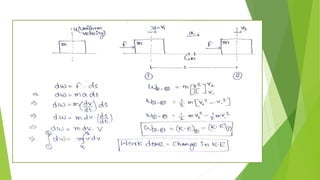
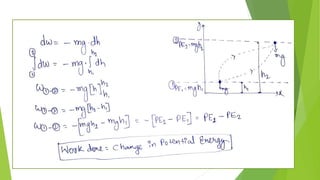
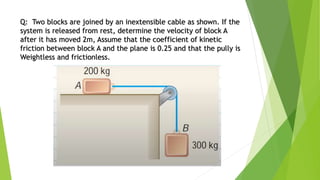
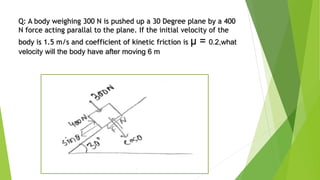
This document summarizes work, energy, and the work-energy principle as applied to connected bodies. It discusses conservative and non-conservative forces, defines work, and states the work-energy theorem for both kinetic and potential energy. The theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic (or potential) energy. The document provides examples and sample problems applying these concepts to blocks connected by a cable or moving up an inclined plane.