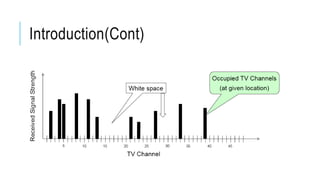
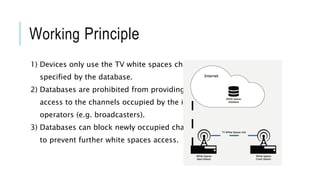
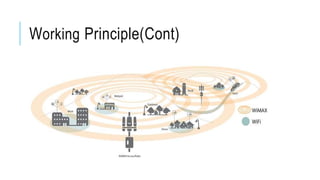
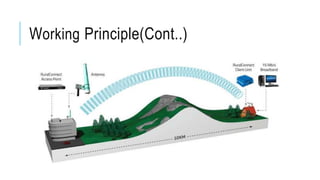
White space technology utilizes unused spectrum reserved for broadcasting TV channels to provide wireless broadband internet access over long distances, especially to rural areas. Devices using white space technology can access spectrum between 470-790 MHz to transmit internet signals up to 10 km through vegetation and buildings. The technology protects primary spectrum users by having devices check an online database for available channels and blocking newly occupied channels to prevent interference.