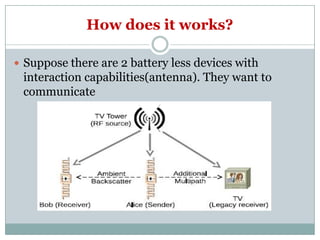
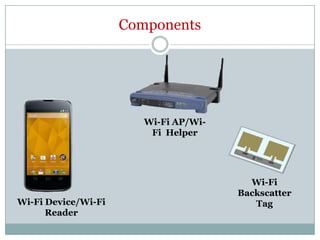
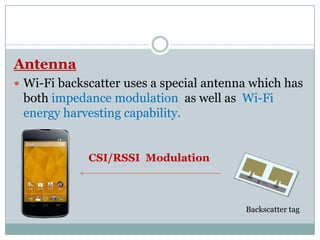
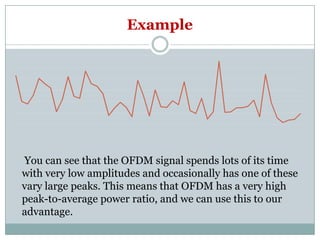
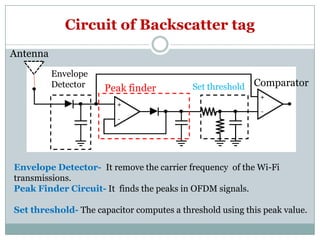
Wi-Fi backscatter is a technology that enables battery-free devices to connect to the internet using ambient RF signals, thereby eliminating the need for new infrastructure. It utilizes a request-response communication model with components such as Wi-Fi devices, access points, and RF-powered tags, allowing low-power devices to send and receive data through modulation of Wi-Fi channels. The system employs advanced techniques for decoding and transmission, leveraging natural features of Wi-Fi signals to overcome challenges in data exchange.