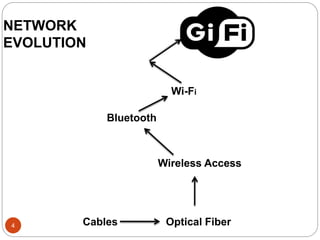
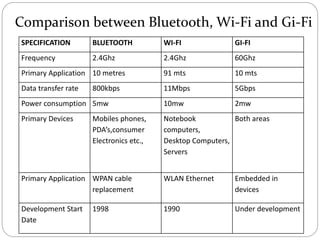
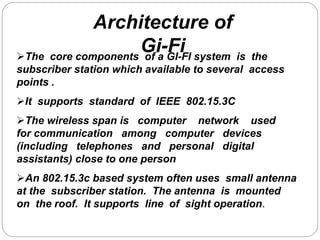
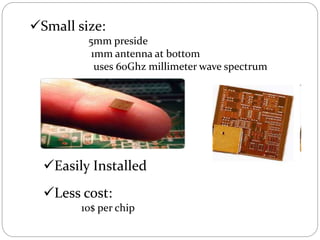
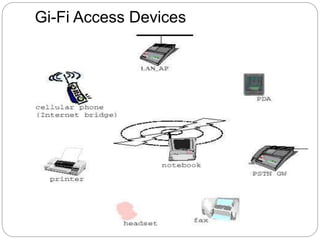
Gi-Fi is a next generation wireless technology that was developed in 2008 to allow for wireless transfer of audio and video data at speeds up to 5 gigabits per second, which is 10 times faster than current wireless technologies. It operates using 60GHz frequency bands and integrated circuits on a single chip. Gi-Fi aims to address limitations of existing technologies like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi that have slower speeds and higher power consumption. It uses techniques like beamforming to avoid interference and supports the IEEE 802.15.3c standard. Potential applications include wireless connectivity for household appliances, offices, and high-speed file transfers.