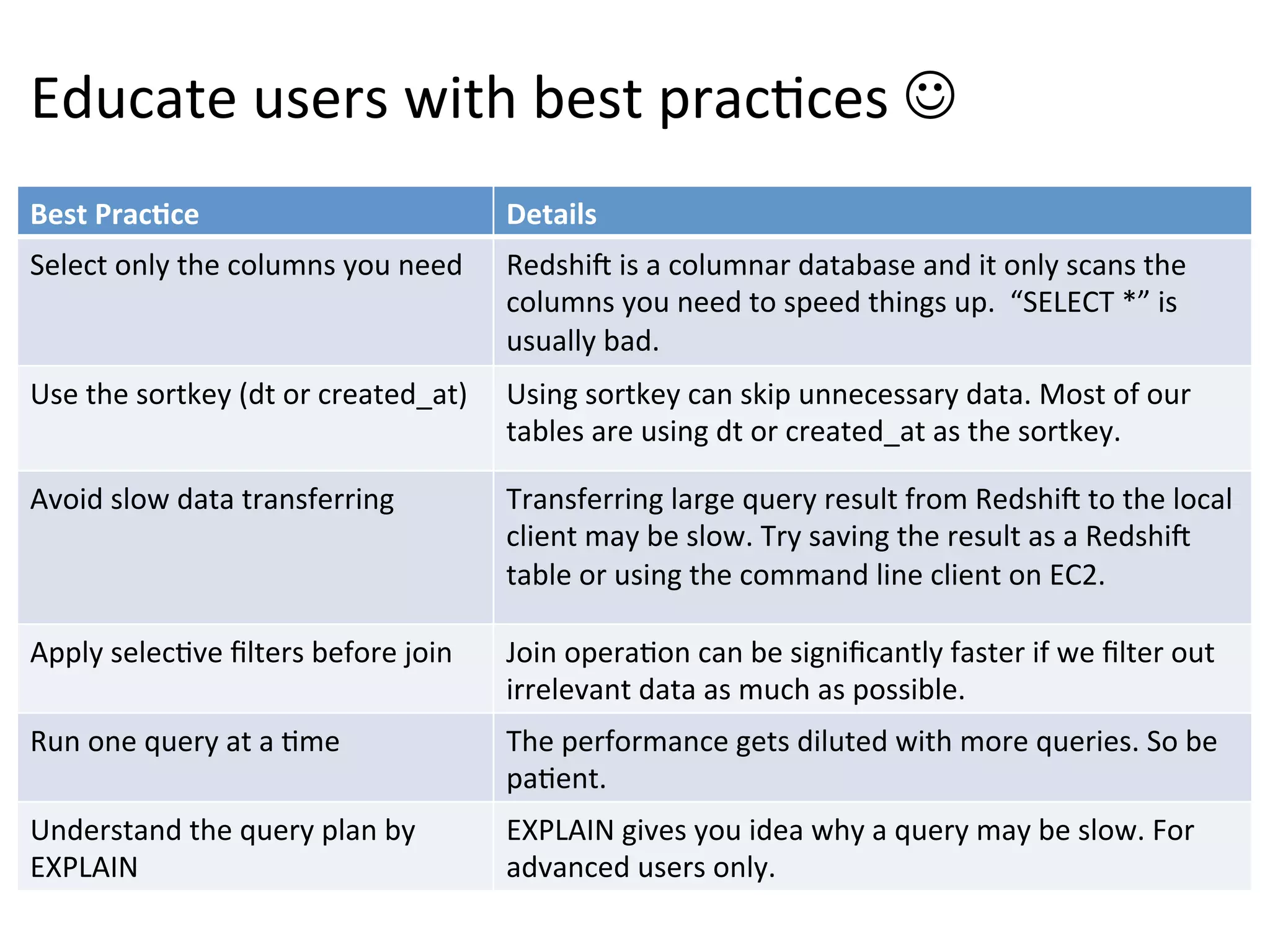
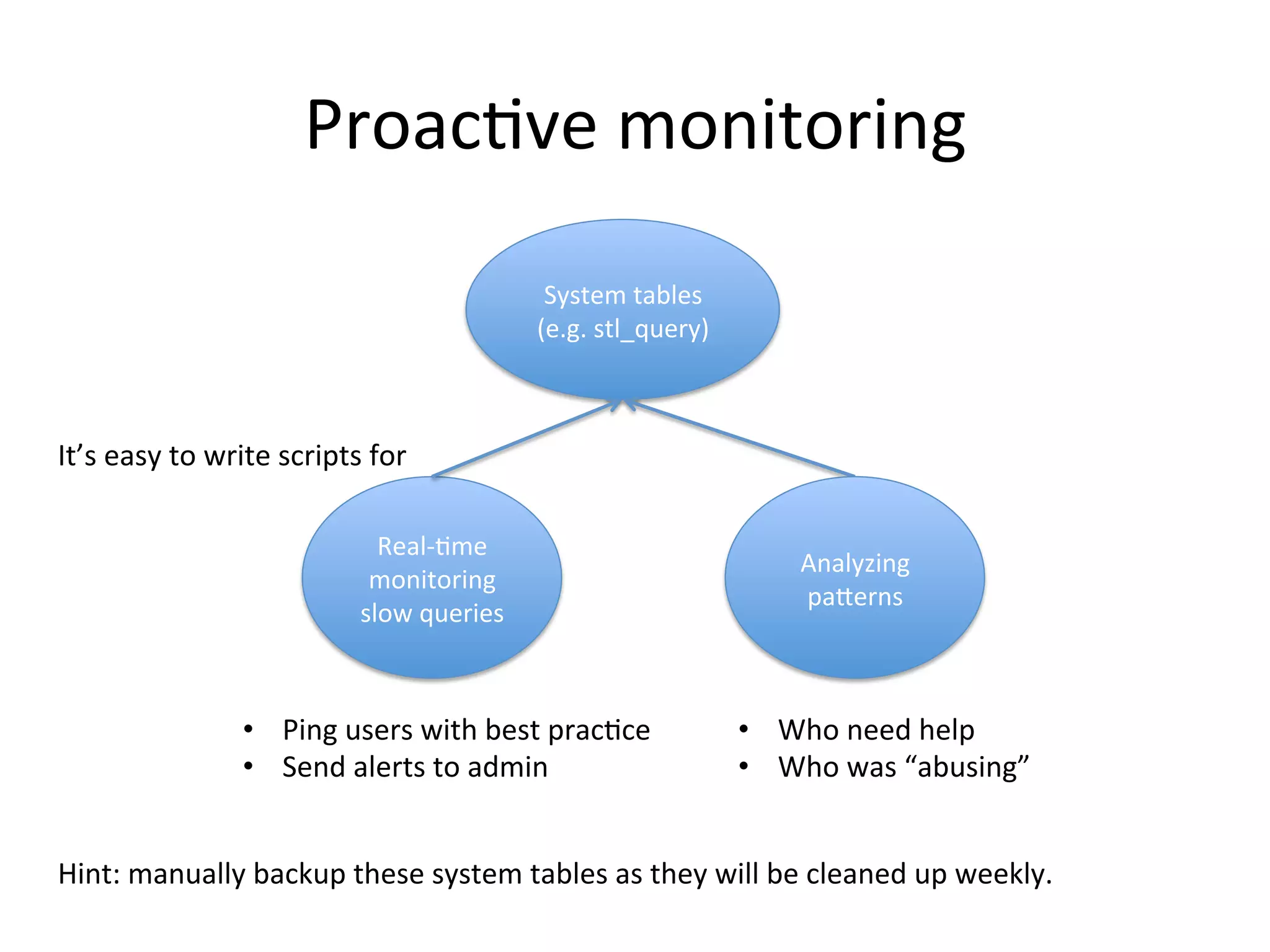
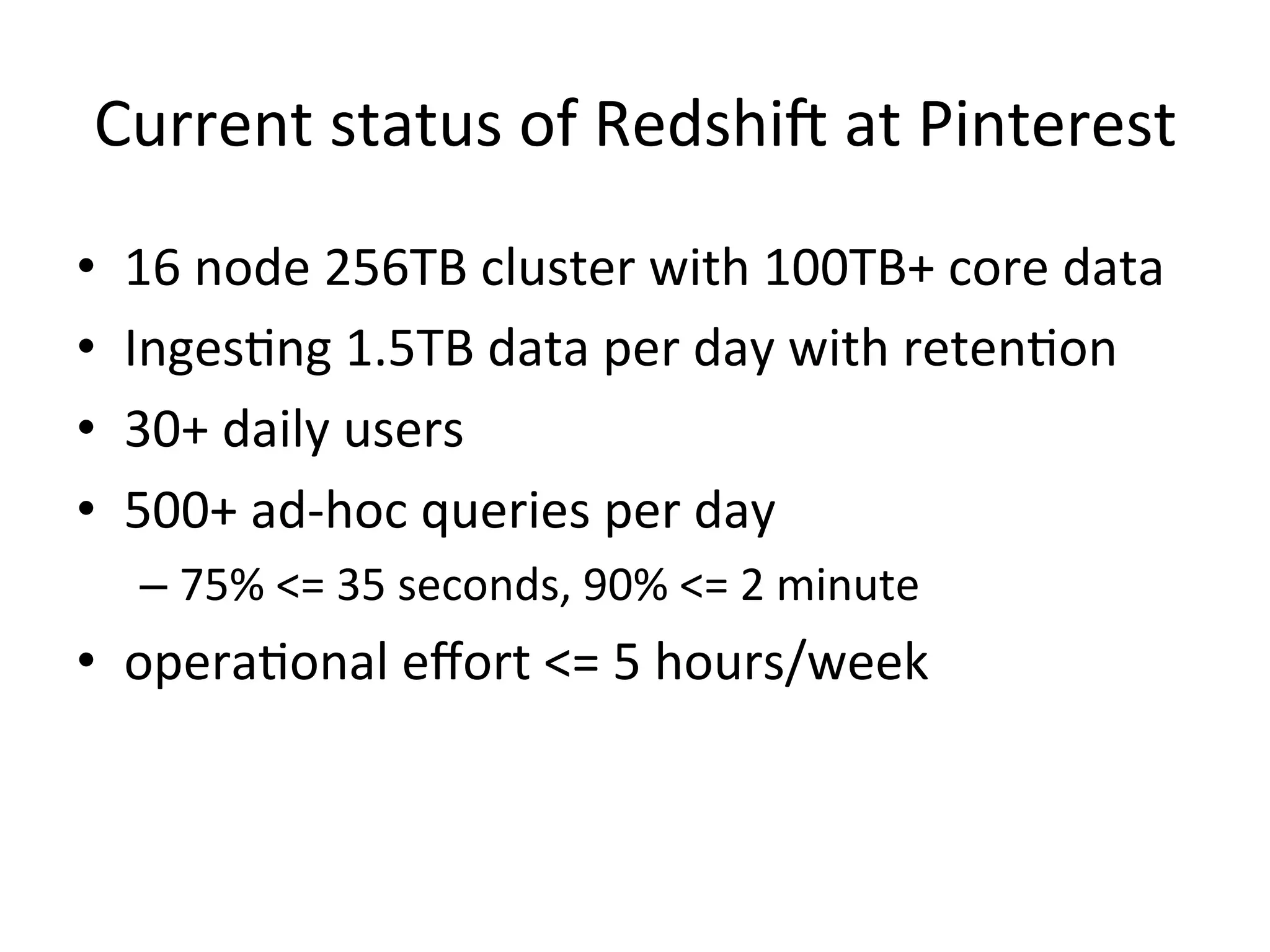
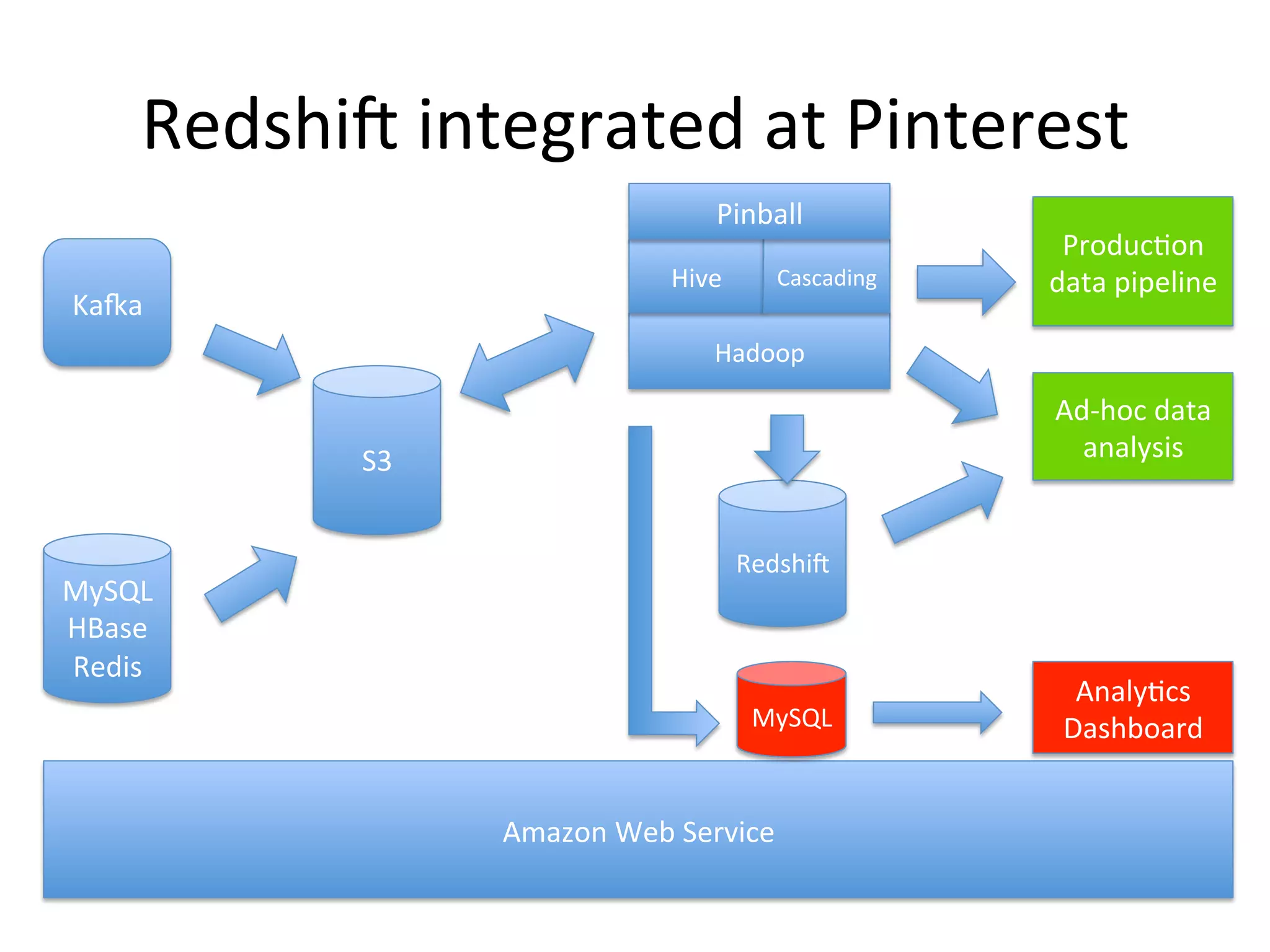
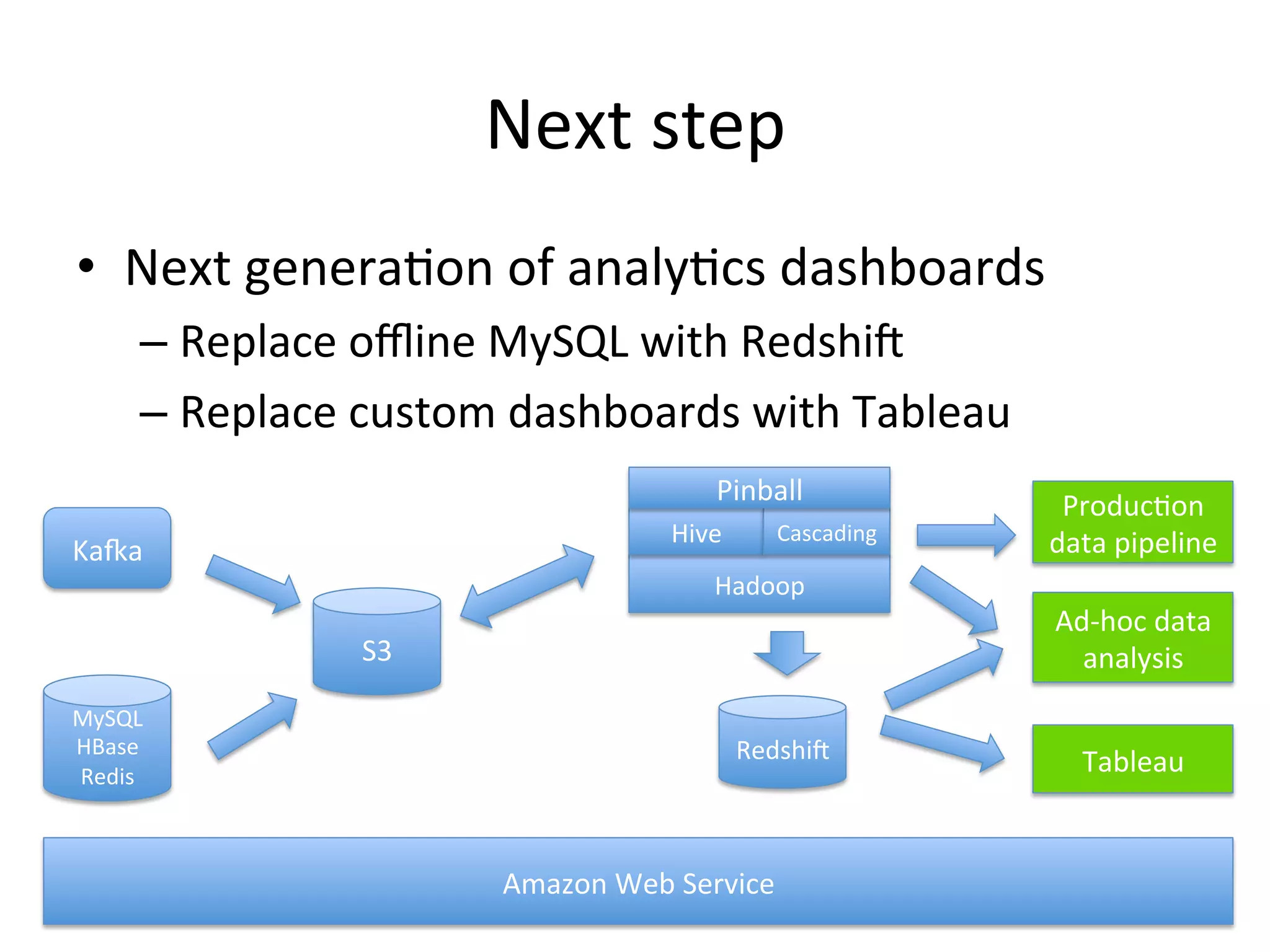
The document discusses how Pinterest leverages Amazon Redshift for interactive data analysis, outlining its advantages in terms of cost, maintenance, and performance compared to other data warehousing solutions like MySQL and Hadoop. It details the ETL process, best practices for optimizing queries, and the current operational status of their Redshift setup, including data ingestion and usage metrics. Future plans include enhancing analytics dashboards and addressing challenges related to SLA for low latency queries and cluster availability.