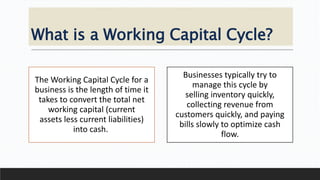
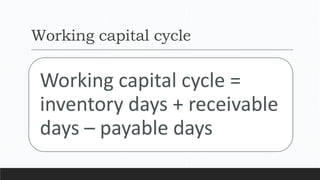
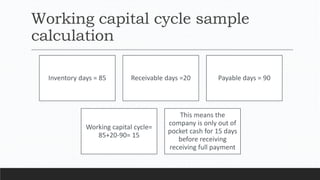
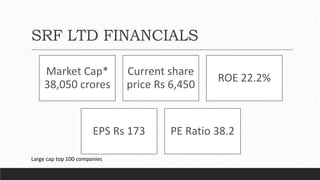
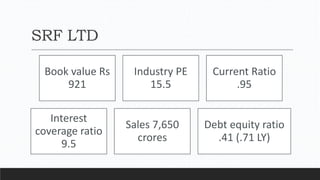
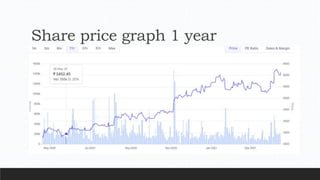
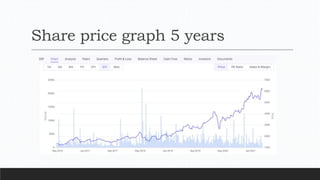
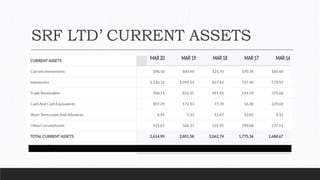
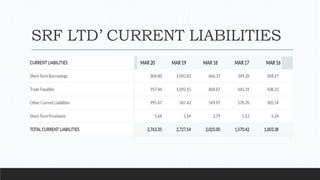
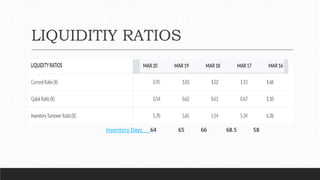
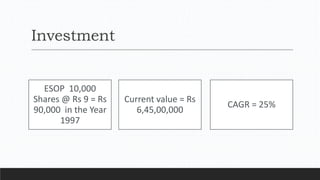
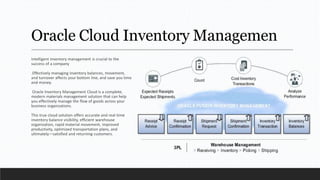
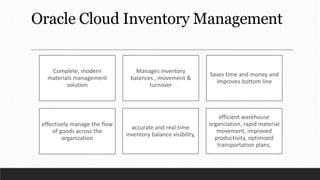
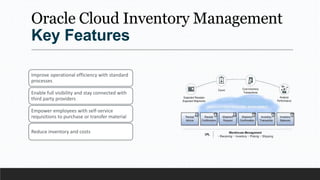
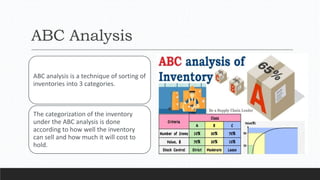
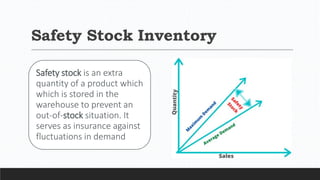
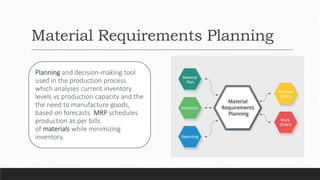
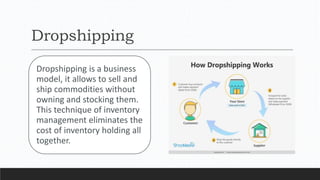
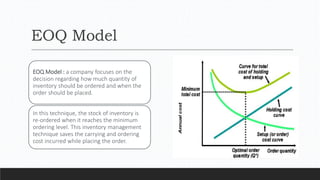
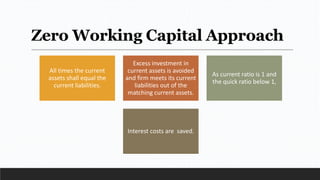
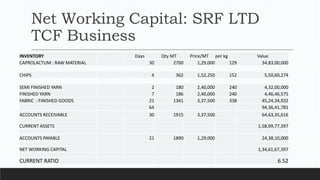
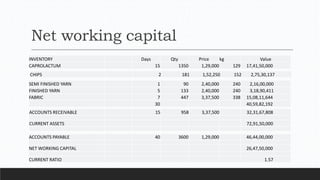
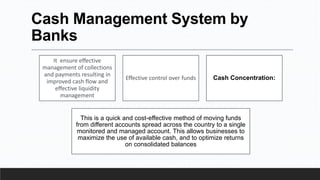
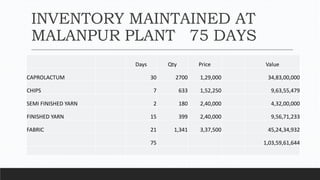
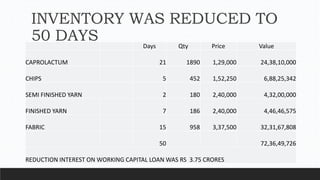
Parvesh Aghi has over 23 years of experience working in finance roles for various companies. He currently works as a visiting faculty at several business schools. He specializes in teaching subjects related to working capital management. Efficient working capital management is important for companies as it helps maintain smooth operations and can improve earnings. Key aspects of working capital management include inventory management, managing accounts receivable, and accounts payable. SRF Ltd is used as a case study, demonstrating techniques like inventory optimization, cash management systems, and the benefits of efficient working capital.