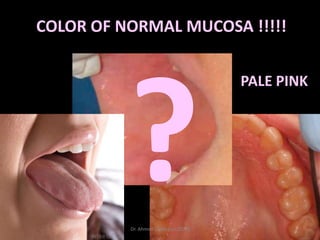
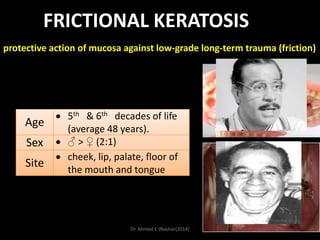
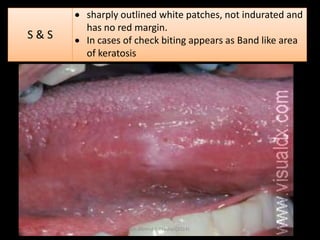
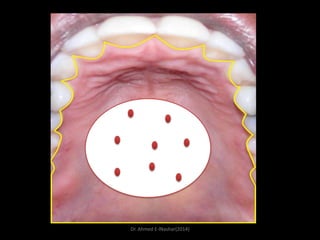
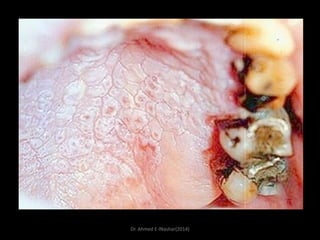
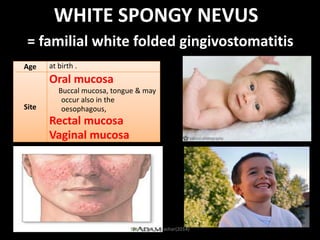
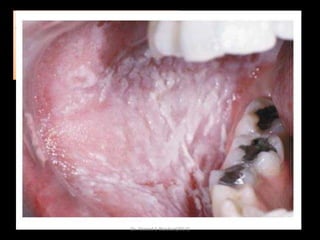
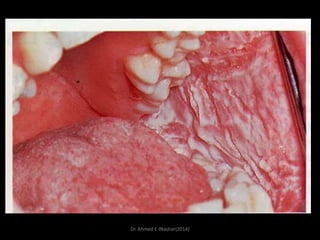
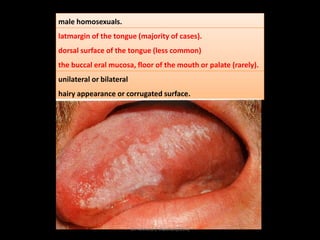
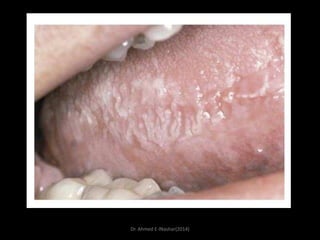
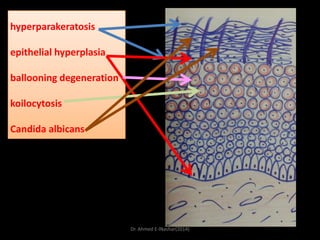
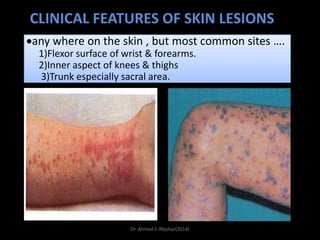
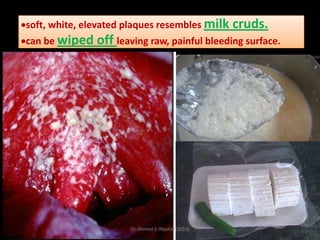
This document discusses white lesions of the oral mucosa. It begins by describing the normal color of oral mucosa and then defines white lesions as areas where the mucosa appears white in color. White lesions are classified as either keratotic or non-keratotic. Specific white lesions discussed in detail include frictional keratosis, nicotinic stomatitis, white spongy nevus, lichen planus, hairy leukoplakia, and leukoplakia. Non-keratotic white lesions discussed are burns, candidosis, and leukodema. For each lesion, the document discusses characteristics such as prevalence, appearance, histopathology, and treatment. The document is authored by