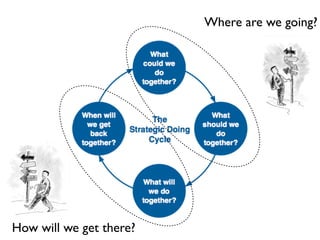
The document discusses Workforce Development 2.0, emphasizing the importance of adopting a systems perspective, using skills as a common language, and creating new career pathway maps. It outlines five key realities for effective workforce development, including managing regional skills banks and fostering strategic collaborations. The implications for policy suggest the need to transition from outdated programs to innovative investments in skill assessments and training opportunities.