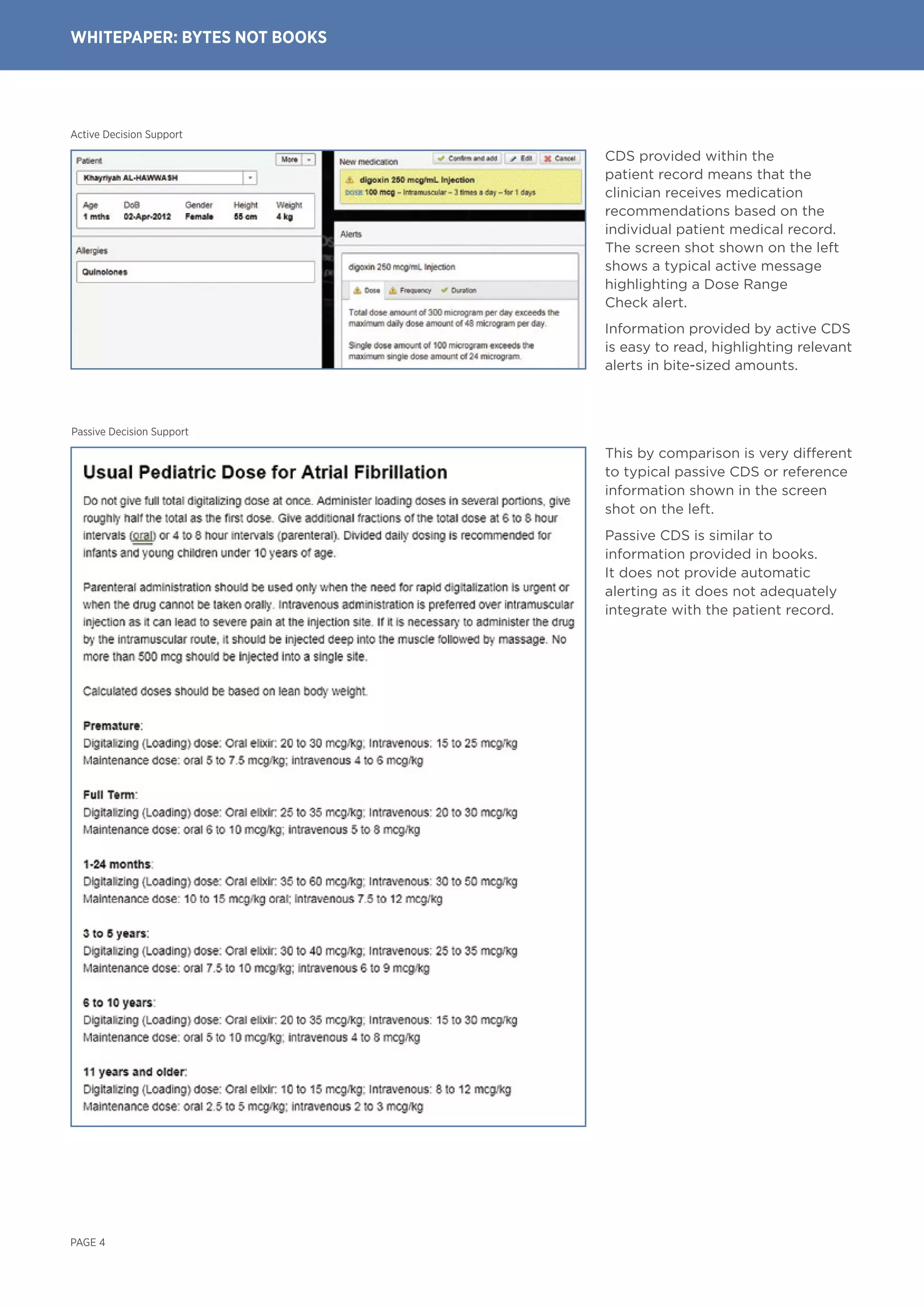
Active clinical decision support (CDS) within medication management more effectively reduces adverse drug events compared to passive CDS. Active CDS provides dynamic alerts and recommendations directly within a patient's electronic health record at the point of care. Studies show active CDS improves clinical outcomes in 68% of trials by guiding clinicians to best practices. In contrast, passive CDS relies on clinicians to search for information without prompts, reducing its effectiveness. The whitepaper concludes active CDS should be the standard for medication management to improve patient safety worldwide.