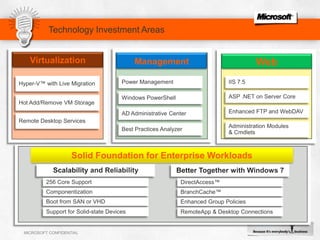
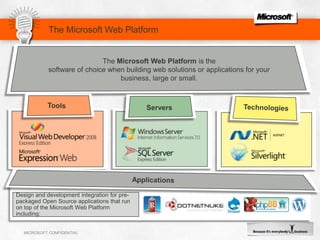
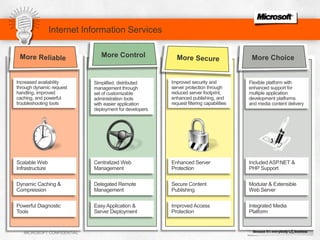
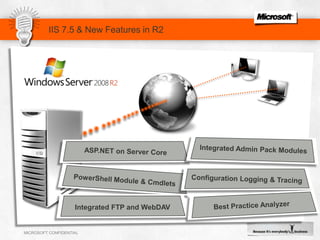
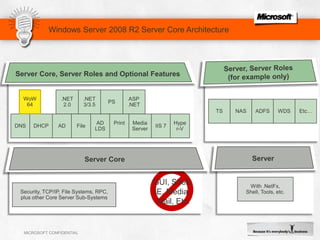
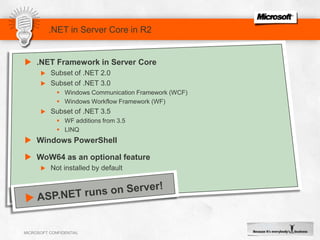
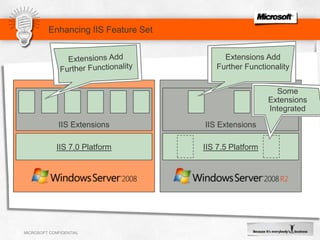
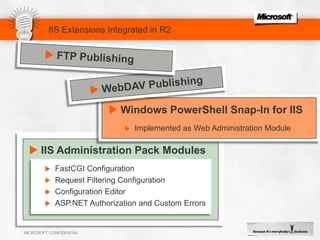
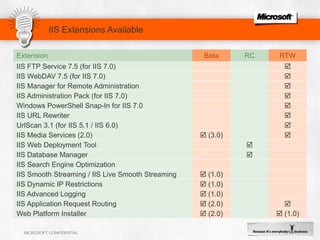
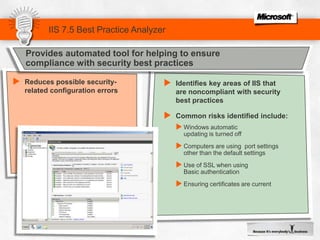
IIS 7.5 in Windows Server 2008 R2 includes enhancements such as ASP.NET support on Server Core, integrated administration modules for features like FTP and WebDAV, and a PowerShell module and cmdlets for management. Other new features include configuration logging and tracing, a Best Practice Analyzer for security compliance, and application auto-start functionality. The presentation discusses these and other recent investments made by Microsoft to improve reliability, security, manageability and the feature set of IIS and the Microsoft web platform.