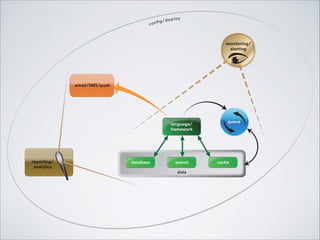
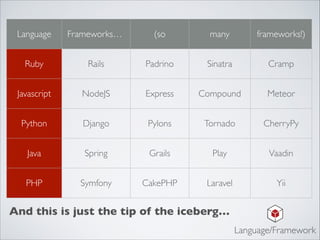
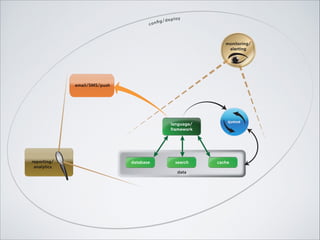
This document outlines the essential components of a modern web application architecture, highlighting nine key anatomical systems: programming language/framework, transactional database, cache, background queue, search, email/sms/push notifications, config/deployment, monitoring, and reporting/analytics. Each component plays a critical role in building scalable and efficient web products, from managing user data and interactions to ensuring system reliability and performance. Additionally, the document encourages collaboration with development teams to evaluate specific needs and implementation timelines for these systems.