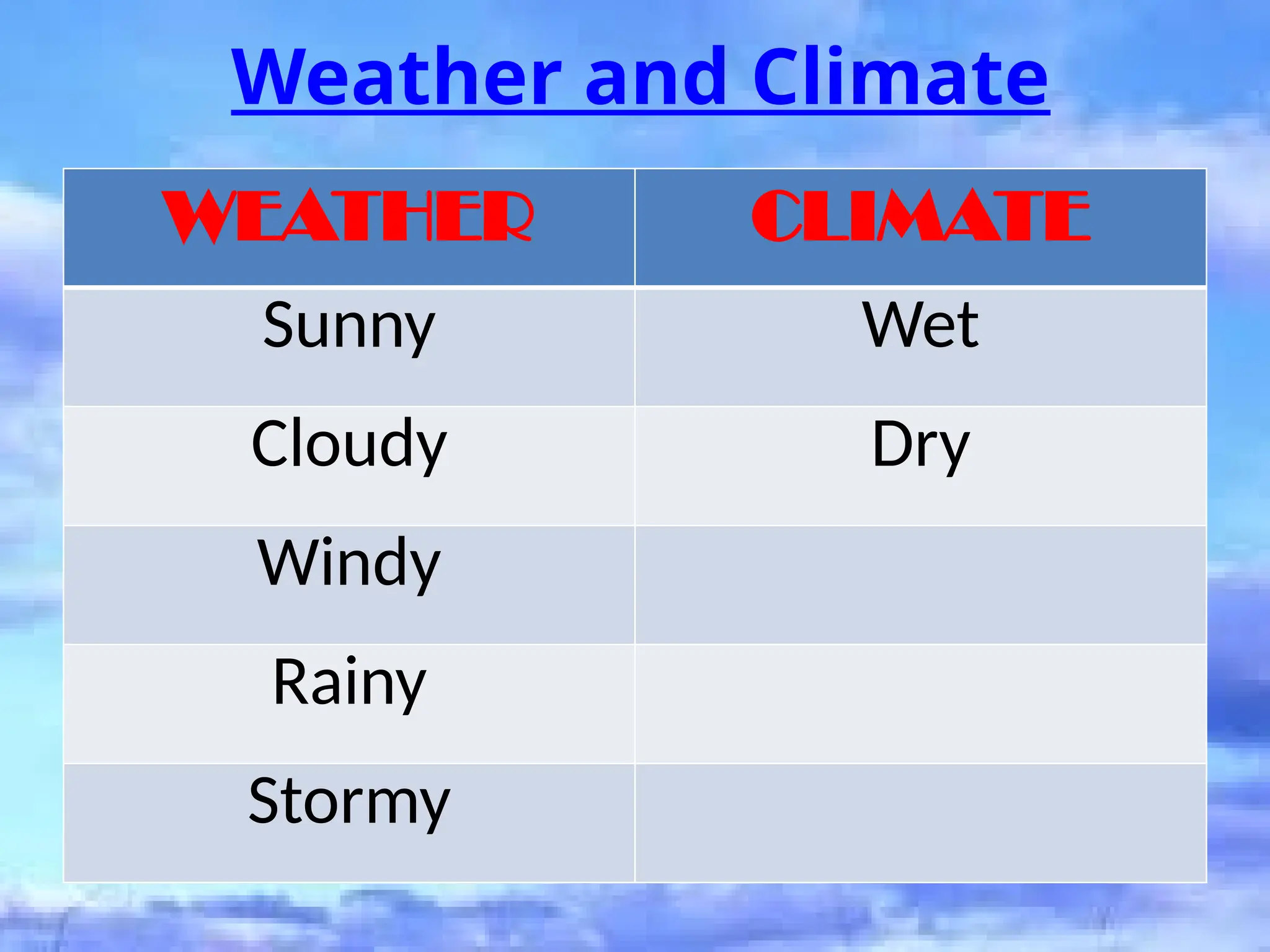
The document discusses weather patterns and climate in the Philippines, focusing on its two main seasons: wet and dry. It describes the characteristics of each season, such as temperature ranges, rainfall patterns, and the influence of prevailing winds on weather. Additionally, it explains the classification of the Philippine climate into four types based on rainfall distribution and seasonality.