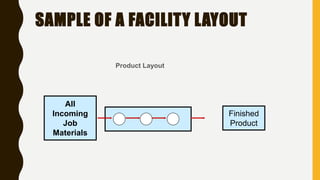
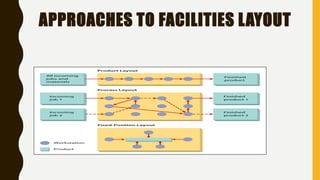
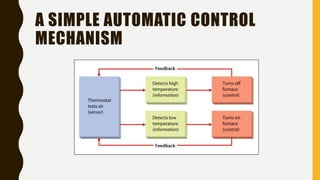
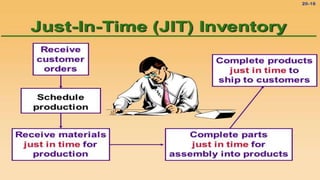
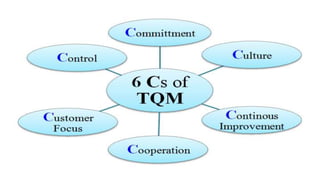
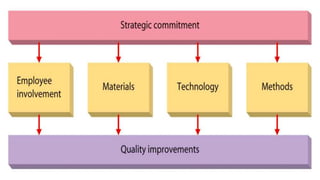
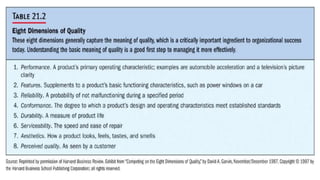
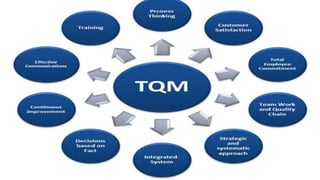
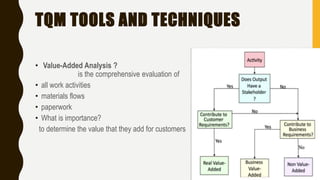
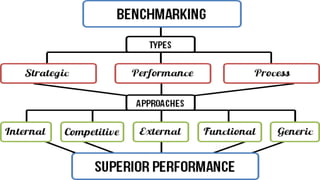
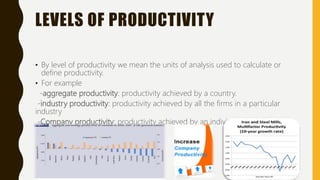
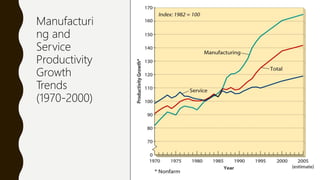
The document introduces a student project team and discusses key concepts in operations management including operations, quality management, productivity, and technology. It defines operations management as the set of activities used to transform inputs into products/services. Ensuring efficient operations is important for competitiveness, performance, quality and productivity. Total quality management and just-in-time inventory systems are discussed as approaches to improve quality and productivity.