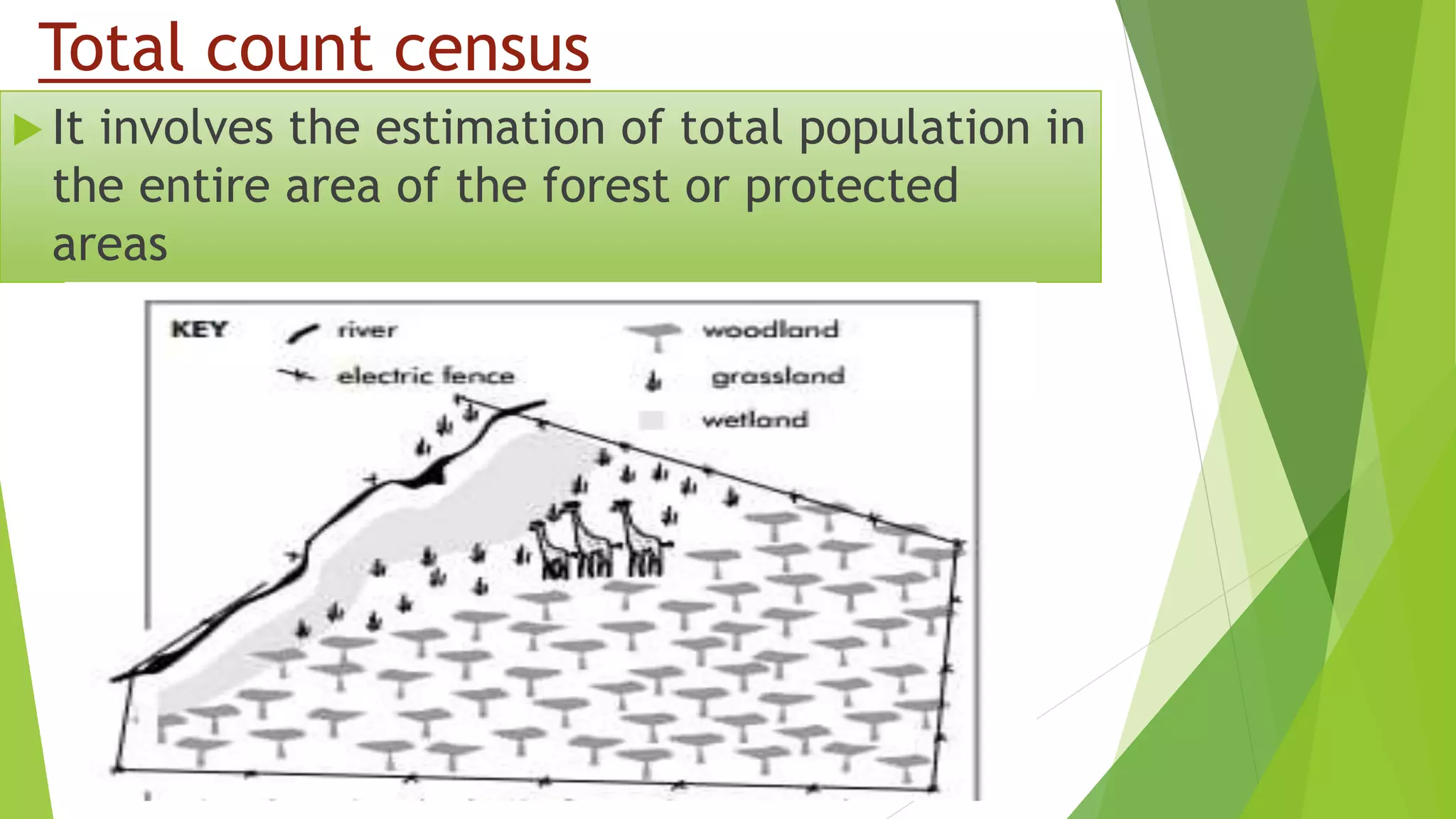
This document discusses various methods for conducting wildlife censuses. It begins by defining wildlife census and describing two main types: total count census and sample count census. It then outlines 14 different census methods including roadside index surveys, dung surveys, water hole surveys, quadrate sampling, distance sampling, camera trapping and line transect surveys. Specific details are provided for several of these methods. The document concludes by stating that wildlife censuses help determine population status, distribution, reproductive behavior and numbers to inform conservation strategies.