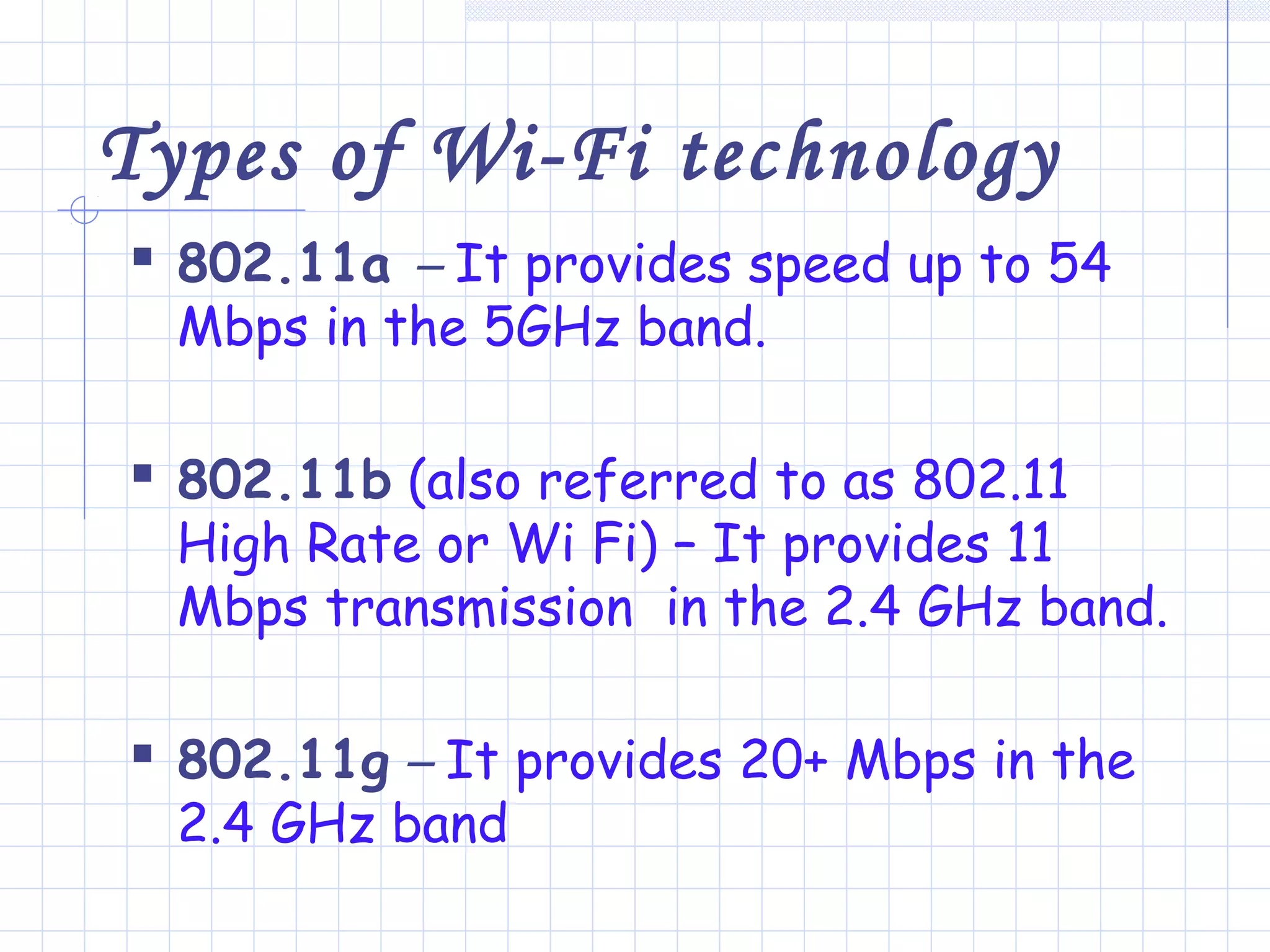
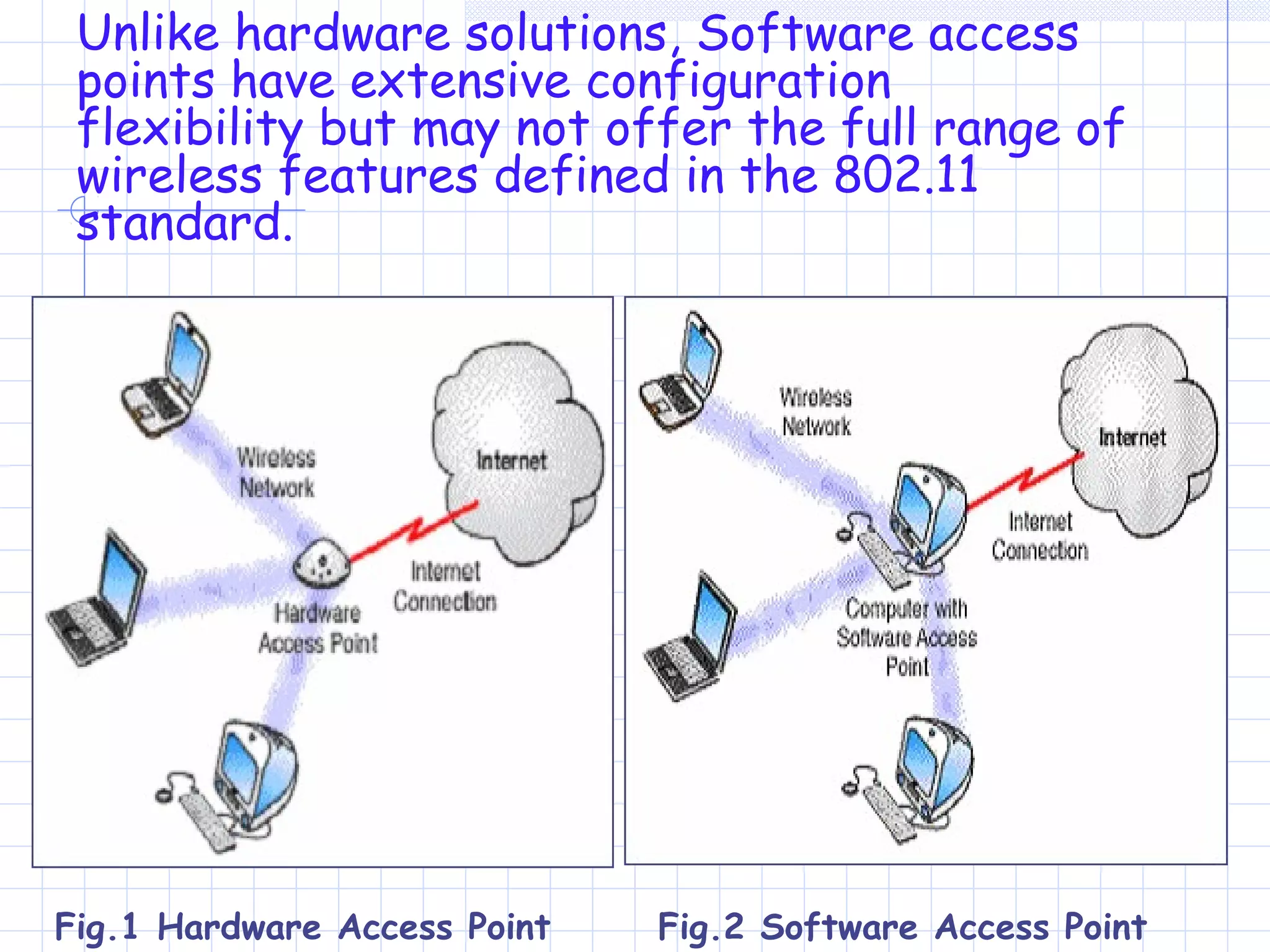
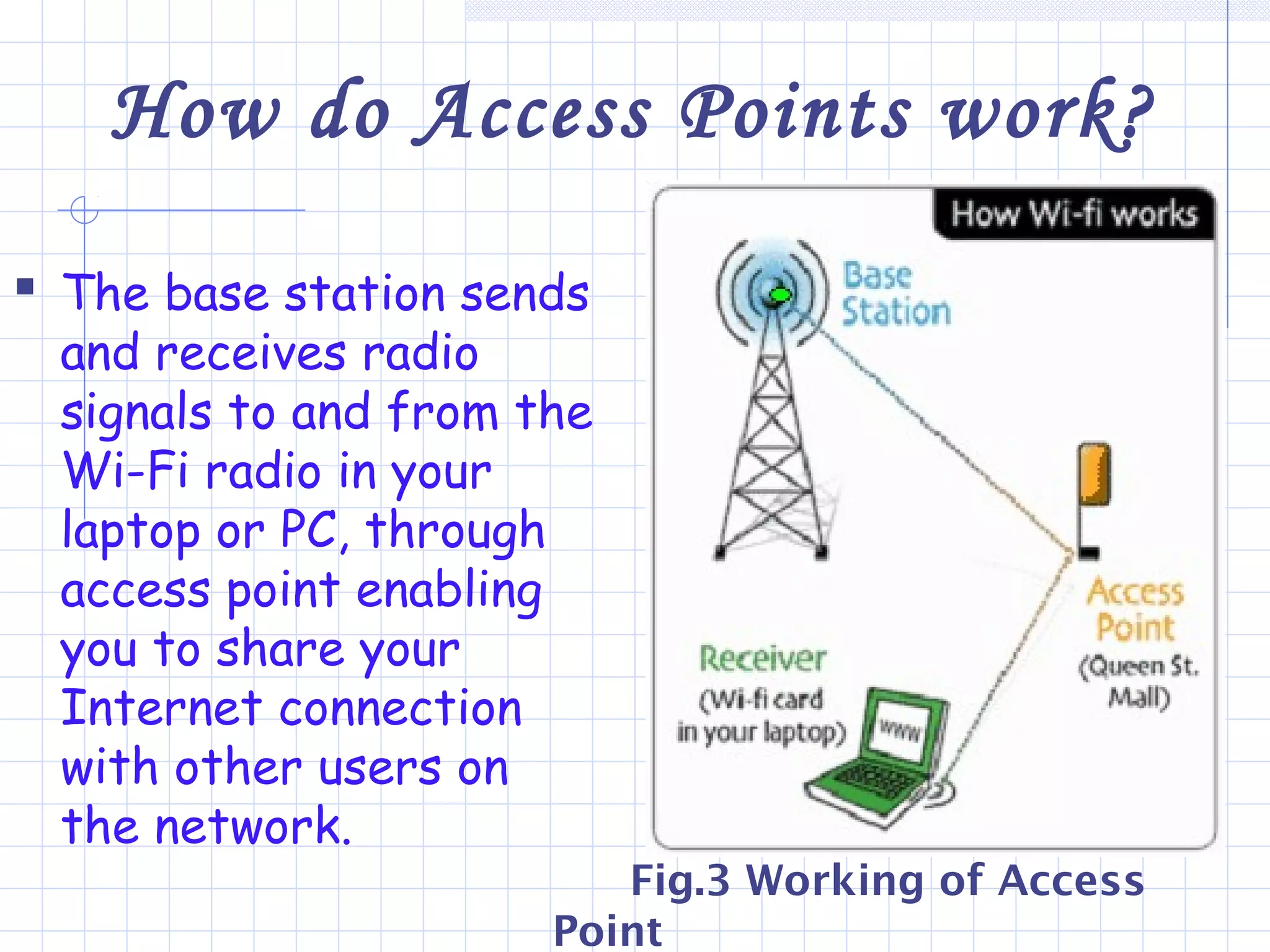
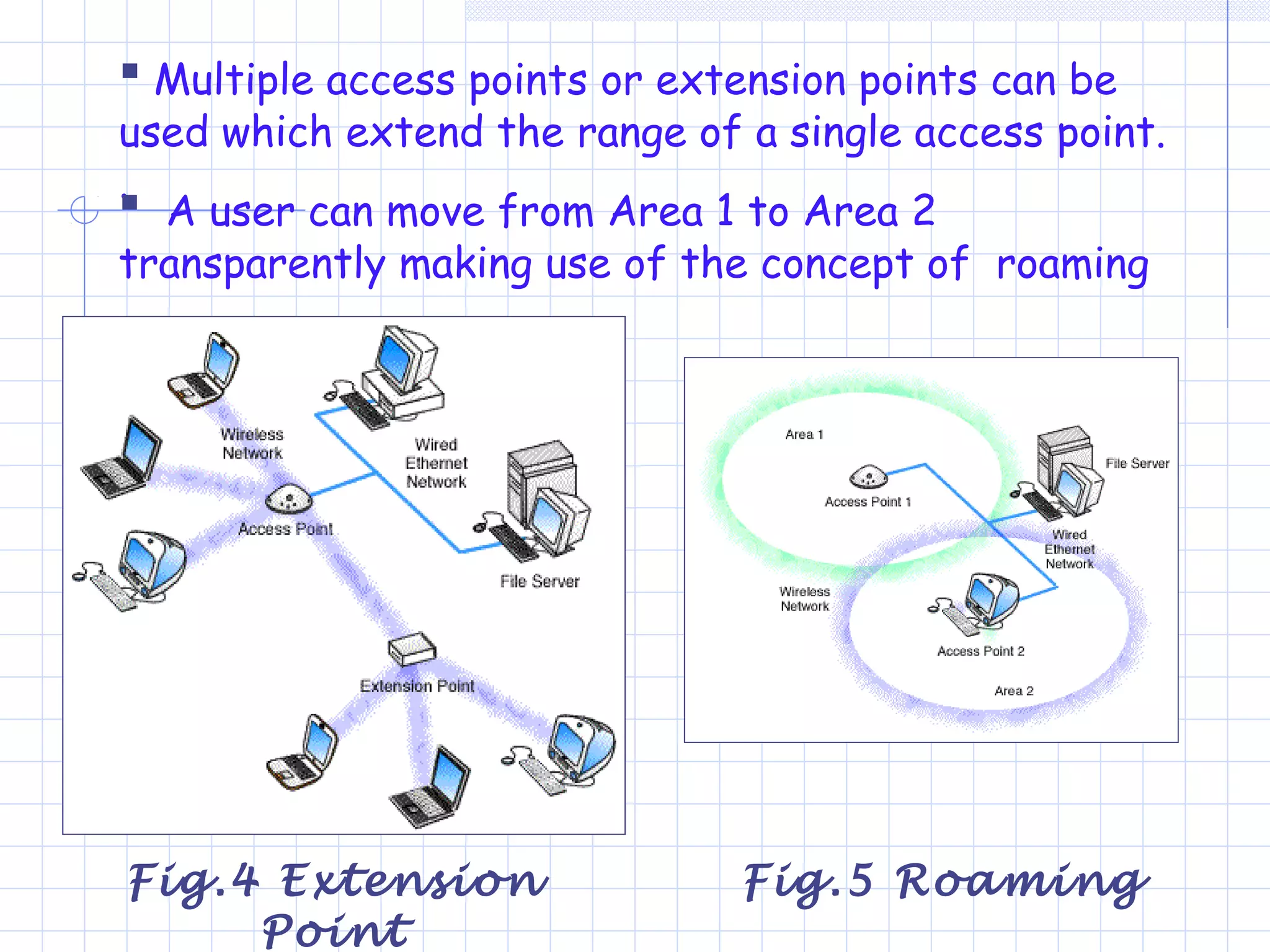
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that allows devices to connect to the internet or communicate with one another wirelessly. It uses radio waves to transmit data over short distances without wires. Wi-Fi networks rely on access points that connect wireless devices to a wired network. Access points work by sending and receiving radio signals that enable wireless devices on the network to share internet connections. Wi-Fi offers benefits like mobility and lower installation costs compared to wired networks. Its popularity continues to grow as more devices become Wi-Fi enabled.