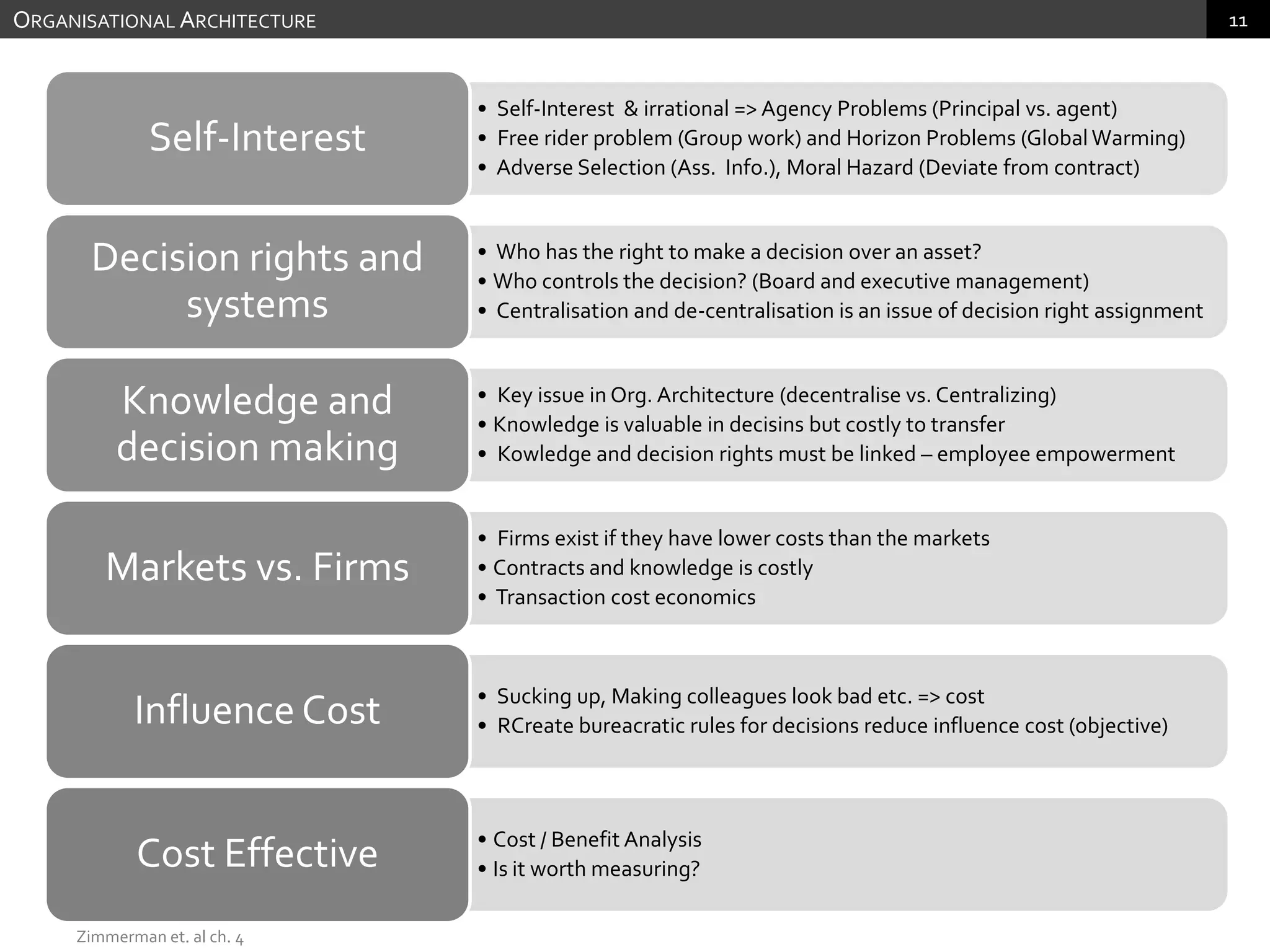
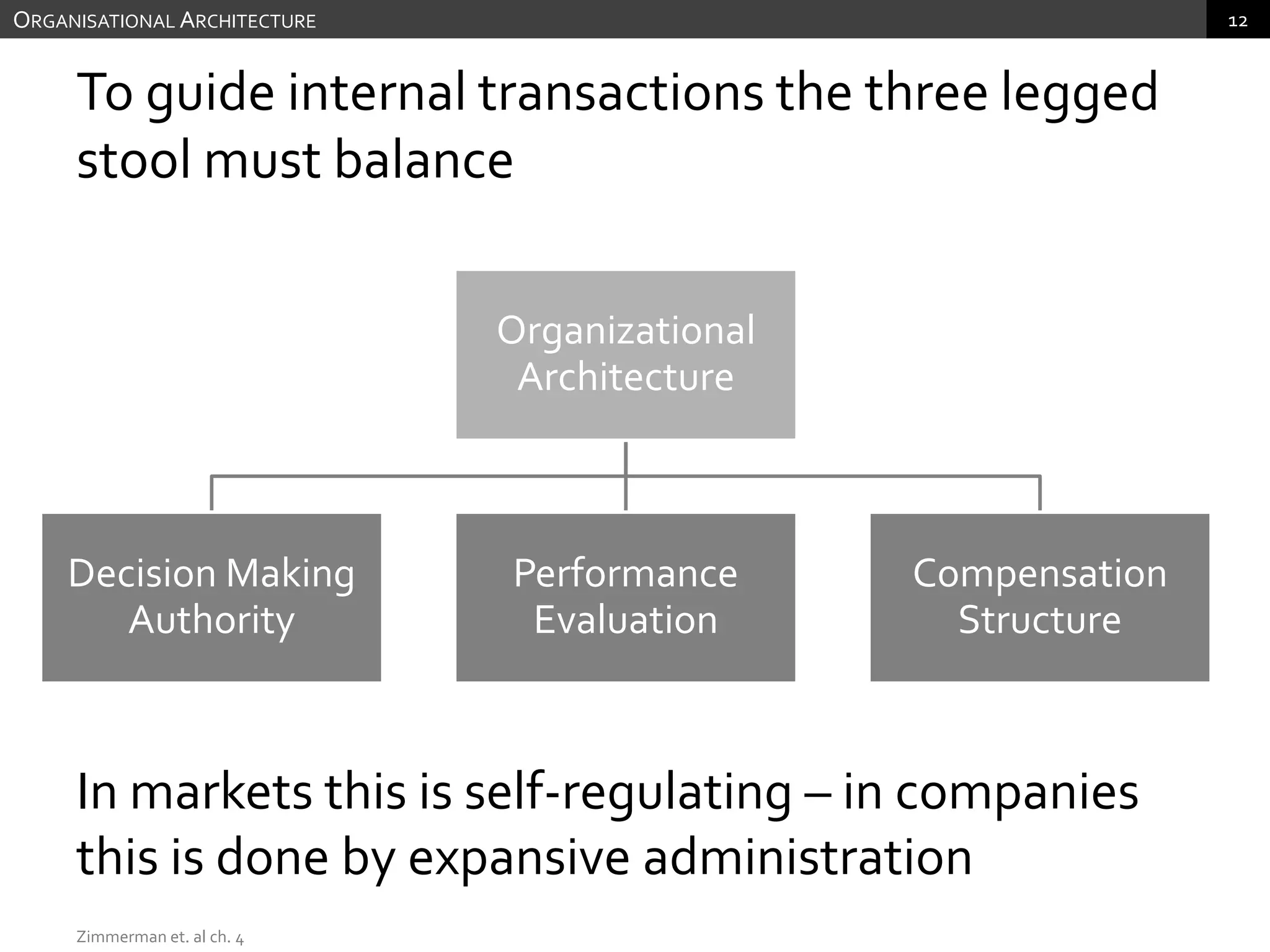
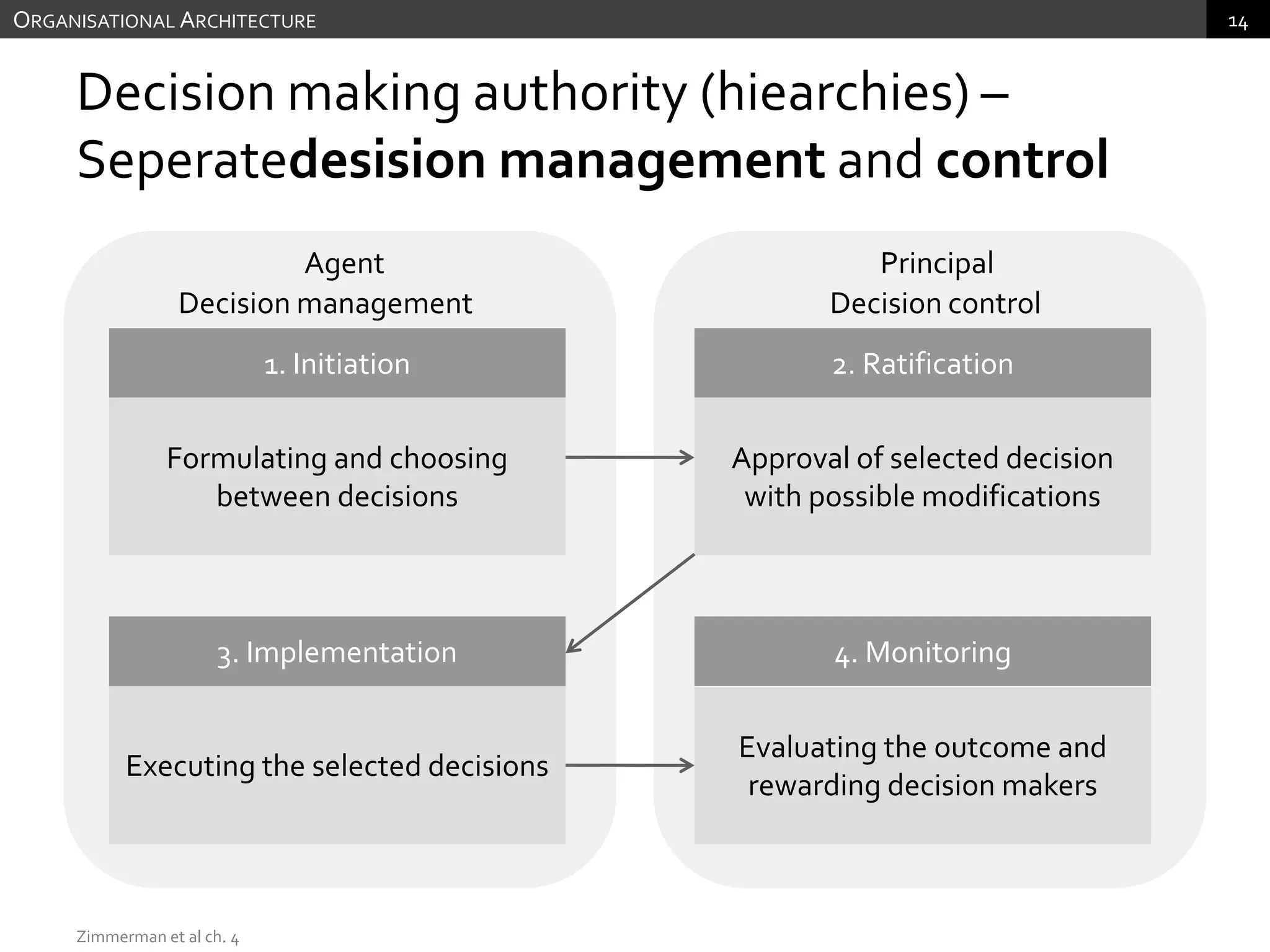
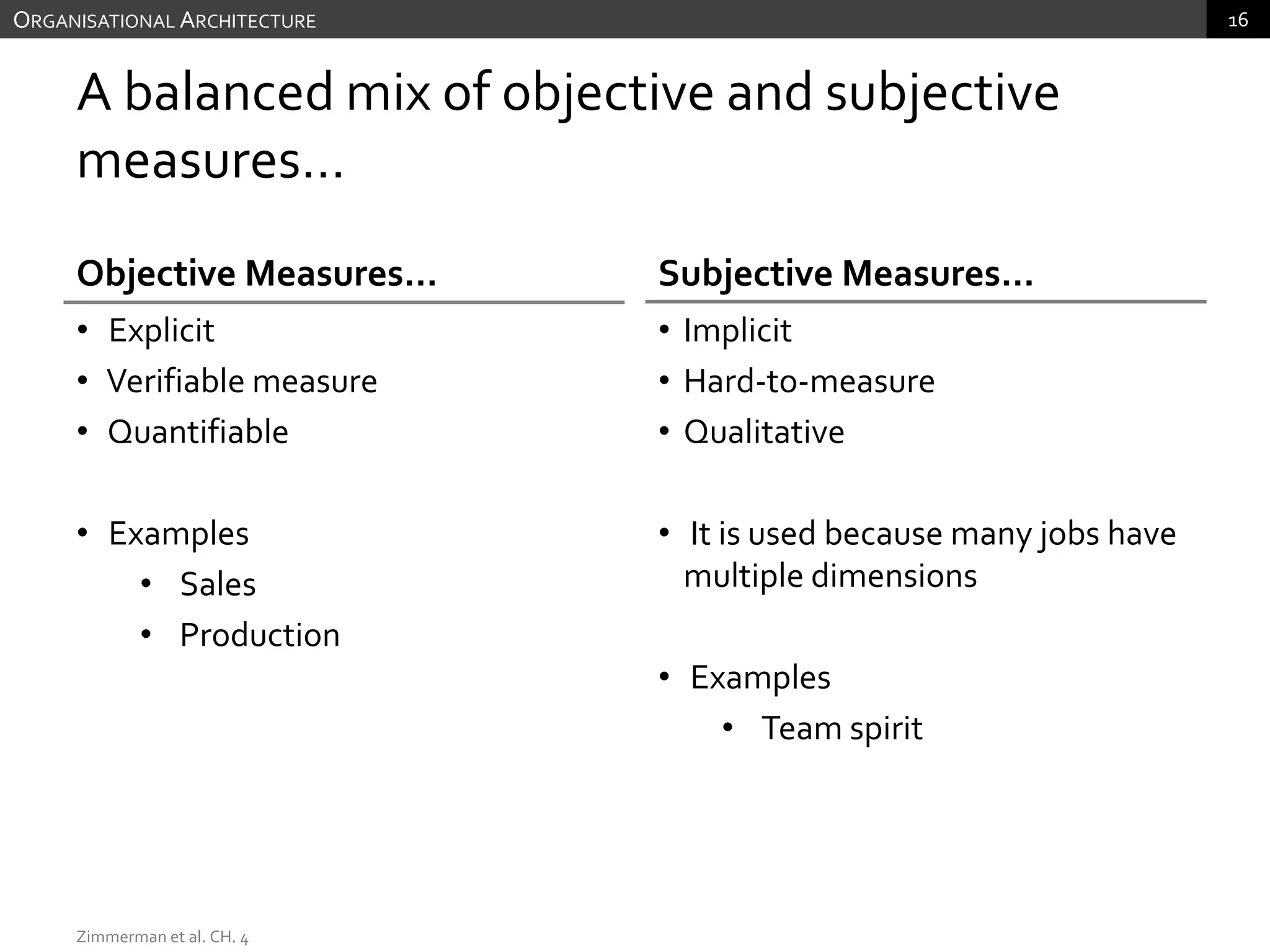
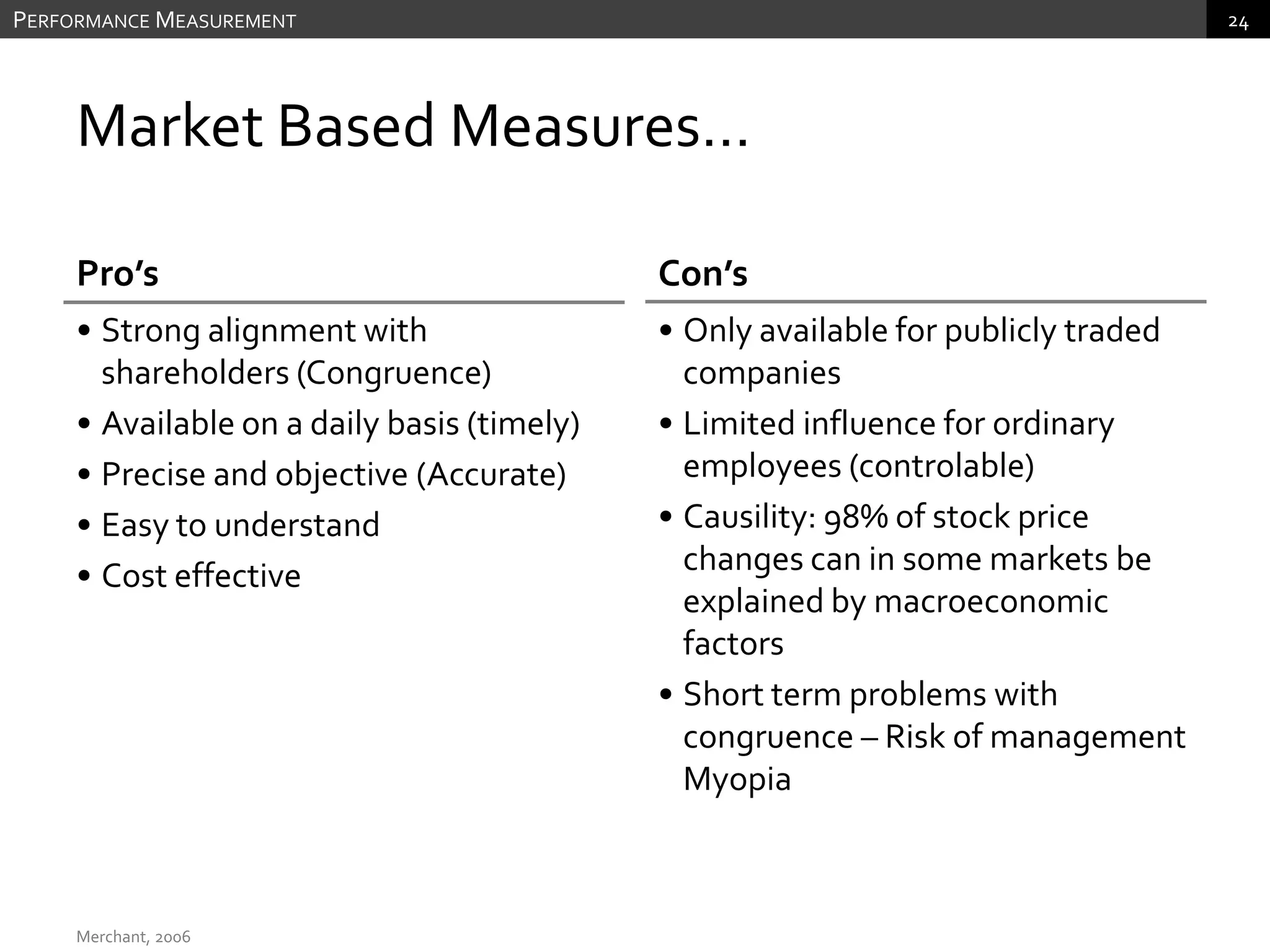
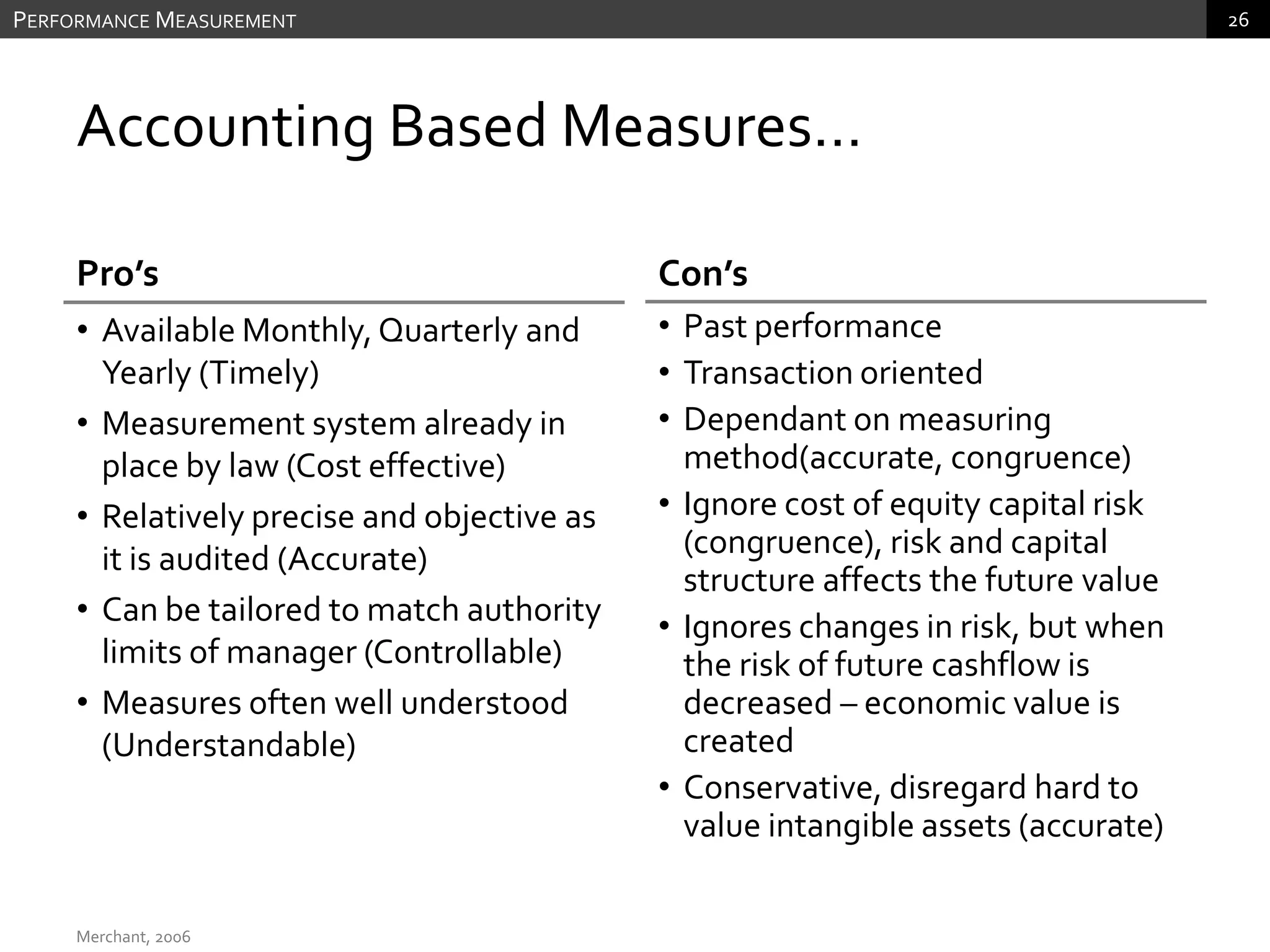
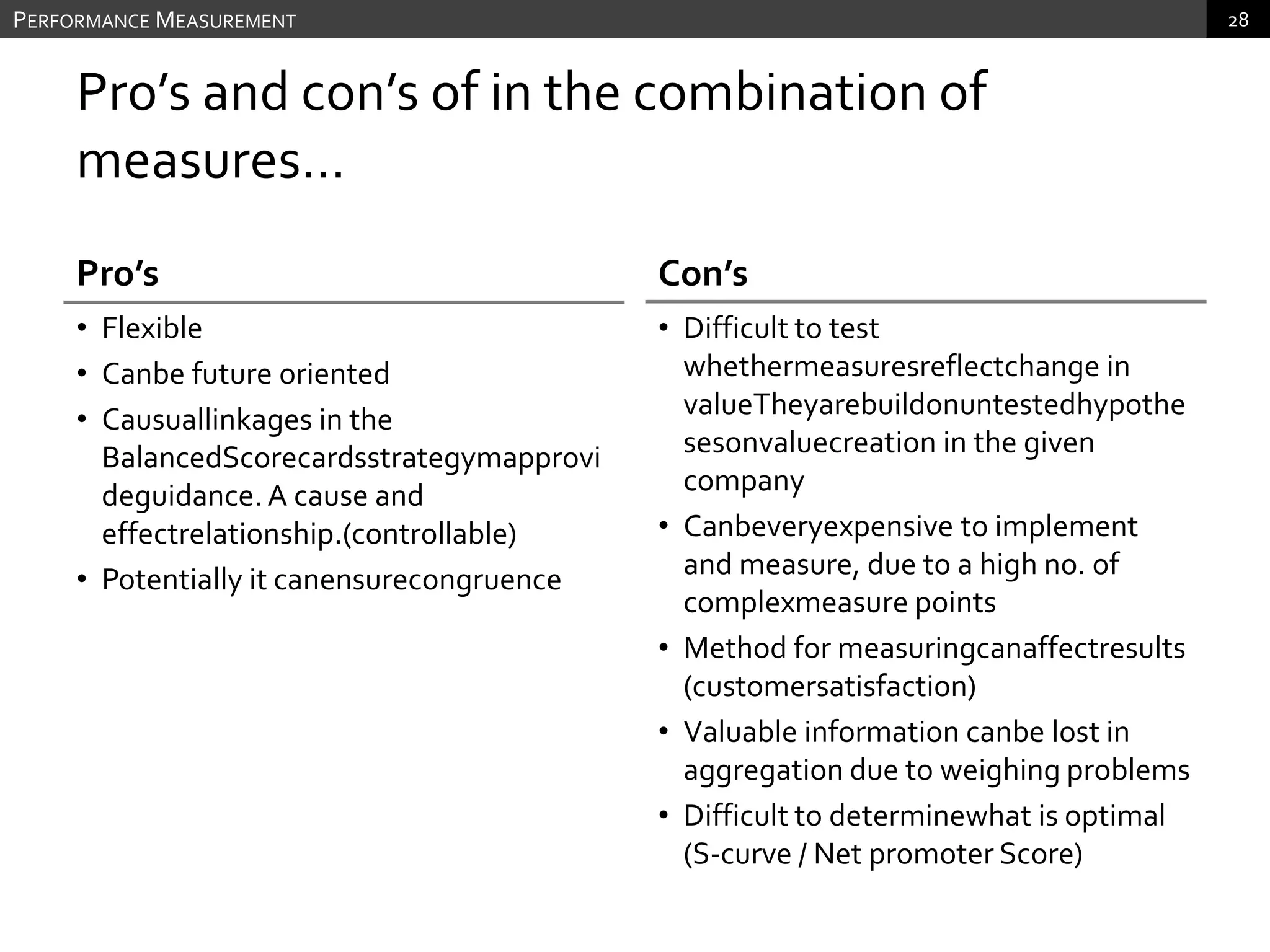
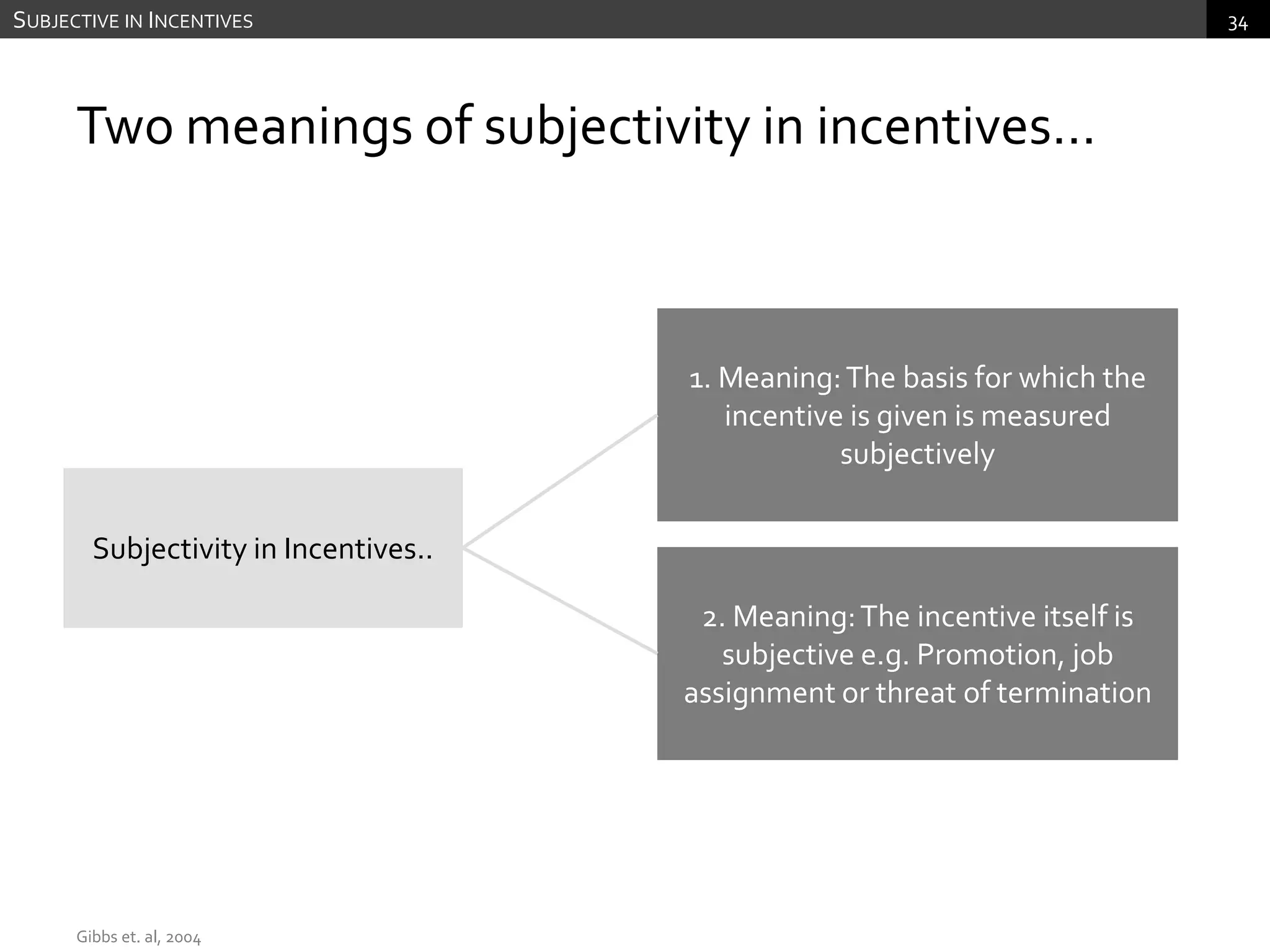
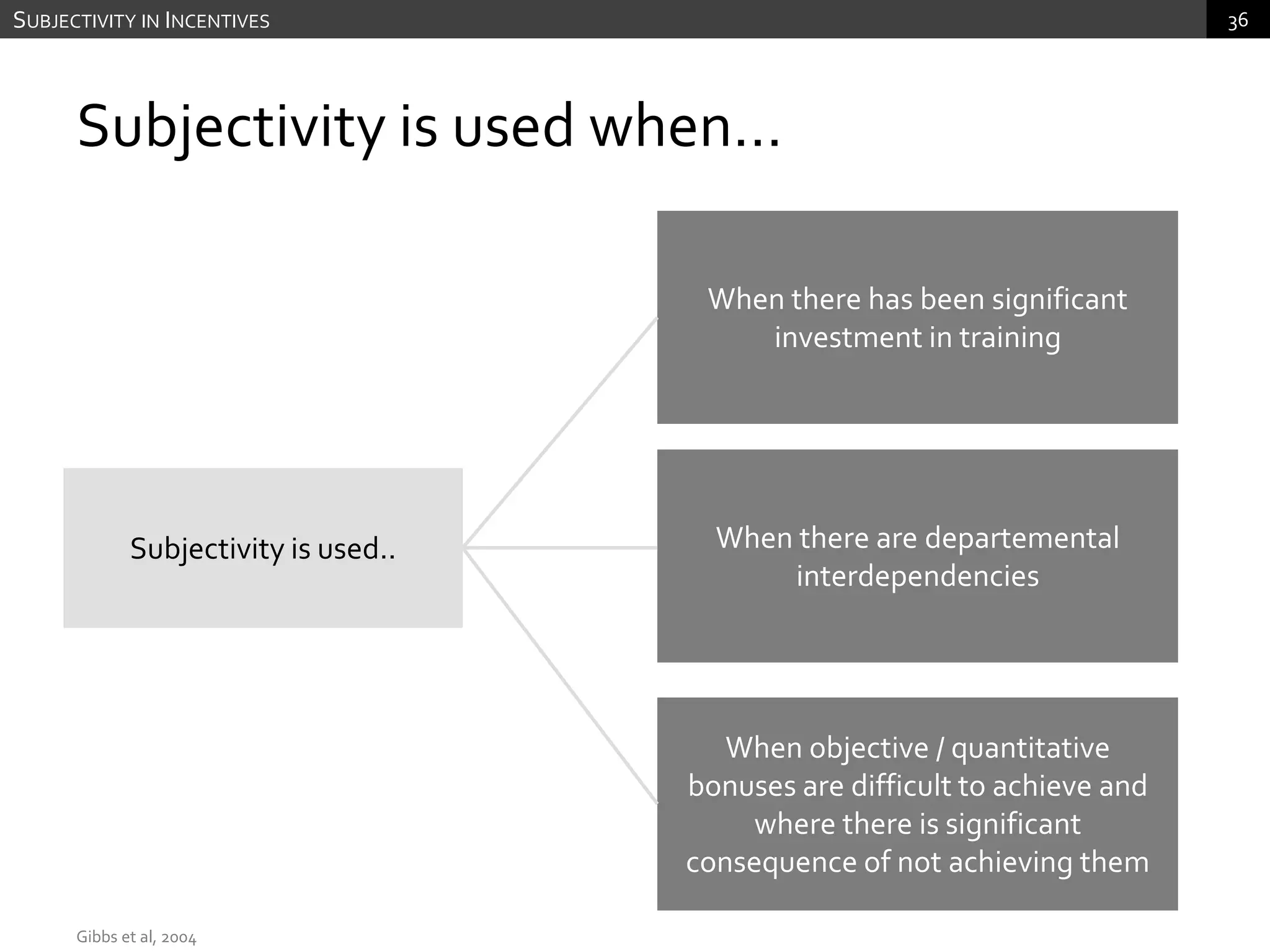
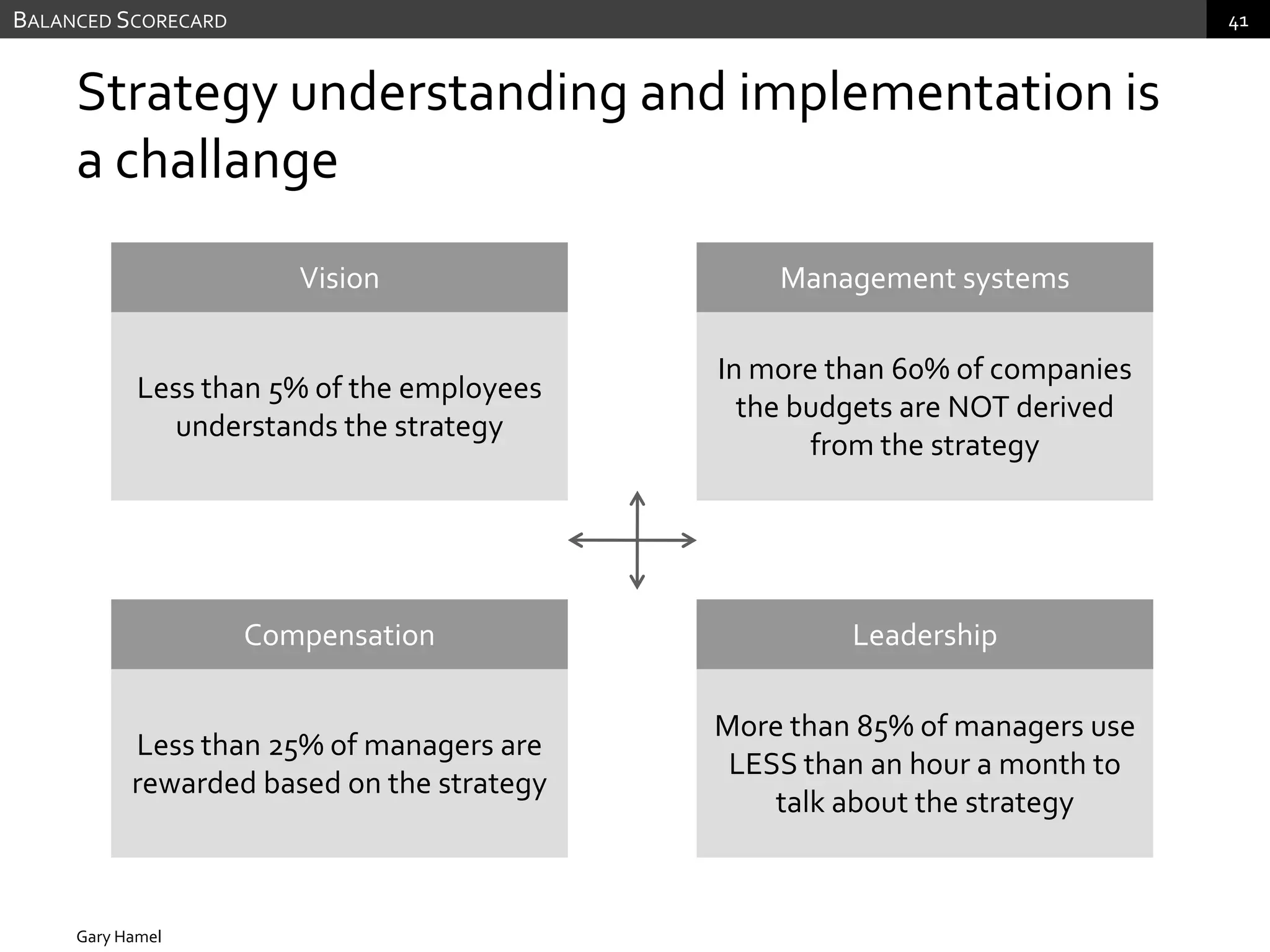
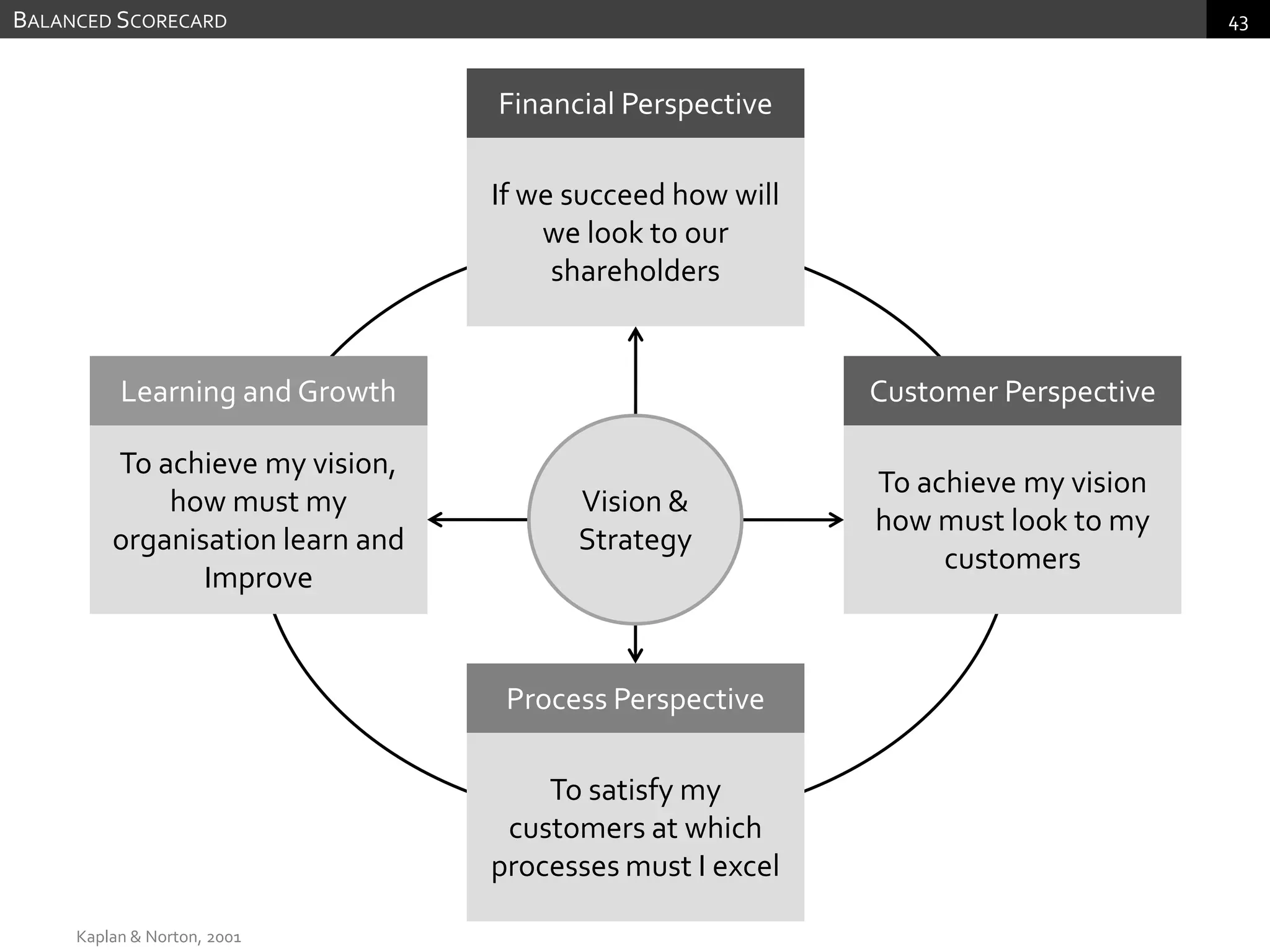
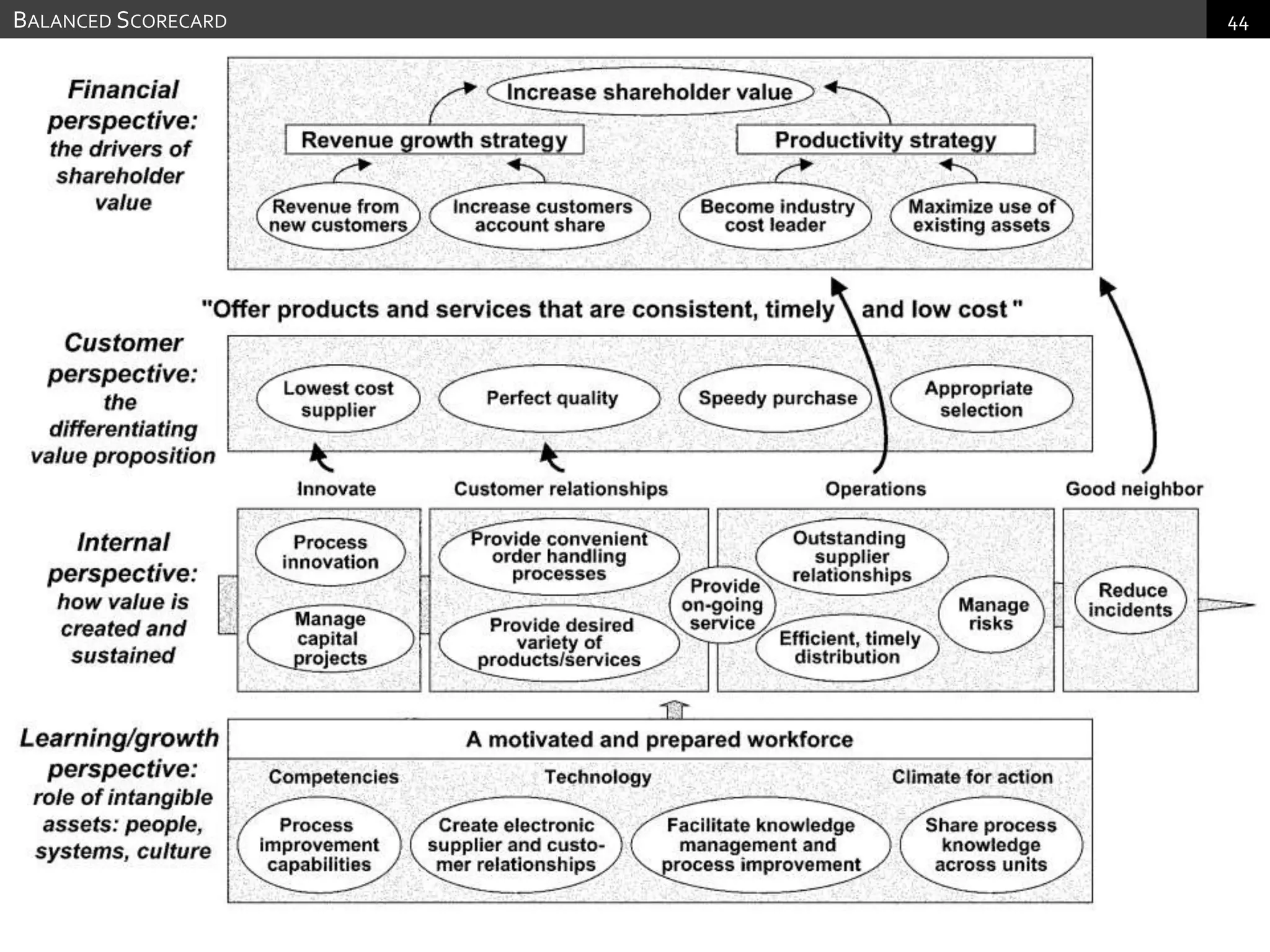
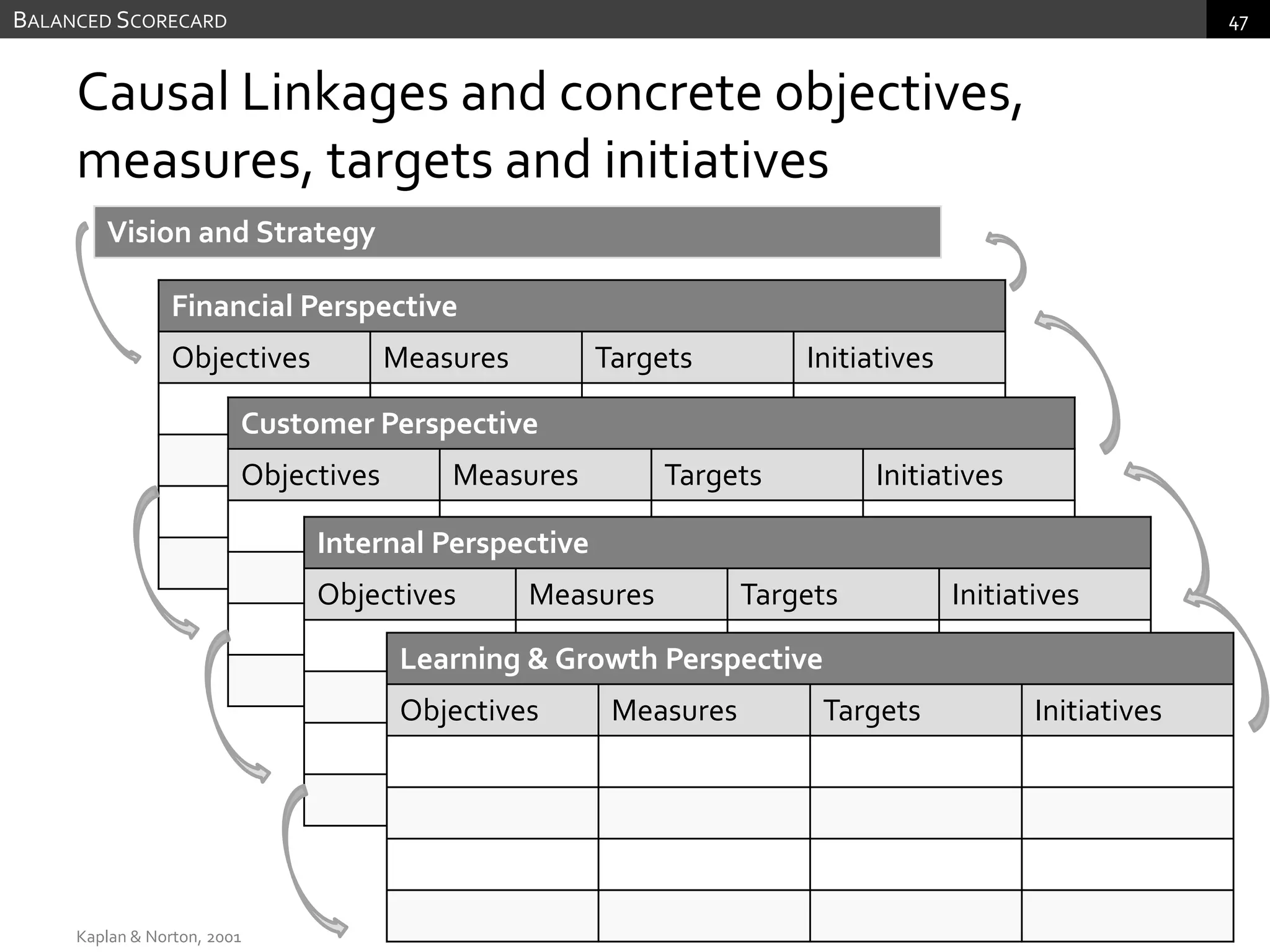
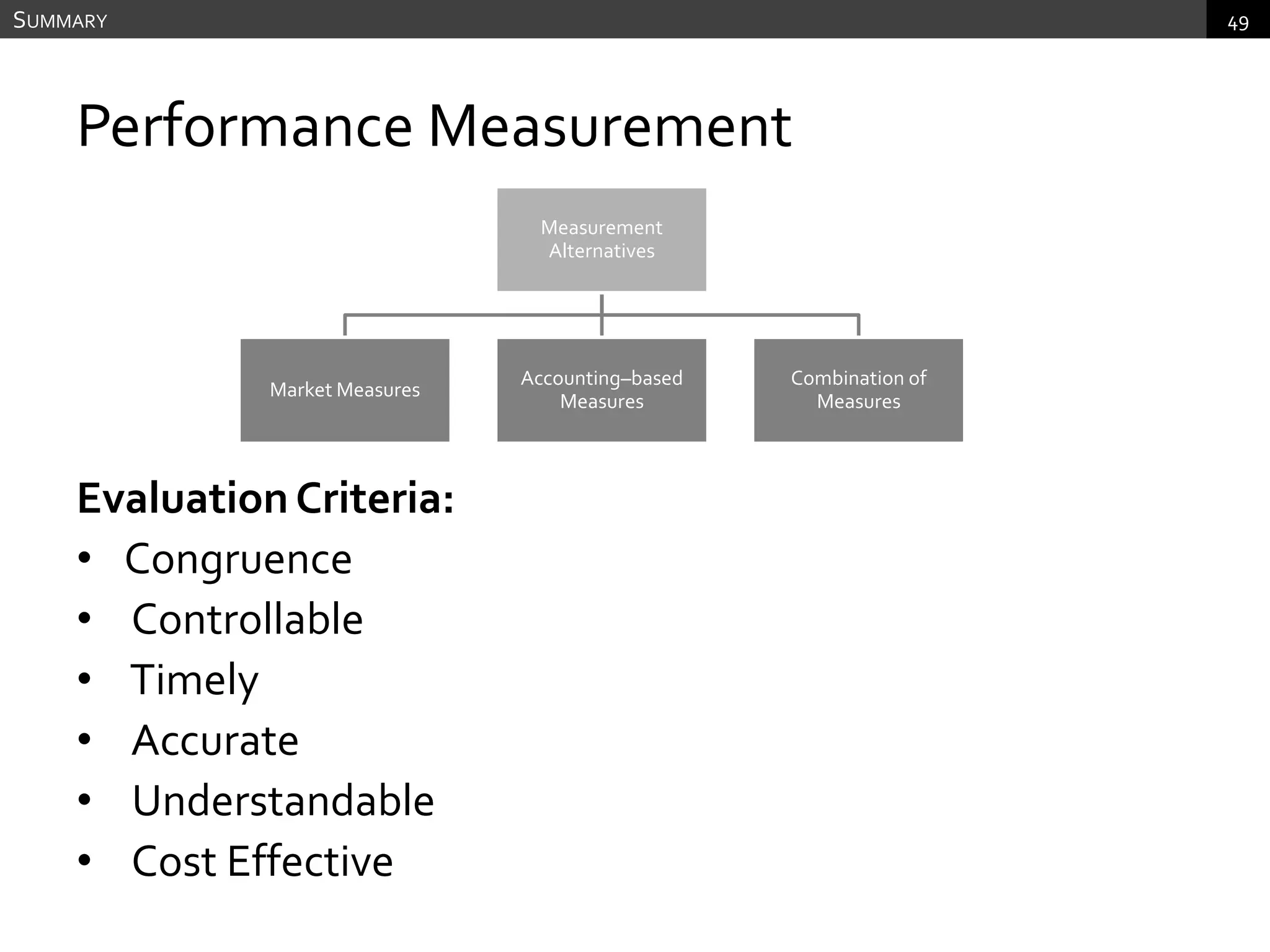
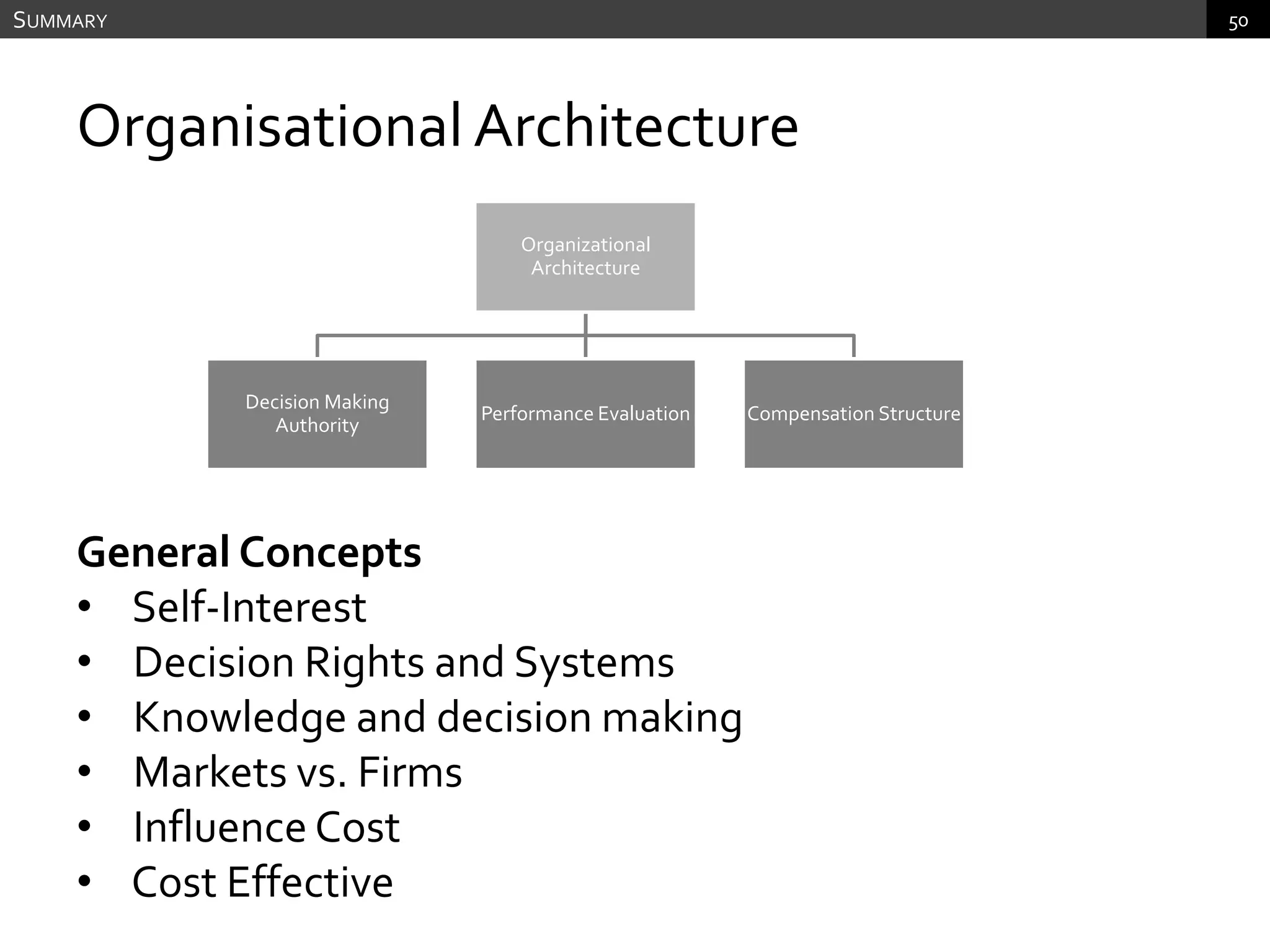
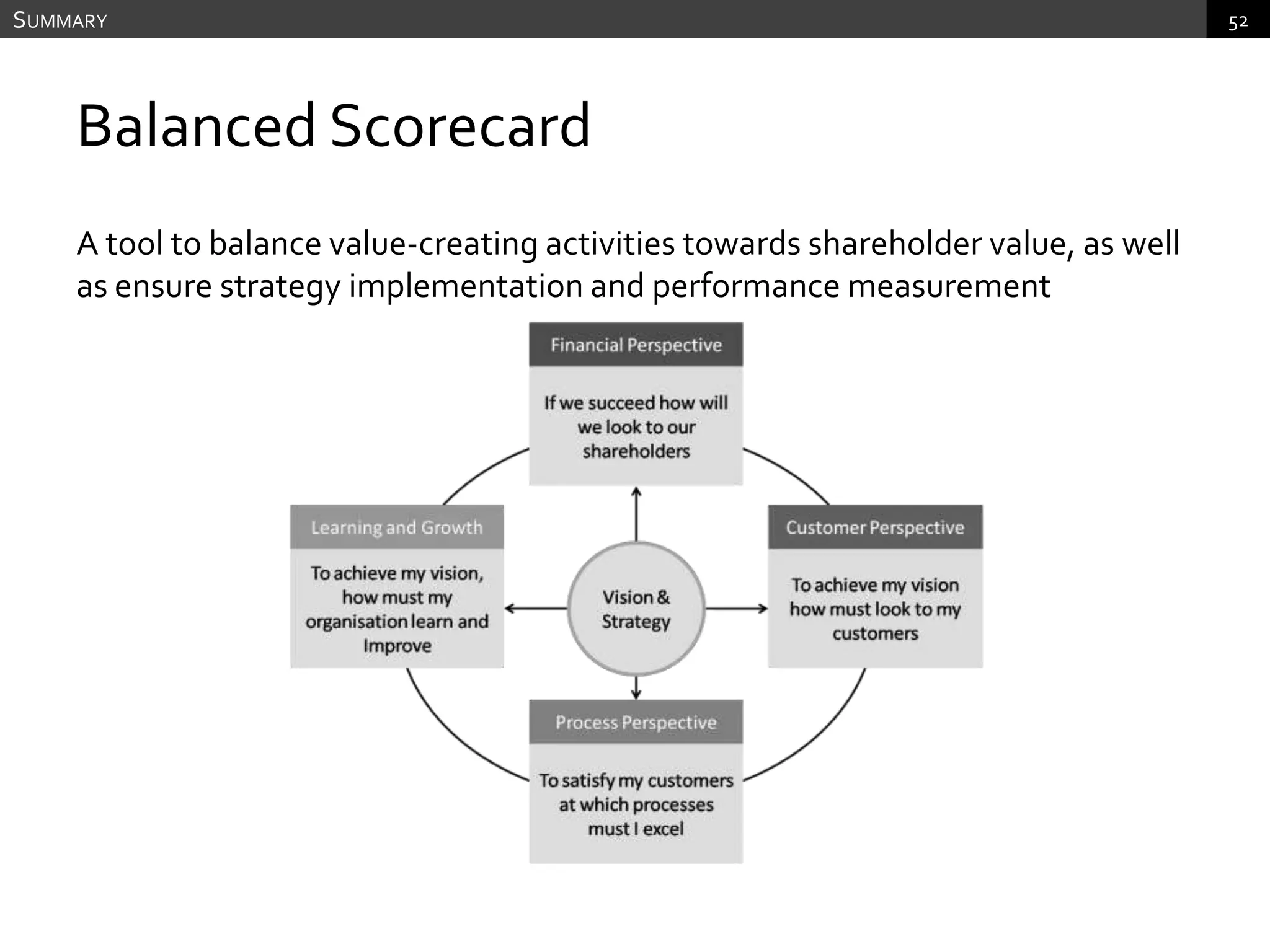
The document discusses performance measurement and management. It describes the balanced scorecard approach which takes a balanced view of value creation by focusing on financial, customer, internal process and learning/growth perspectives. It also discusses using a combination of objective and subjective measures to evaluate performance, as no single measure can fully reflect performance. Subjectivity in incentives may be used when targets are difficult to achieve or quantify, or when there are interdependencies between departments. Organizational architecture must balance decision rights, performance evaluation and compensation structures to properly incentivize employees.