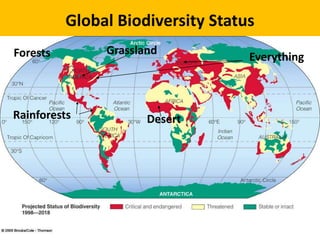
The document presents principles and roles of wildlife conservation, including definitions, goals, and major causes of endangerment. It emphasizes the need for sustainable practices, biodiversity protection, and the importance of both legal frameworks and international cooperation to protect wildlife. Conservation measures and recommendations are provided to enhance awareness and reduce illegal wildlife trade.