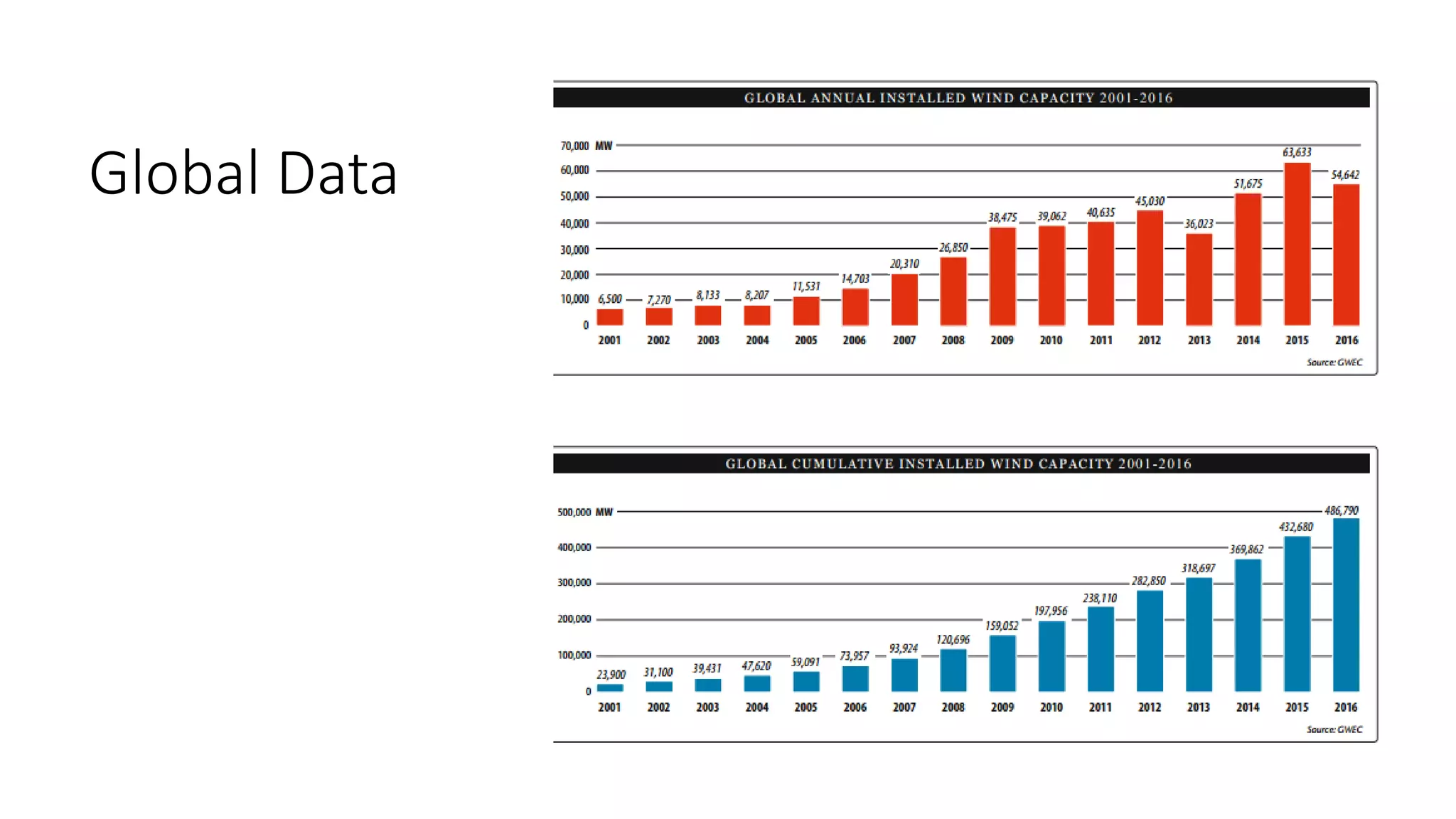
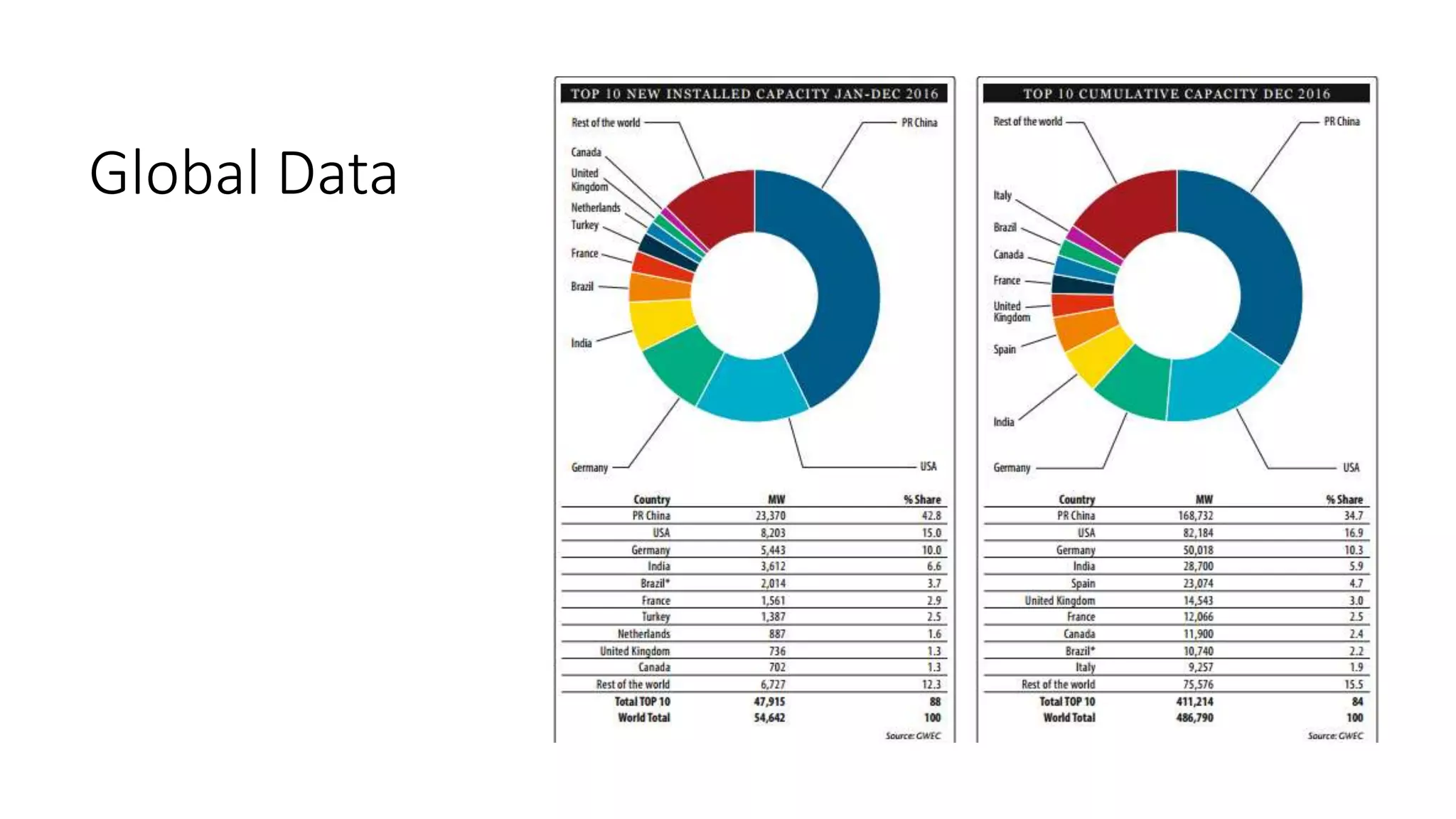
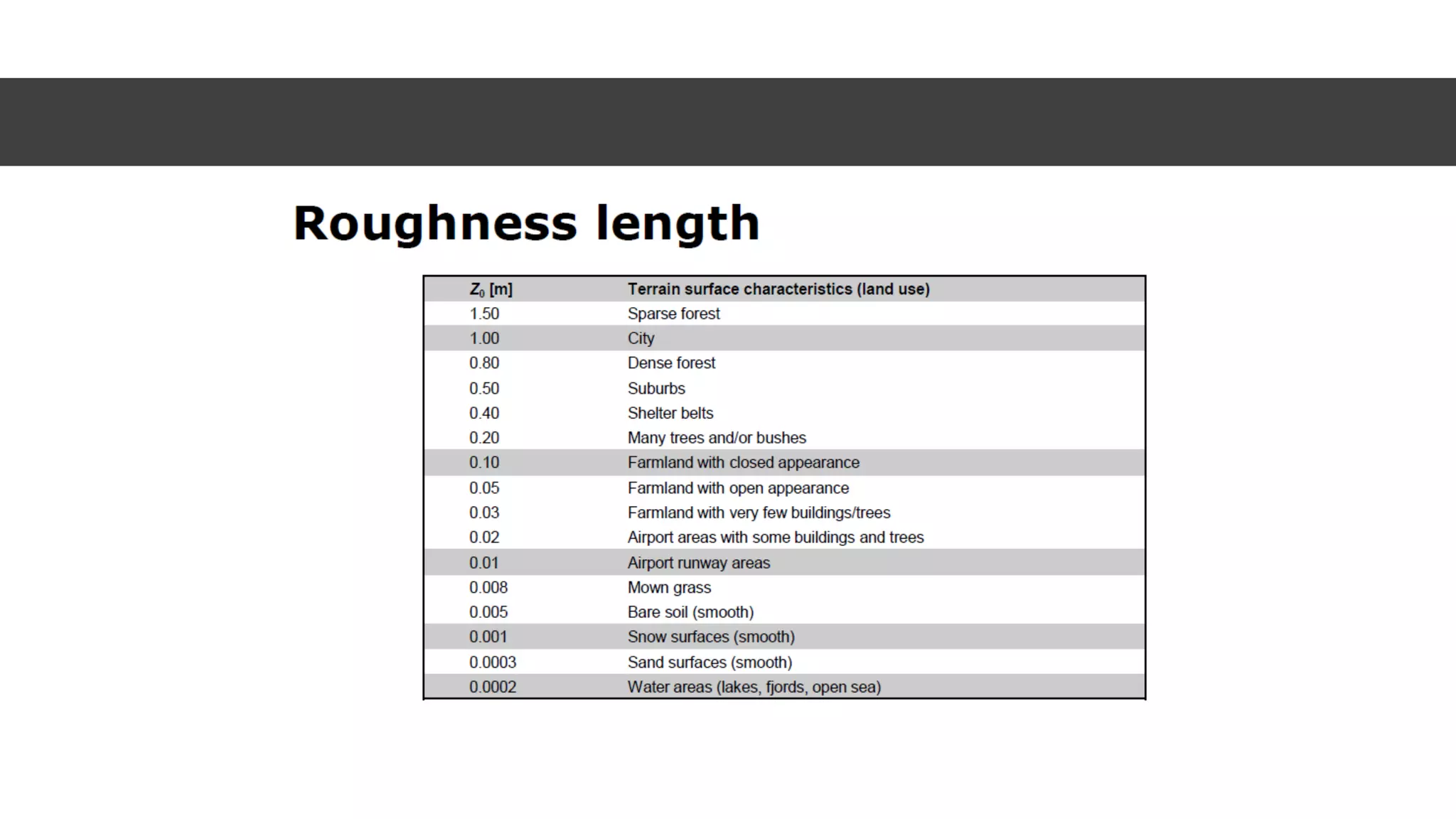
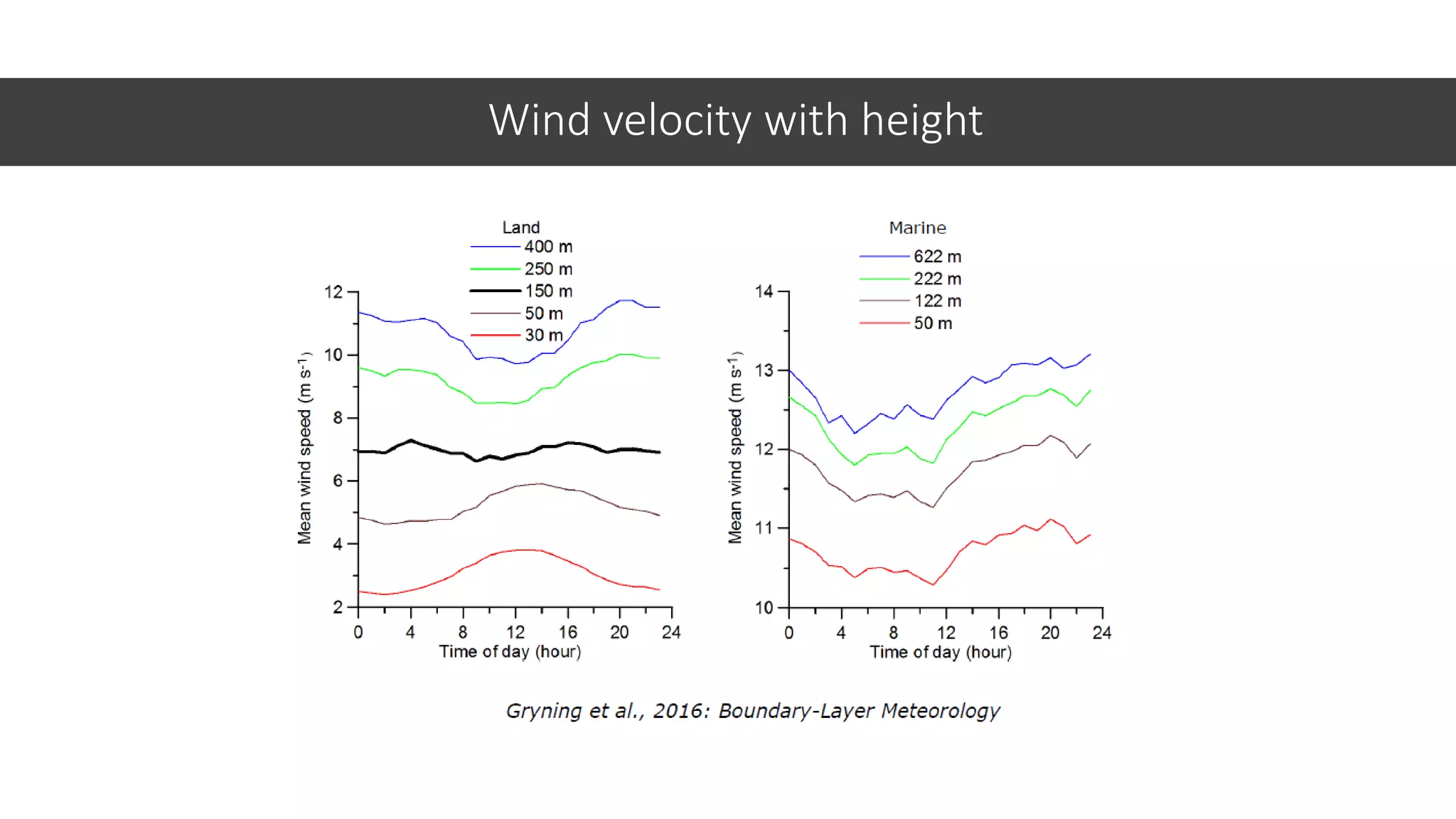
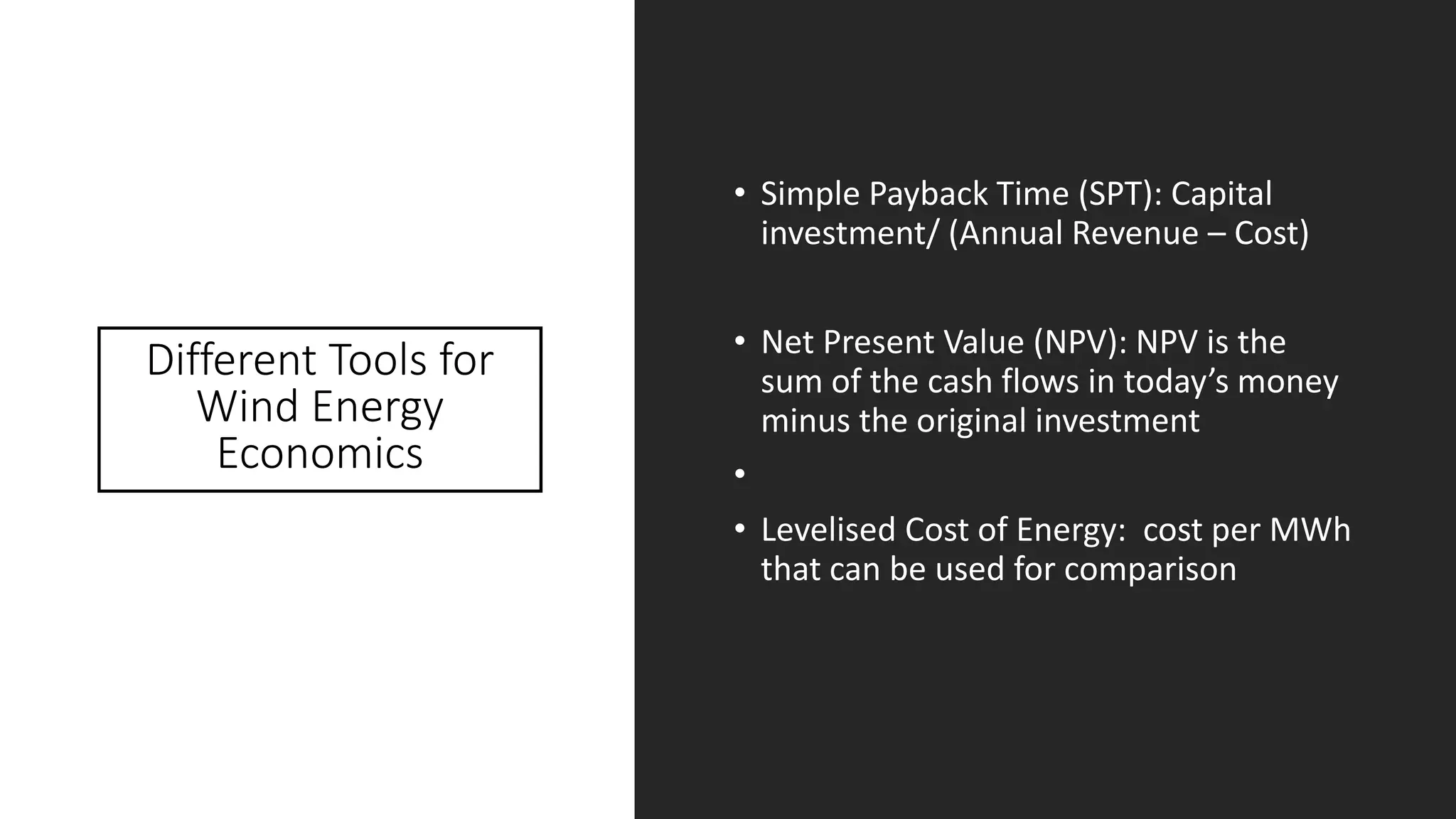
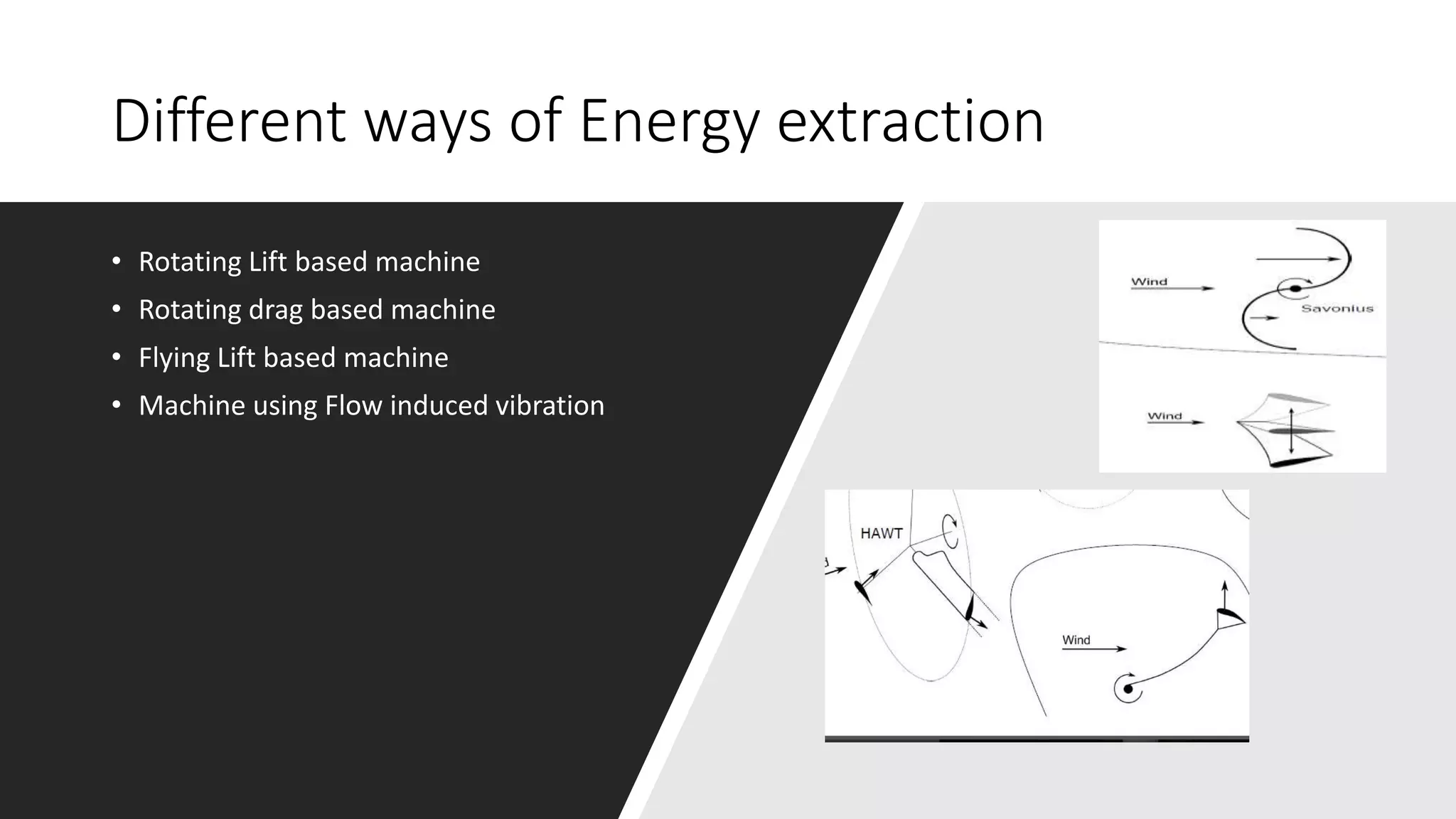
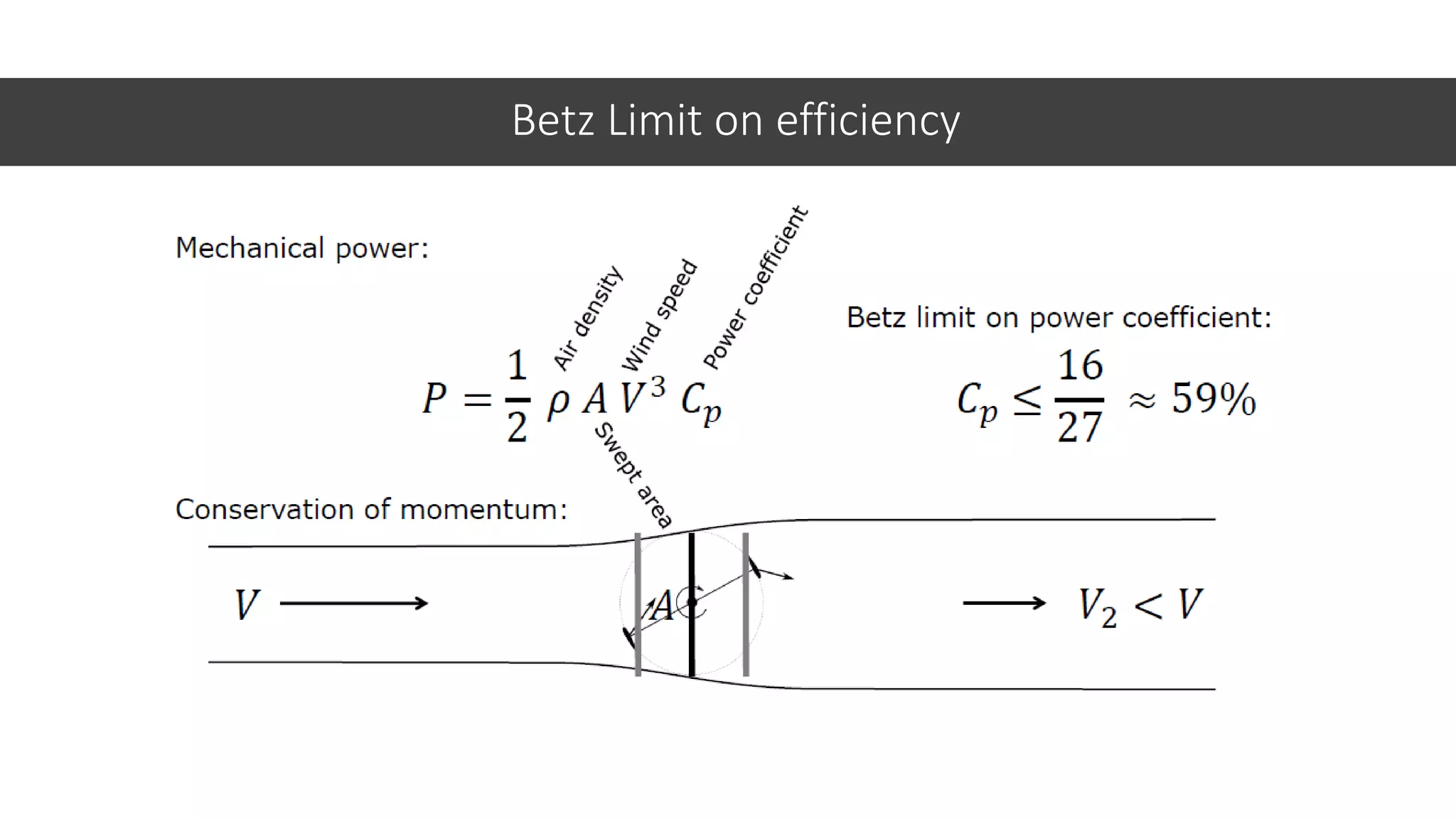
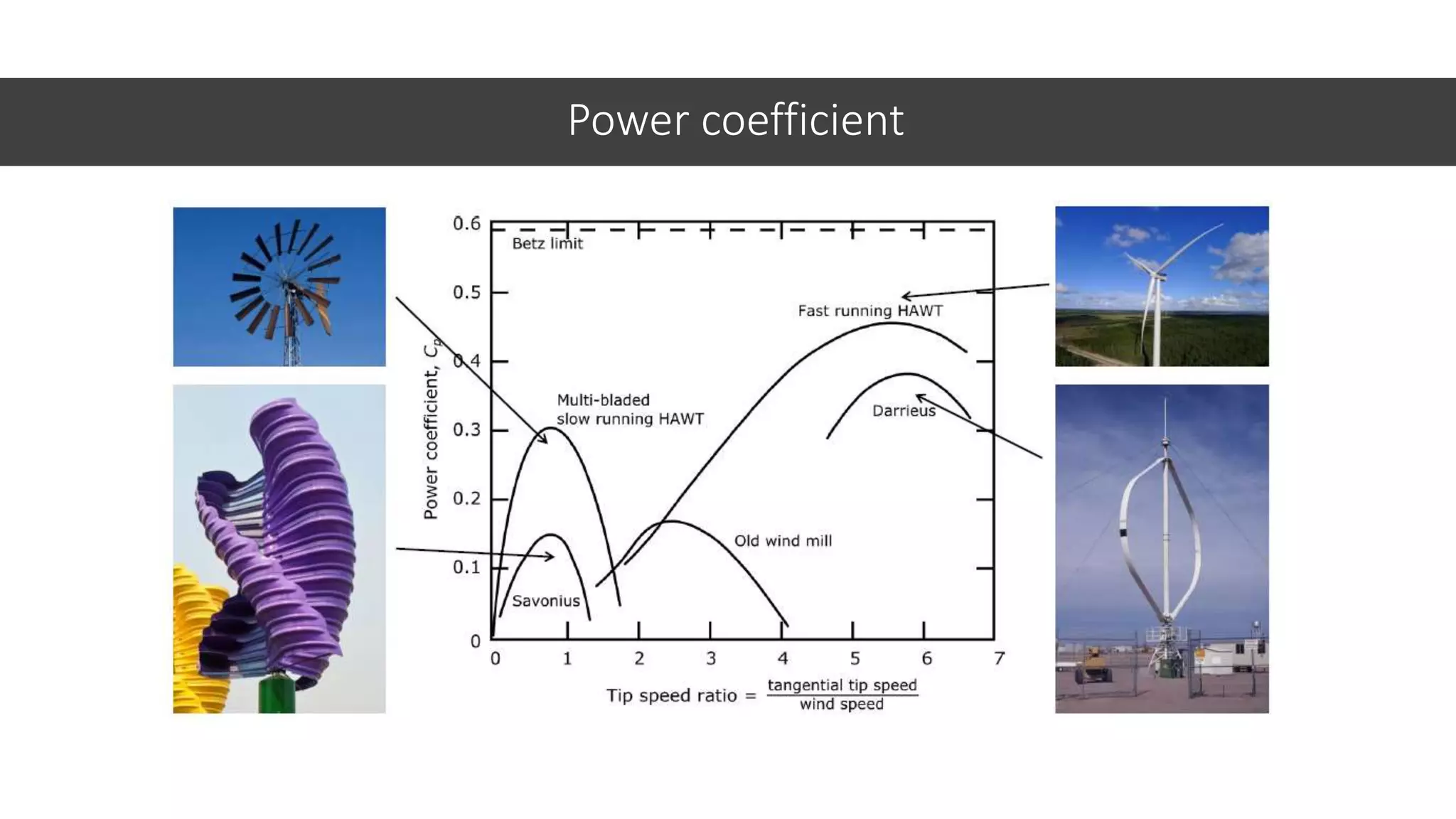
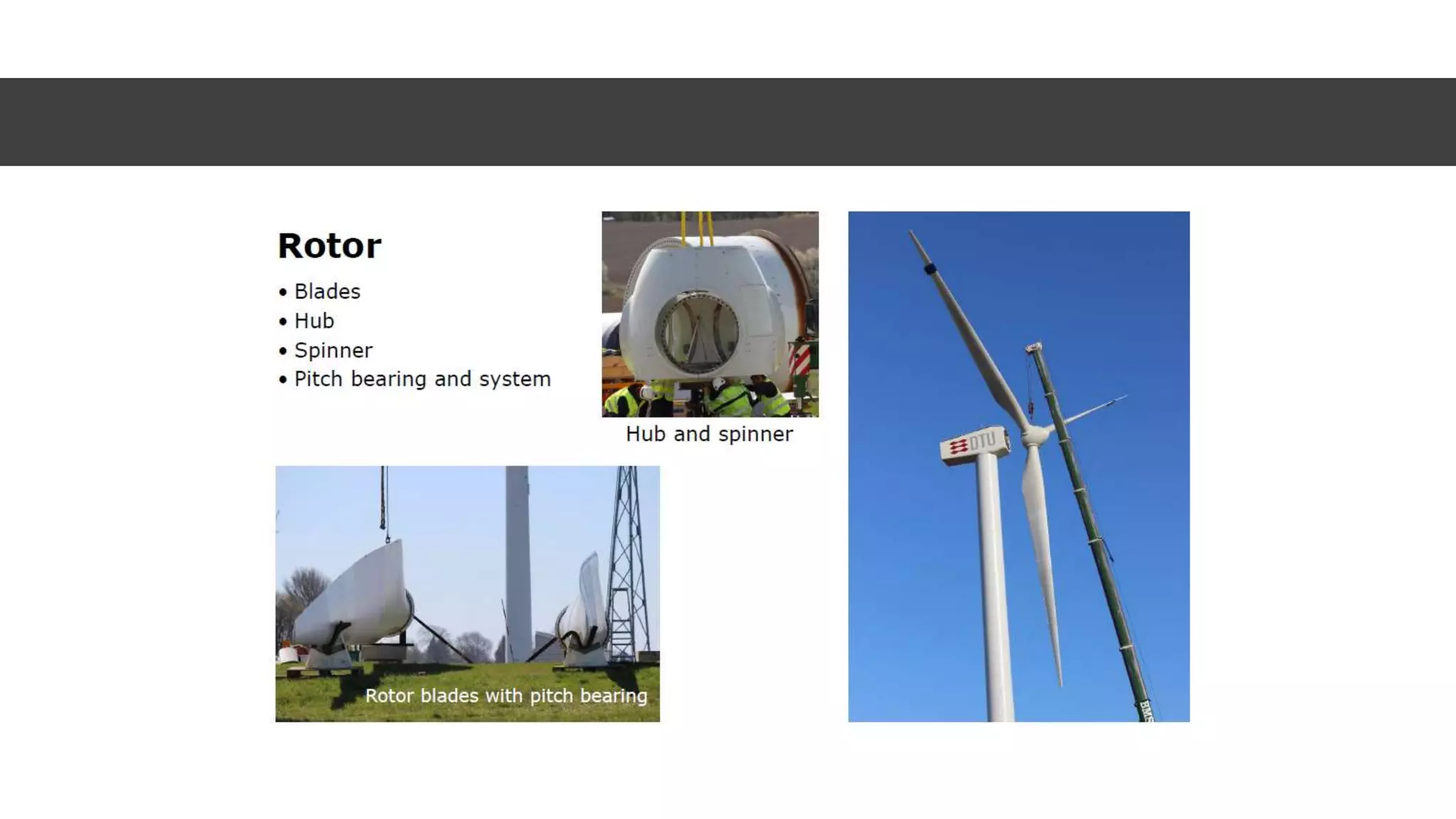
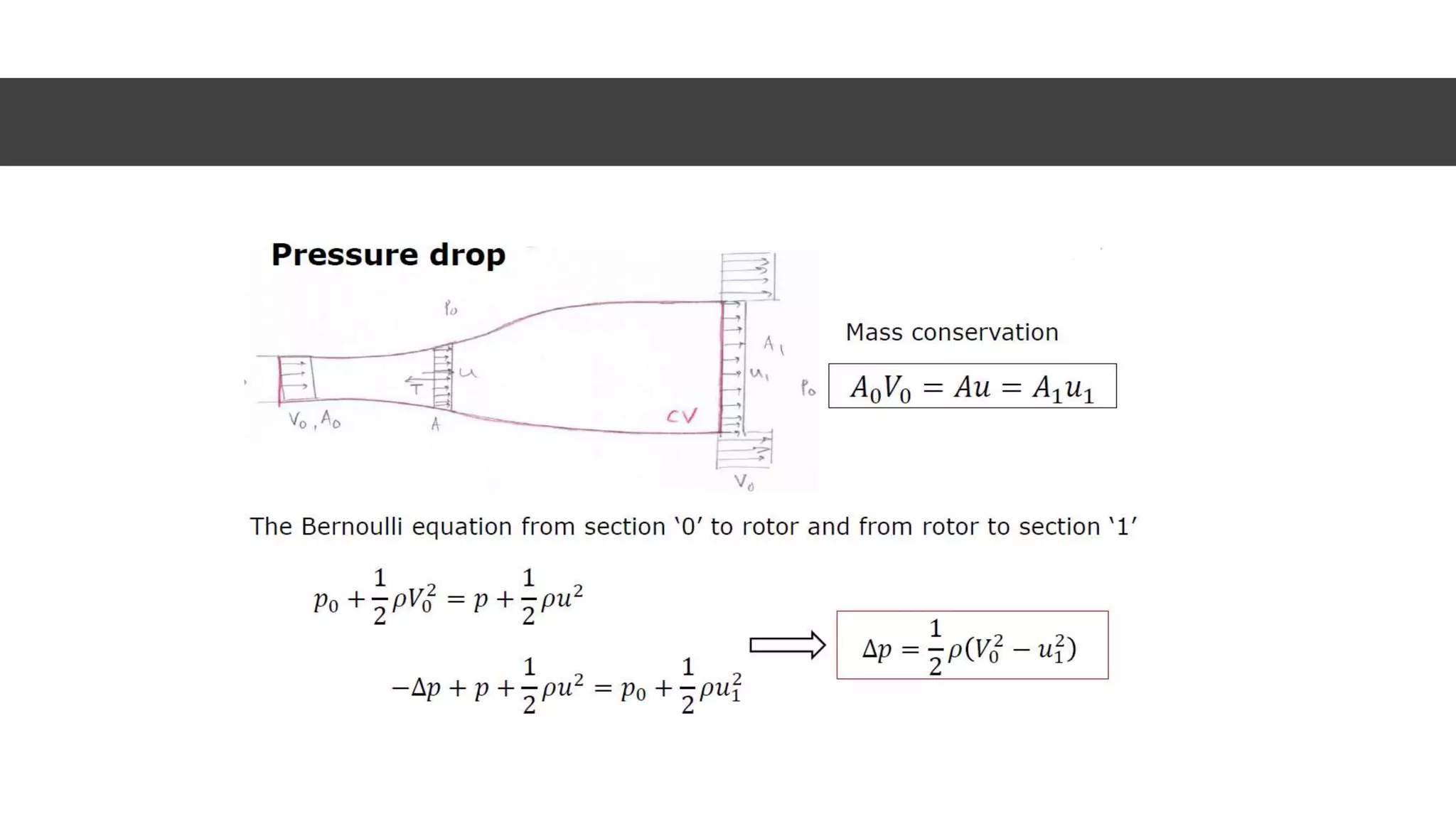
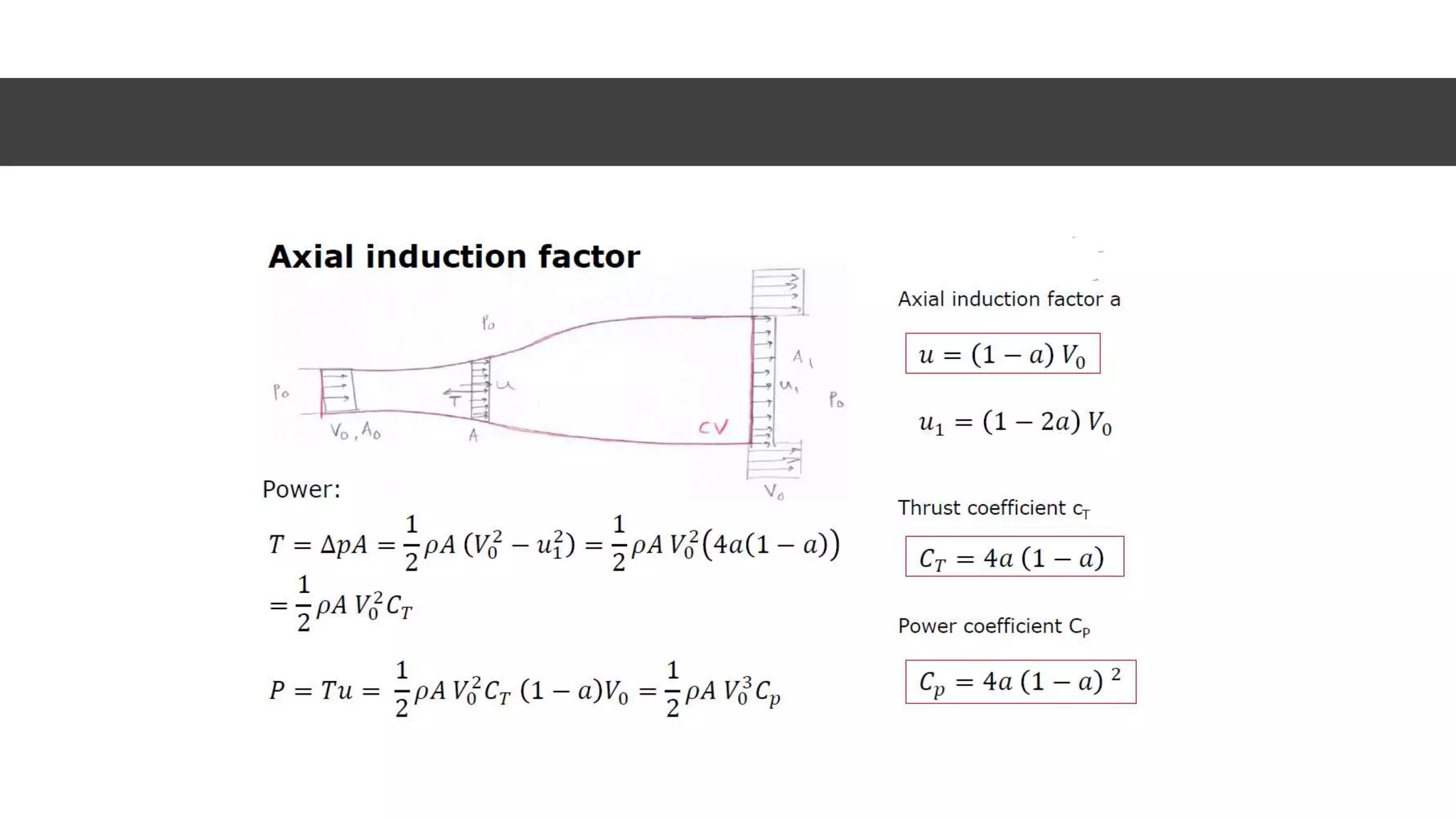
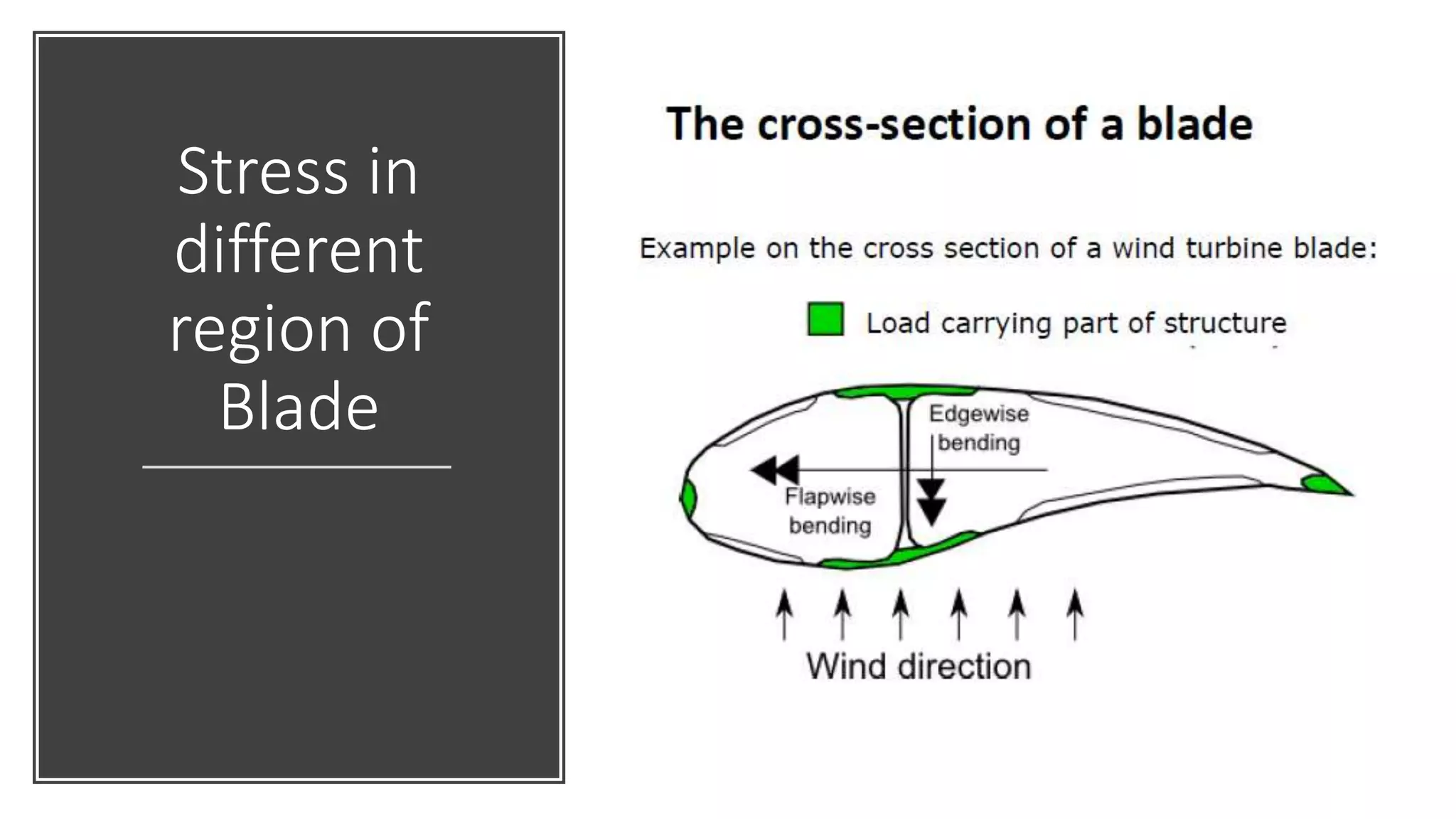
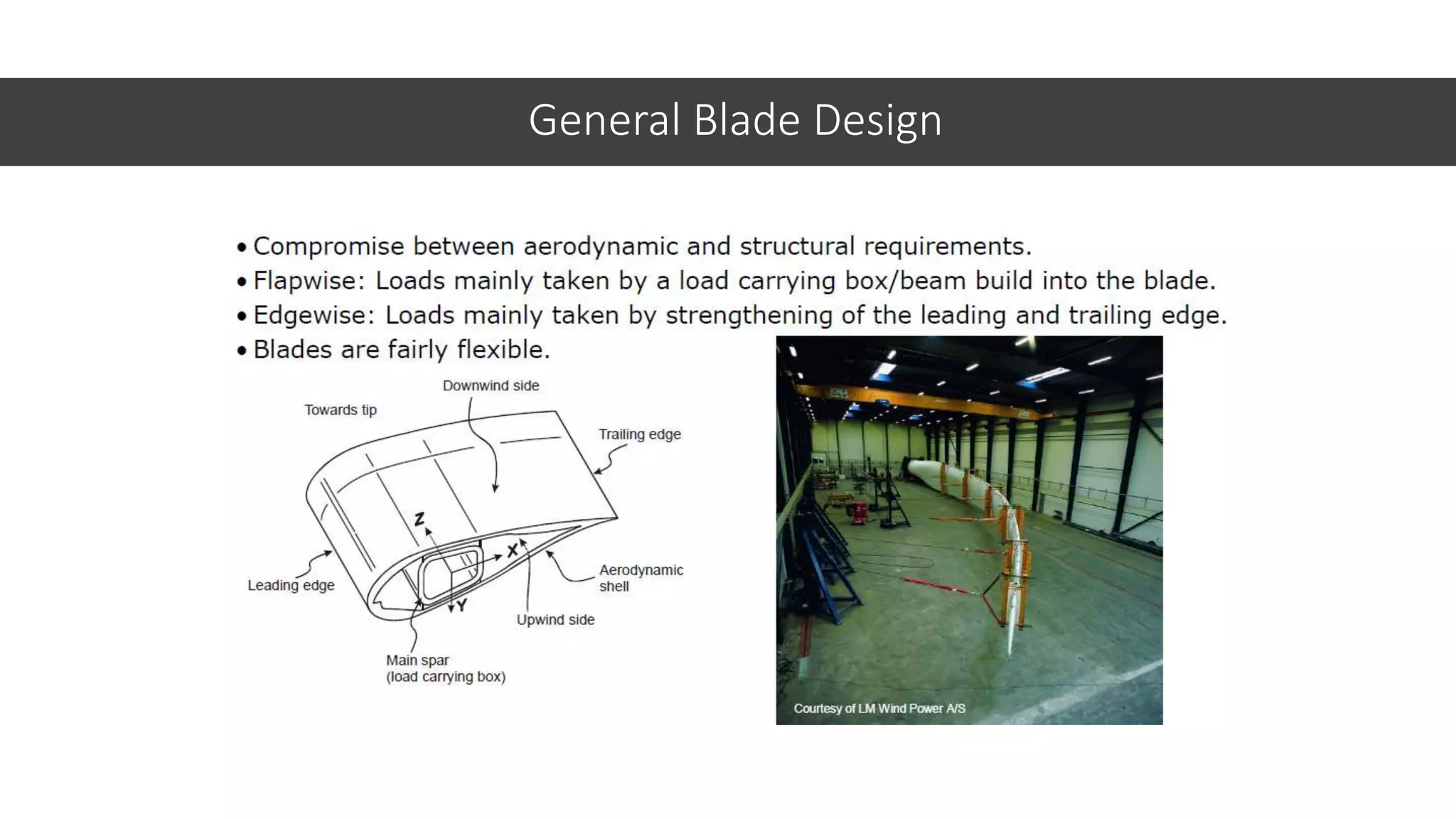
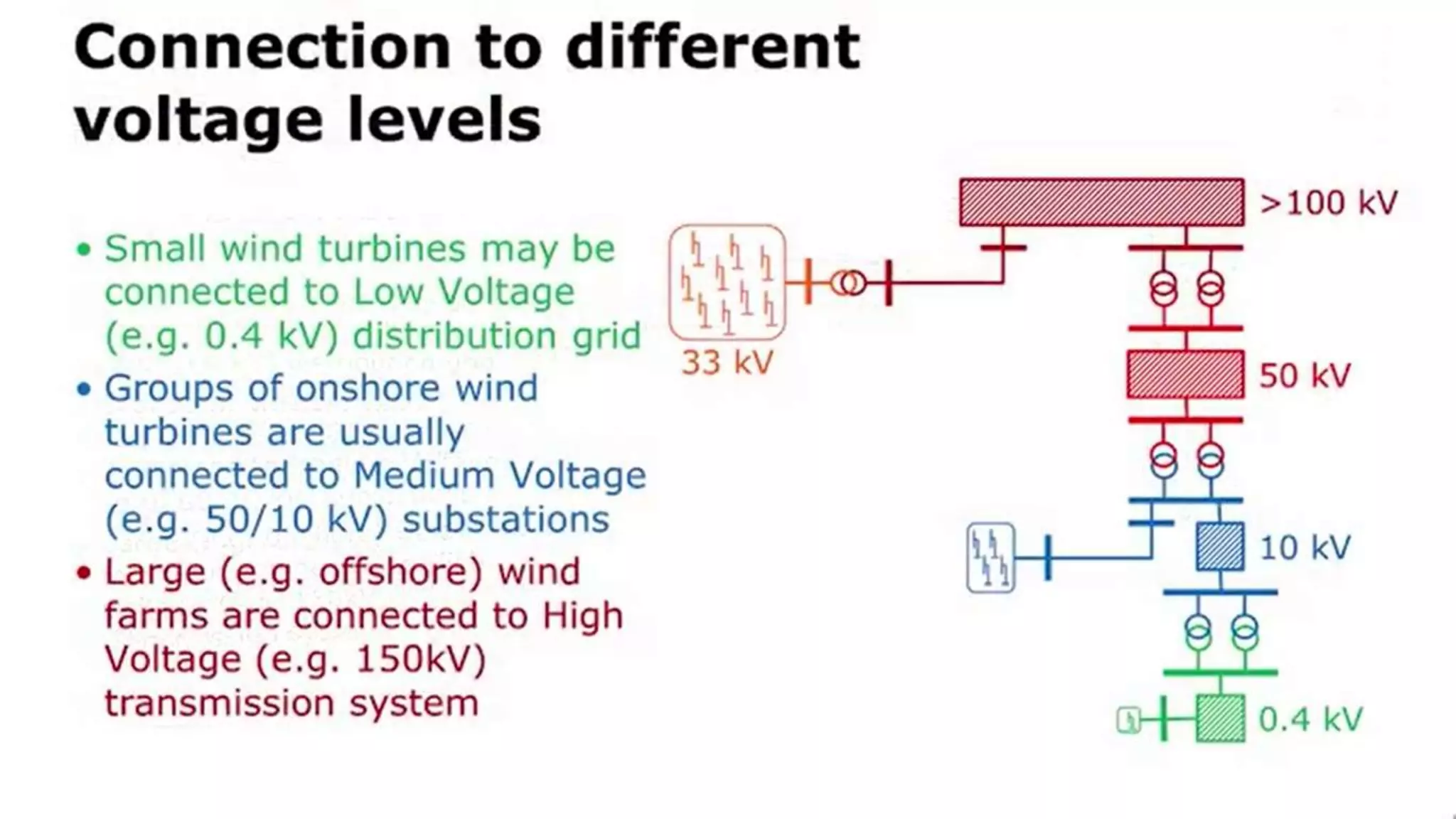
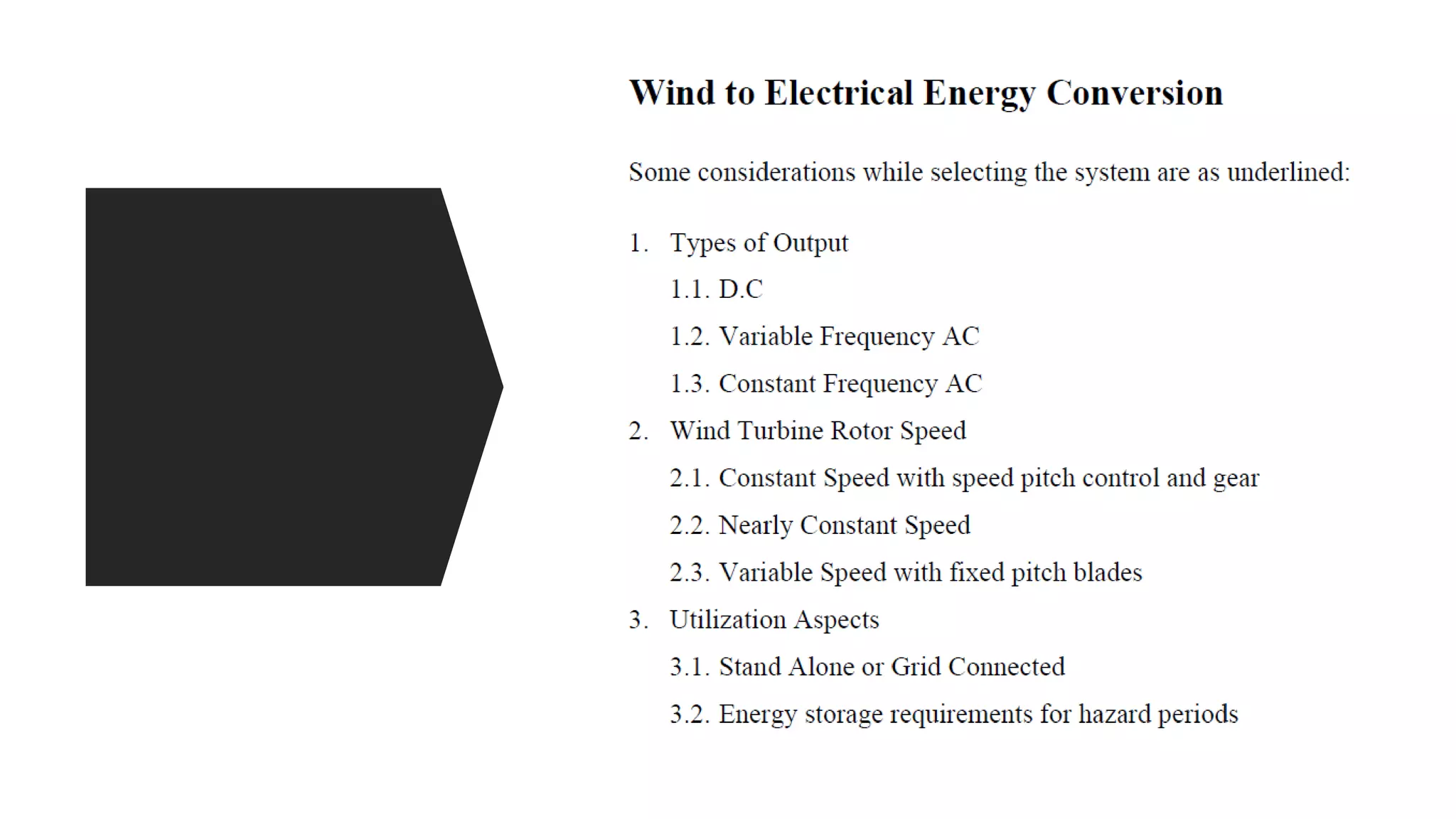
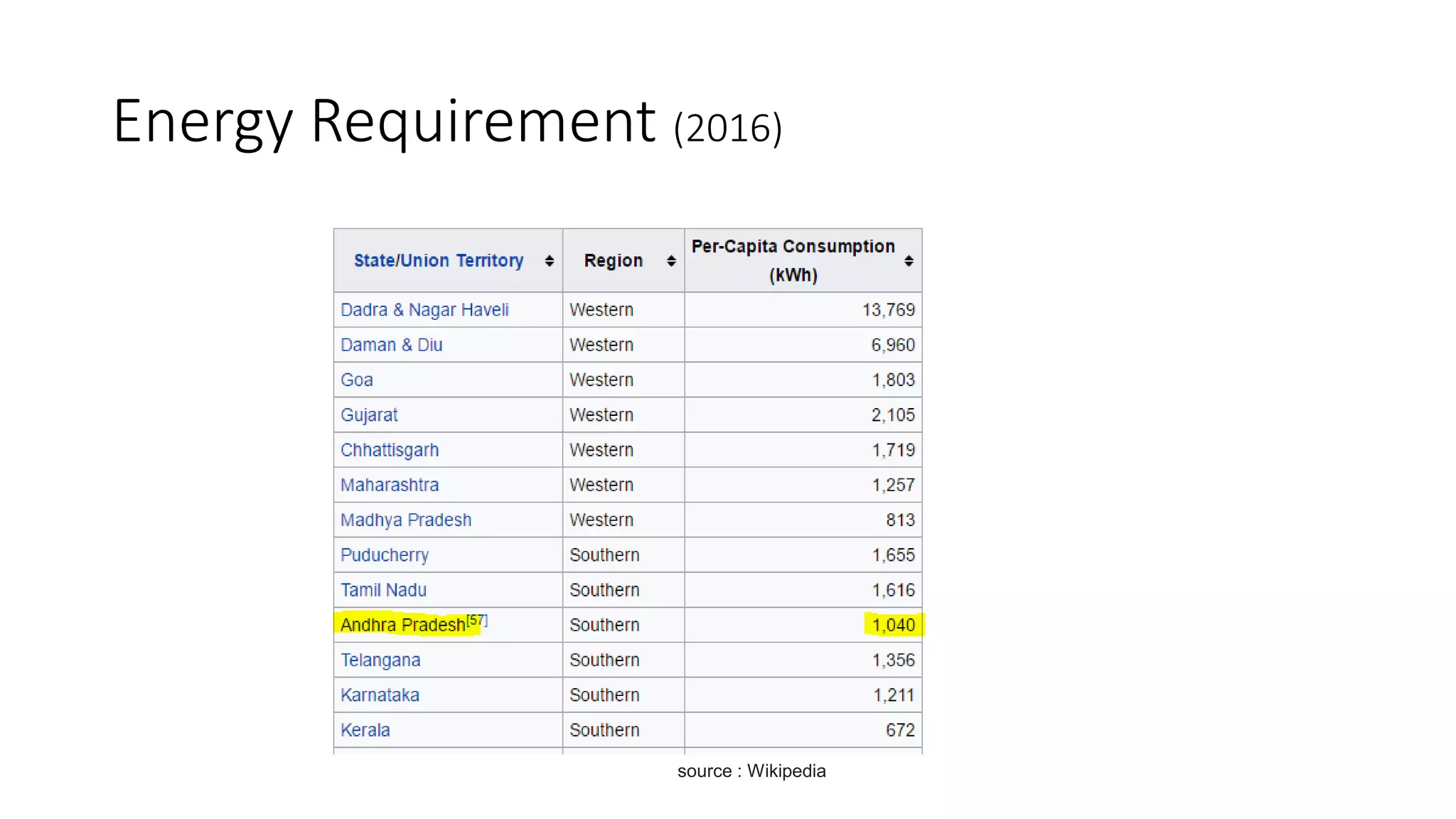
This document discusses factors to consider when installing a wind power plant. It compares wind power to nuclear and solar power, noting wind power plants are less complex and costly than nuclear but require more land and maintenance than solar. Key factors for installing wind power include wind resources, environmental impacts, economics, and grid connection requirements. The document also provides an example analysis for installing a 100MW wind farm in Visakhapatnam, India to help meet the region's energy needs.