This document presents a workshop on using Git for version control, detailing commands for setting up a local repository, staging changes, committing files, and managing remote repositories. It includes practical examples, beginning with repository initialization and culminating in cloning and pushing files. The aim is to empower users to effectively track changes in their projects using Git.
![PREPARED AND PRESENTED BY
Dr.Saajid Abuluaih, PhD
3ed of April, 2021
J I S T & A R C H E P R E S E N T S
Web−Based Second−Life
School Management System
Workshop
Team: "Fantastic−Team”, Project: "GatherRound”
[ G I T ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop3ed-apr-git-210404194102/75/Workshop-3ed-Apr-Git-1-2048.jpg)


![© 2021 Arche1.co.jp All rights reserved. P A G E 4
Git is software for tracking changes in any set of files, usually used for coordinating work
among programmers collaboratively developing source code during software development.
Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows.
[Source]
What is “version control”, and why should you care? Version control is a system that
records changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions
later. For the examples in this book, you will use software source code as the files being
version controlled, though in reality you can do this with nearly any type of file on a
computer. [Source]
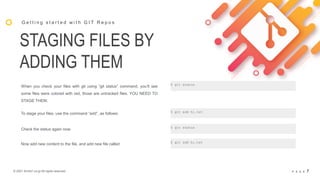
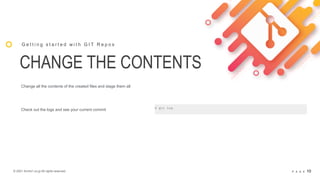
GIT
G e t t i n g s t a r t e d w i t h G I T R e p o s
If you installed git already, check its version: $ git --version](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop3ed-apr-git-210404194102/85/Workshop-3ed-Apr-Git-4-320.jpg)
![© 2021 Arche1.co.jp All rights reserved. P A G E 5
you can easily set up an alias for each command using git config. Check the
examples that you may want to set up for your own, [source]:
GIT CONFIG GLOBAL
G e t t i n g s t a r t e d w i t h G I T R e p o s
$ git config --global user.name “MyFirstName MyLastName"
$ git config --global user.email MyEmailAddress@example.com
$ git config --global -l
$ git config --global alias.co checkout
$ git config --global alias.br branch
$ git config --global alias.ci commit
$ git config --global alias.st status
Git uses a series of configuration files to determine non-default behavior that
you may want. The first place Git looks for these values is in the system-wide
[path]/etc/gitconfig file, which contains settings that are applied to every user
on the system and all of their repositories. If you pass the option --system to git
config, it reads and writes from this file specifically. [source]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop3ed-apr-git-210404194102/85/Workshop-3ed-Apr-Git-5-320.jpg)





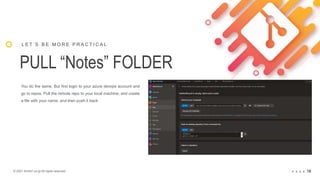
![© 2021 Arche1.co.jp All rights reserved. P A G E 13
PUSH AND PULL
G e t t i n g s t a r t e d w i t h G I T R e p o s
$ git pull
$ git push
The most common command that we will use very frequently along
with “add”, and “commit” are:
• “pull”: which is used to fetch and download content for a remote
repository and immediately update the local repository to match
the coming-in content. [source]
• “push”: is used to upload local repository content to a remote
repository. Pushing is the function of transferring commits from
local to a remote repos. It is the counterpart to git fetch (pull)
[source]
Distributed version control
[source]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop3ed-apr-git-210404194102/85/Workshop-3ed-Apr-Git-13-320.jpg)