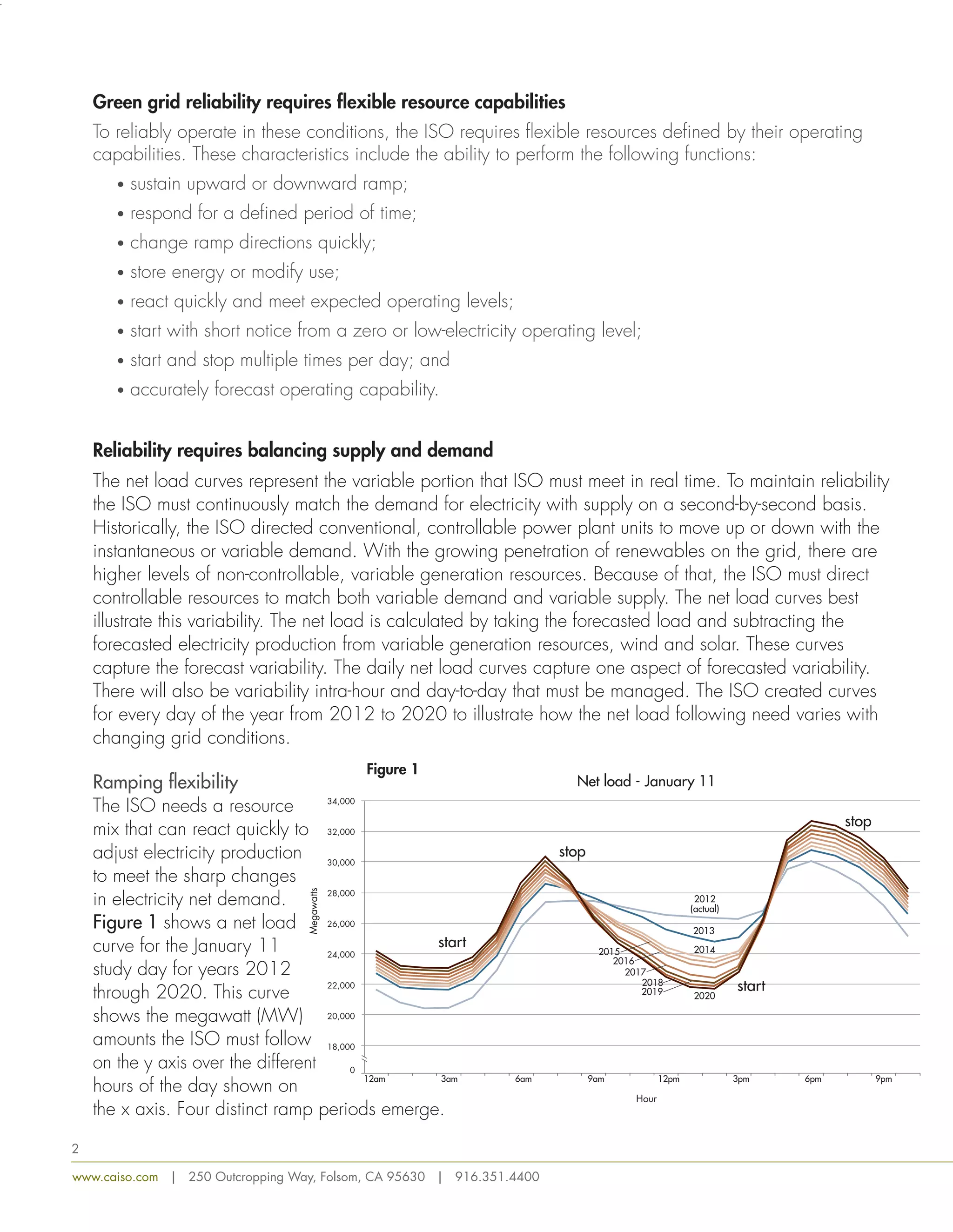
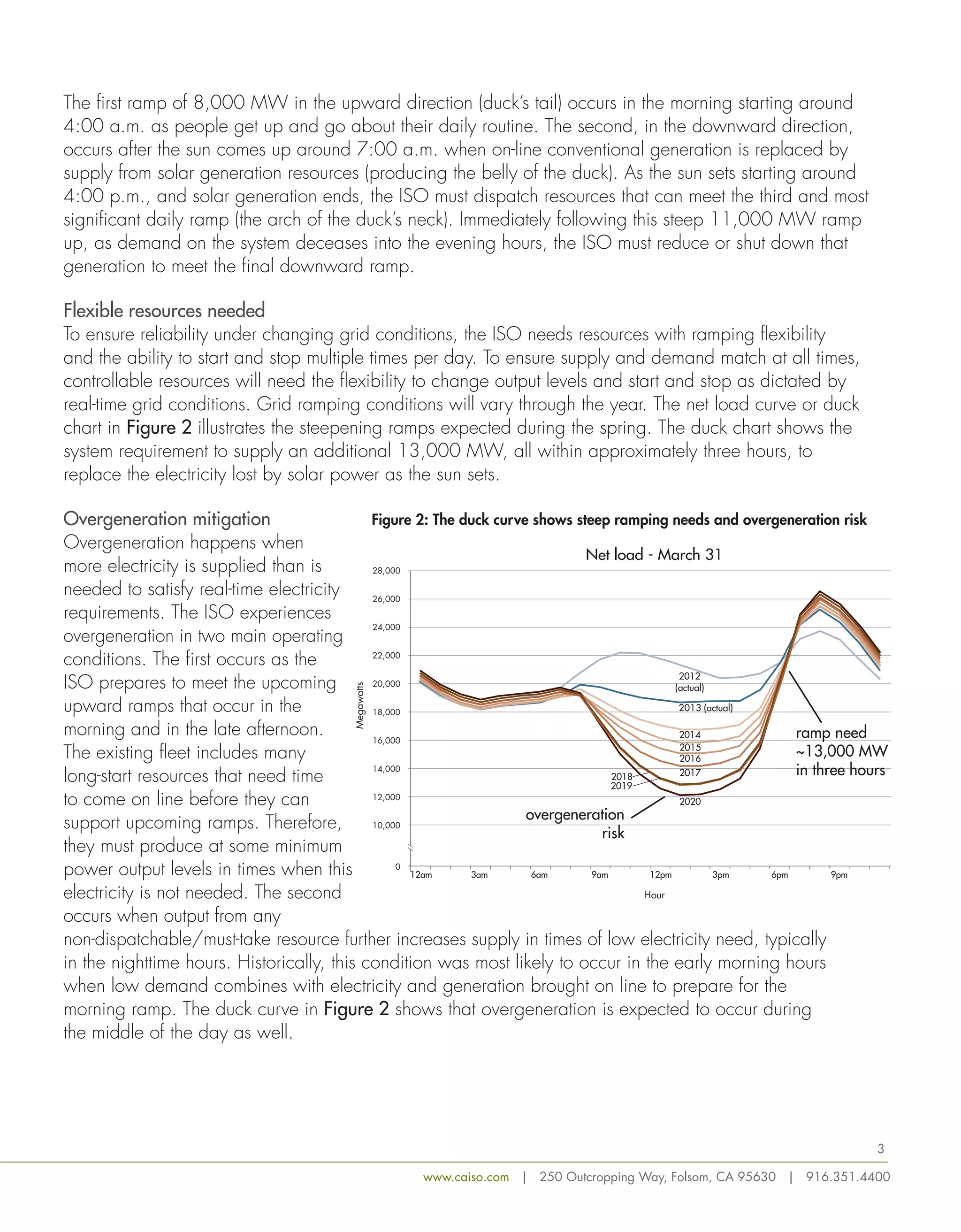
This document discusses how the increasing use of renewable energy is changing net load patterns on the electric grid in California. It introduces the concept of the "duck curve" which depicts steep ramps in net load in the mornings and evenings as solar power comes online and offline. To reliably operate under these changing conditions, the grid requires flexible resources that can quickly adjust power production through ramping, storage and demand response. Issues like overgeneration and reduced frequency response may occur and will require mitigation strategies to maintain reliability as renewable penetration increases.