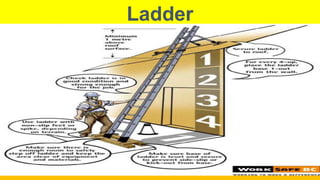
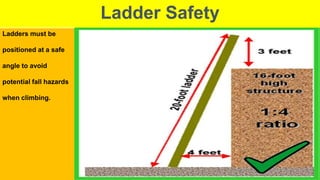
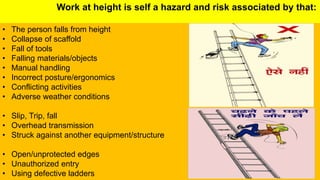
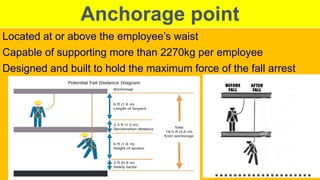
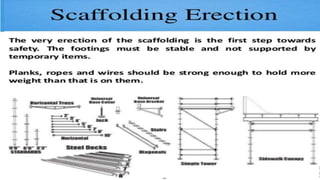
This document outlines essential training for scaffolding and heat stress prevention, including symptoms of heat stress and how to respond. It emphasizes ladder safety, fall protection, and proper scaffold construction while adhering to OSHA standards. Key components of personal fall arrest systems and the importance of inspections and safe practices in scaffolding are also highlighted.