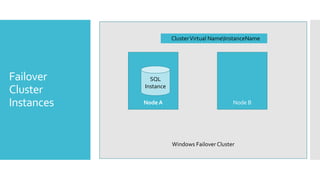
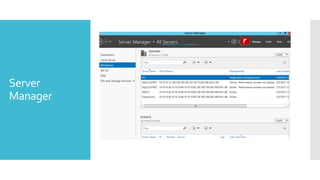
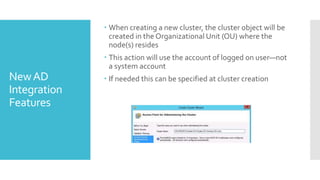
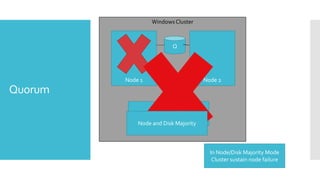
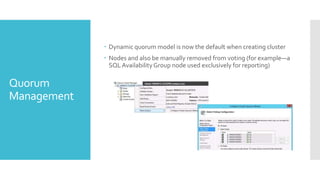
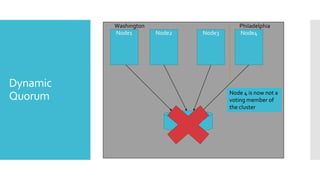
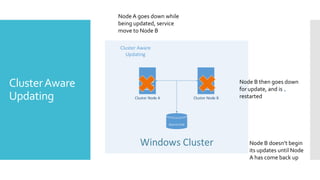
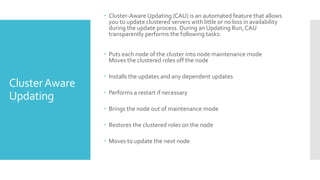
This document summarizes new features in Windows Server 2012 Failover Clustering. Key points include: increased scalability up to 4,000 Hyper-V VMs per cluster; easier cluster management through Server Manager; automated cluster-aware updating to reduce downtime during updates; and more flexible quorum management and task scheduling. The majority of changes improve flexibility and management of large Hyper-V virtual environments.