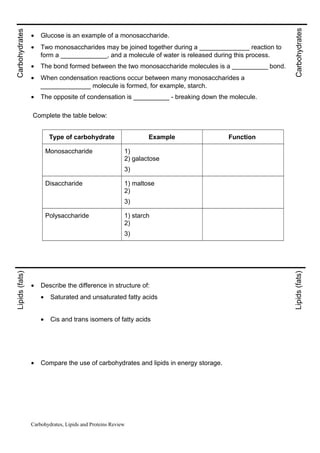
This document provides a review of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. It includes diagrams of amino acid and monosaccharide structures. Condensation reactions are described which join monomers like amino acids and monosaccharides into polymers like proteins and polysaccharides. These reactions release water. Hydrolysis reactions break these polymers down. Characteristics of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, and cis and trans fatty acid isomers are outlined. Carbohydrates and lipids are compared in their use for energy storage. Glycerol and fatty acid condensation into lipid molecules is depicted, along with the insolubility of most lipids due to their nonpolar hydrocarbon chains.