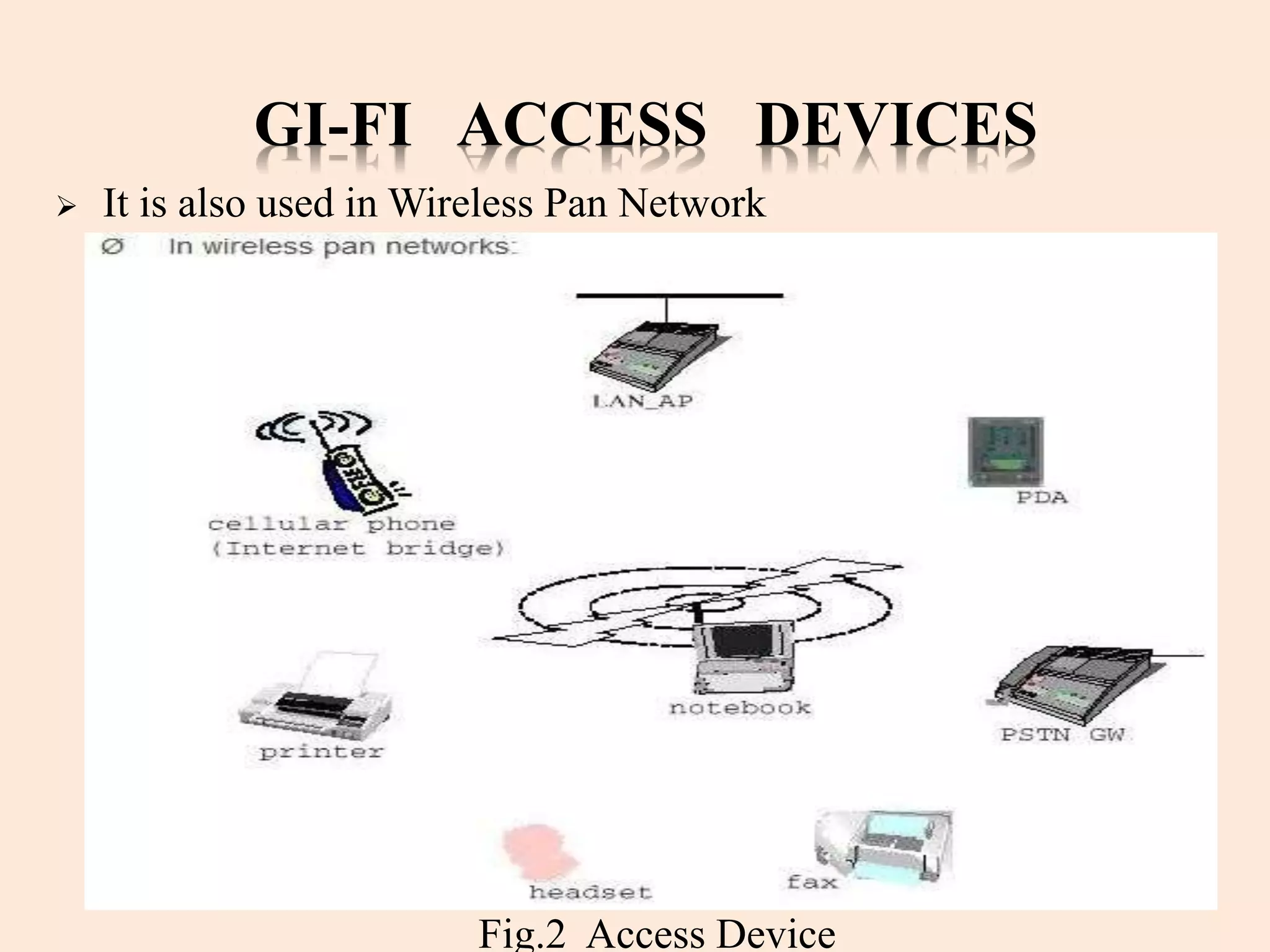
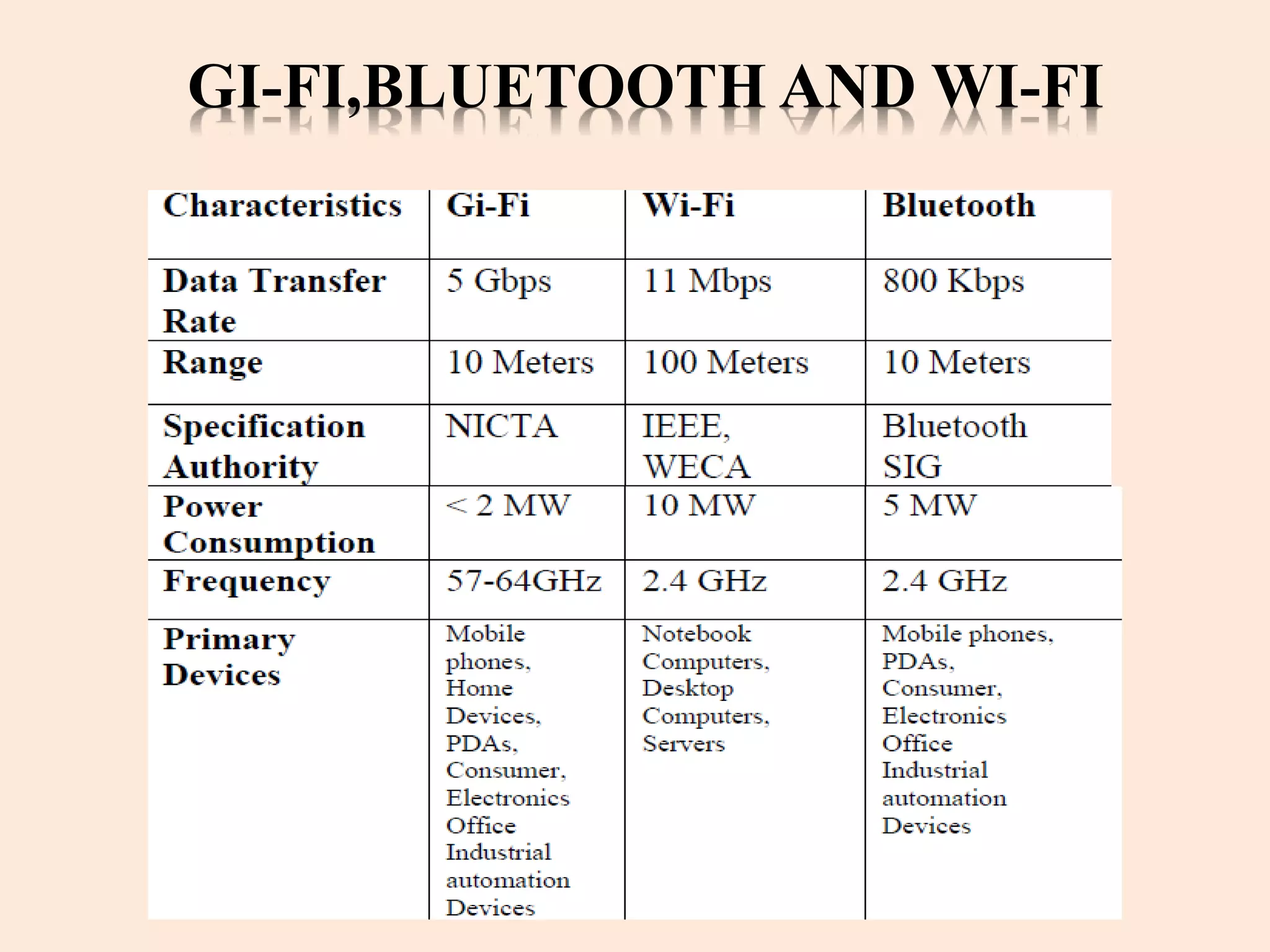
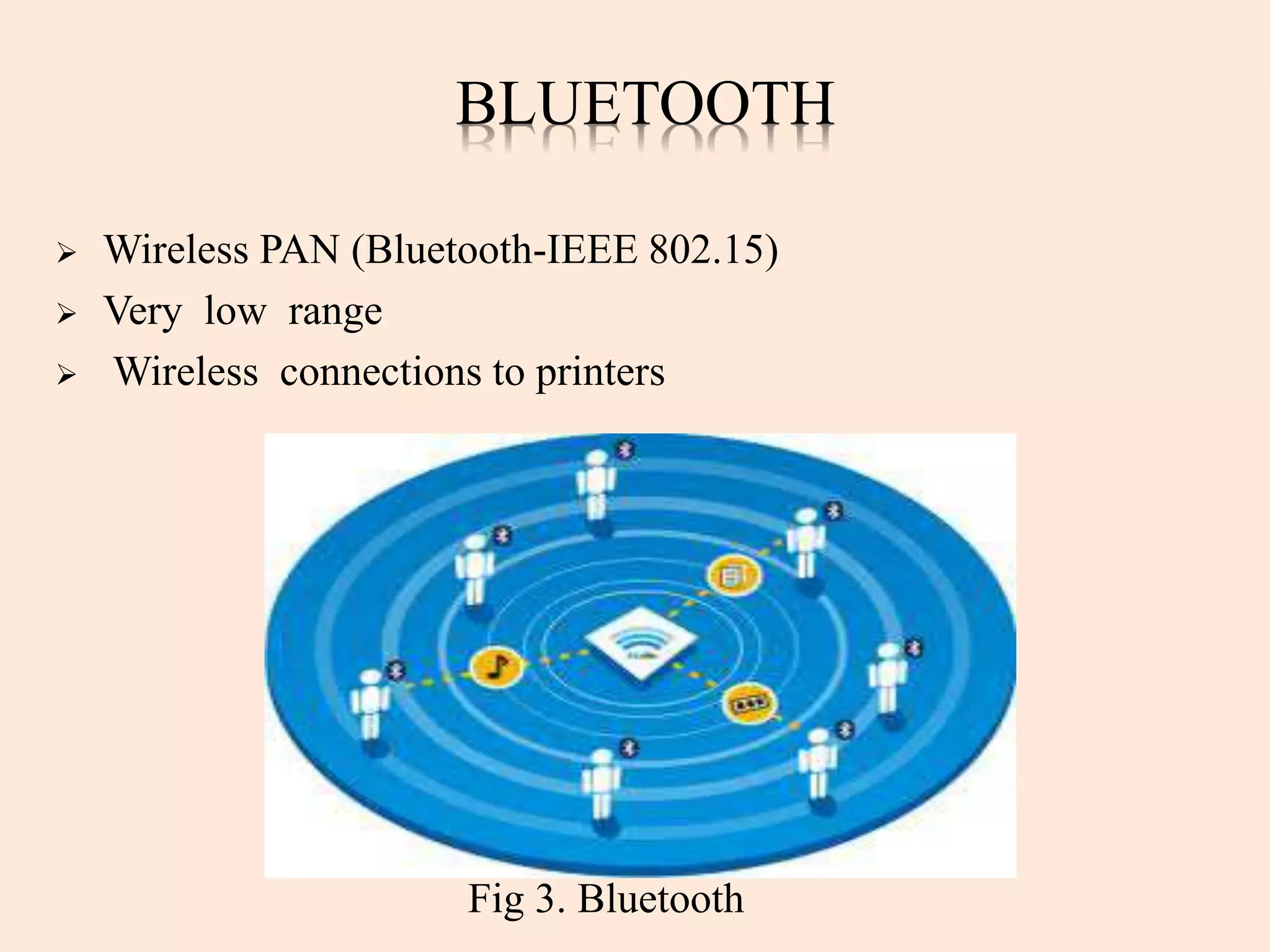
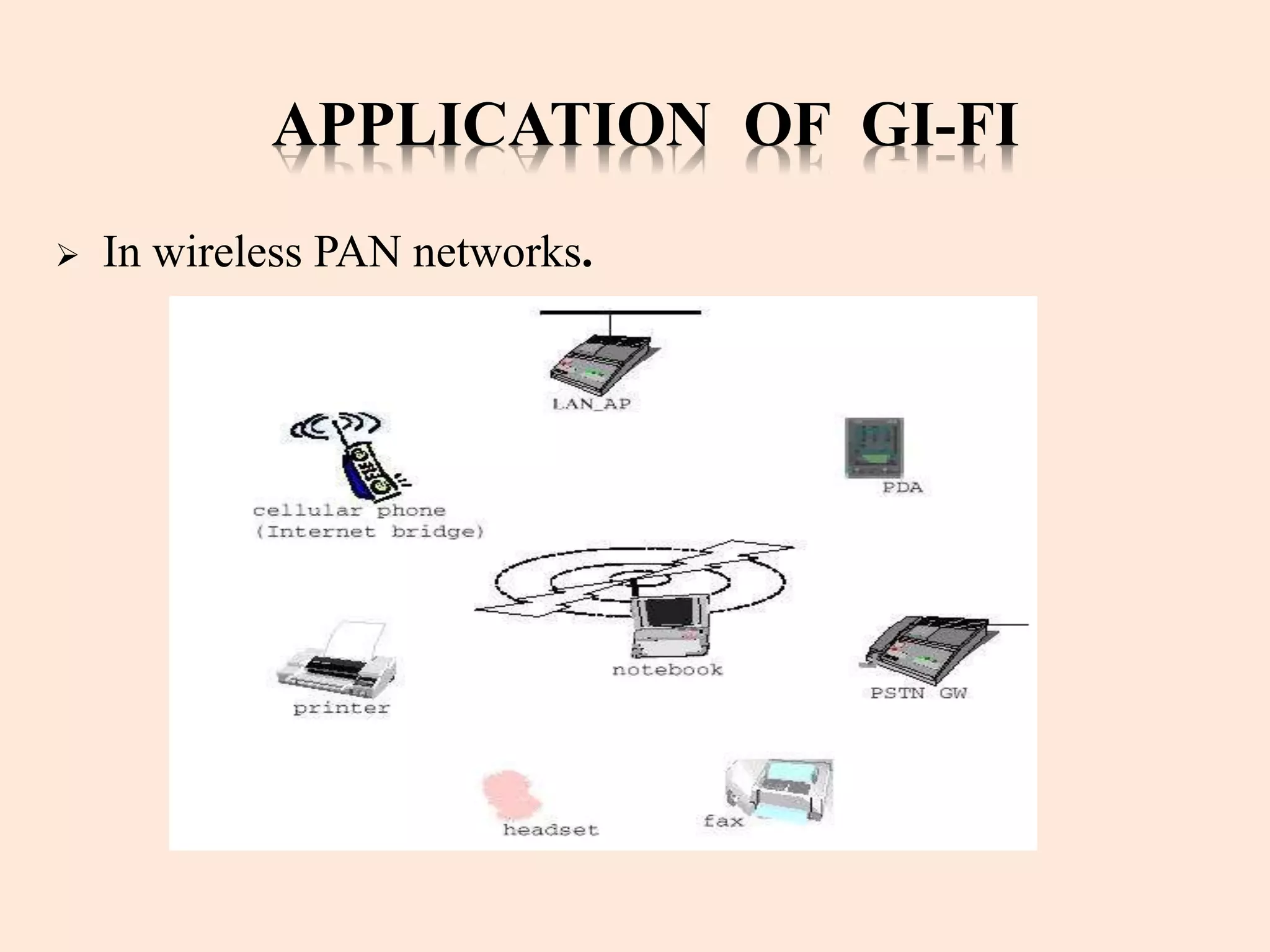
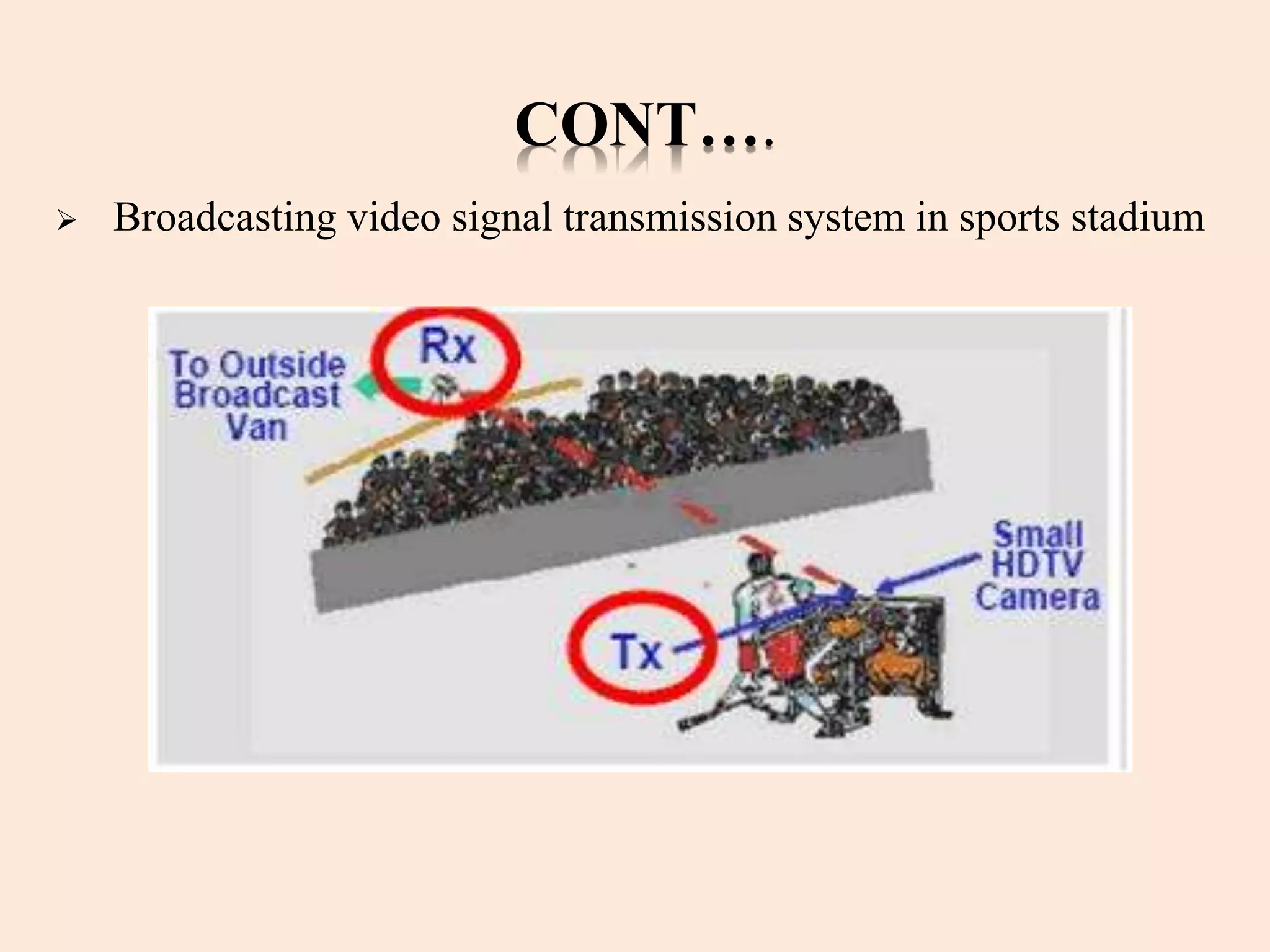
Gi-Fi, or Gigabit wireless, is a new technology enabling wireless data transfer at speeds up to 5 gigabits per second, operating at a frequency of 60 GHz. It offers significant advantages over Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, such as higher speed, lower power consumption, and a smaller physical footprint, with a projected dominance in wireless networking within five years. Applications for Gi-Fi include wireless PAN networks, inter-vehicle communication systems, and high-speed video broadcasting.














![REFERENCE S
1. GI-FI technology “Wikipedia”
2. www.ieee.org
3. Gowtham S Shetty, ―Gi-Fi: Next Generation Wireless
Technology, Seminar report, Visvesvaraya Technological
university Belgaum, 2011
4. Electronista Staff, “NICTA Gi-fi Chipset”, [Online], Available at:
http://www.electronista.com/articles/08/02/22/nicta.gifi.chipset/,
February 2008
5. S.Dheeraj, S.Gopichand, “Gi-Fi: New Era of Wireless
Technology”, [Online], Available at:
http://www.yuvaengineers.com/?p=570, 2010.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptfinalgi-fitechnology-160805043554/75/gi-fi-the-next-generation-wireless-technology-28-2048.jpg)
