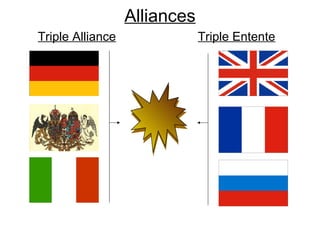
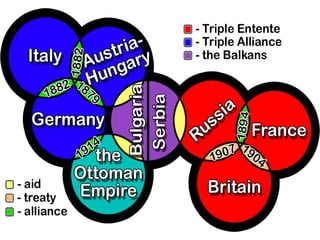
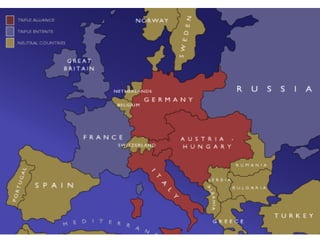
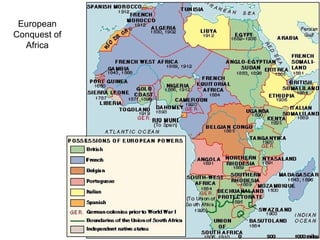
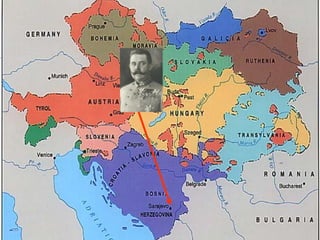
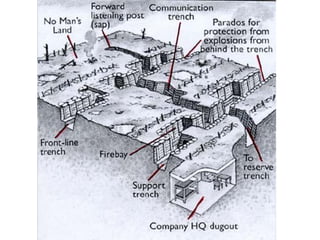
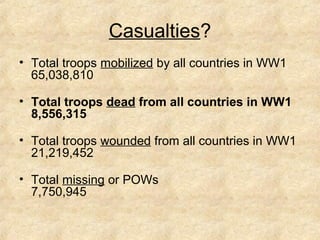
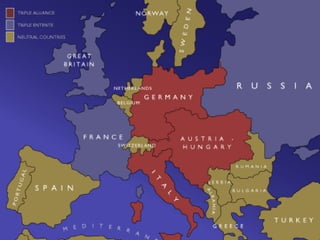
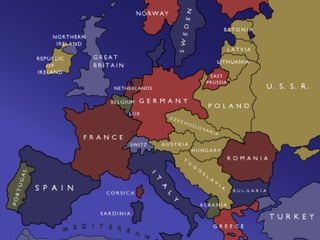
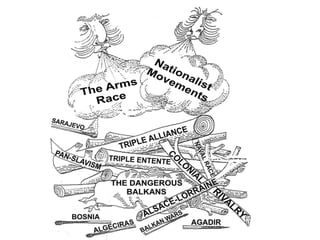
The causes of WWI included rising militarism, alliances between European powers, nationalism, and imperialism. Major European countries had significantly increased their military spending in the decade before WWI. Countries formed alliances that pulled them into the war, such as Germany supporting Austria-Hungary against Serbia, which was supported by Russia. Nationalism in countries like Serbia and Germany contributed to tensions. Imperialism led countries to compete for colonies in Africa and markets for their goods. The immediate trigger for war was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria by Serbian nationalists in 1914.