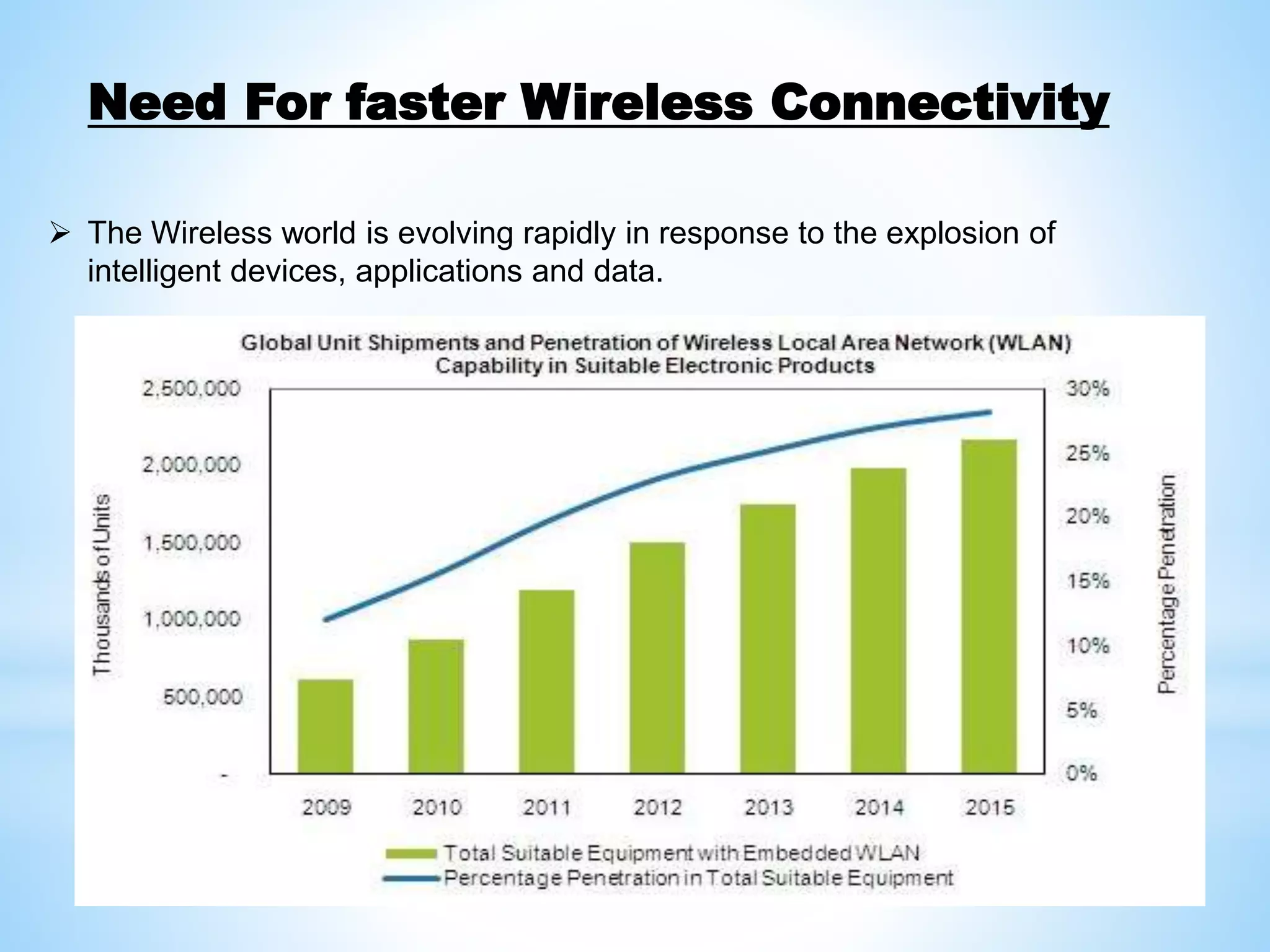
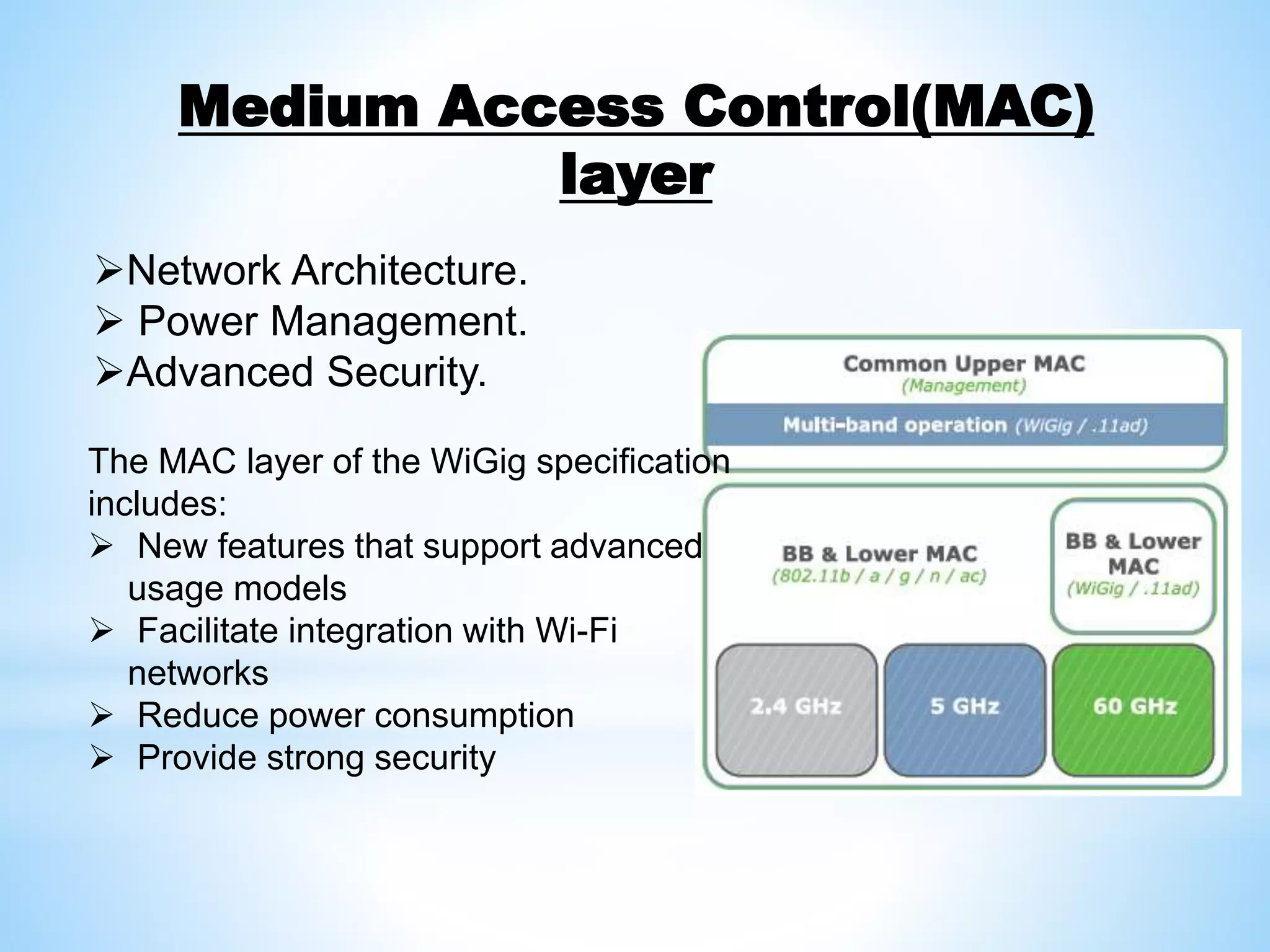
WiGig is a new wireless networking technology that provides data rates up to 7Gbps, over 10 times faster than the fastest existing WiFi networks. It operates in the 60GHz frequency band, which provides more available spectrum bandwidth. The WiGig specification defines the physical layer for transmitting data as well as protocol layers to implement interfaces for applications like HDMI and USB wirelessly. It is well suited for applications requiring high speed data transfer such as wireless docking and storage.