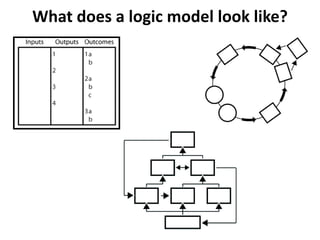
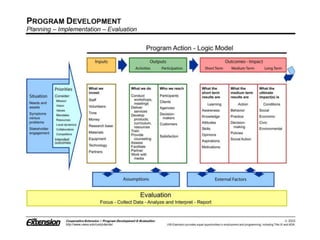
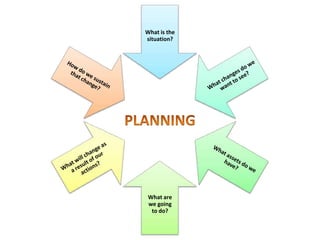
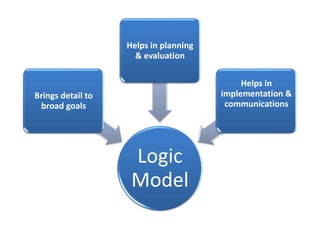
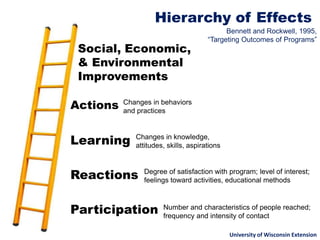
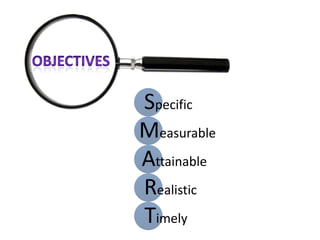
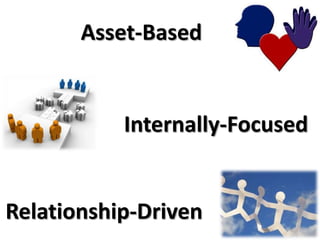
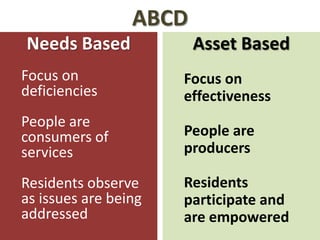
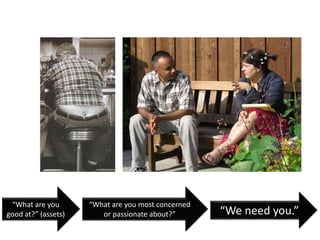
The document explains the concept of logic models, illustrating their role in program evaluation by visually representing the relationship between program activities and intended outcomes. It discusses the benefits of using logic models for planning, communication, and consensus-building while also acknowledging their limitations, such as not capturing actual outcomes or the complexities of human relationships. Additionally, it highlights the importance of an asset-based community development approach, encouraging residents to identify and utilize their strengths for effective community engagement.