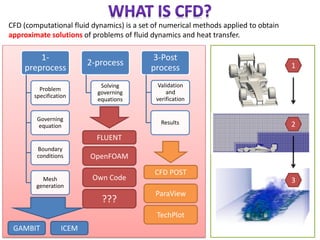
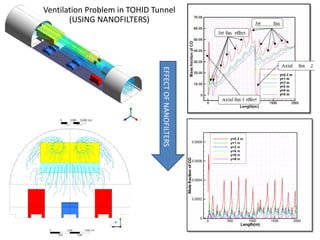
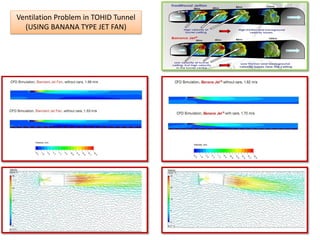
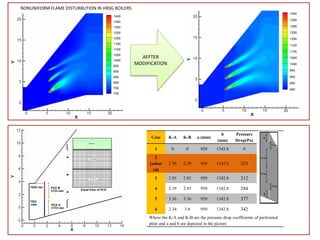
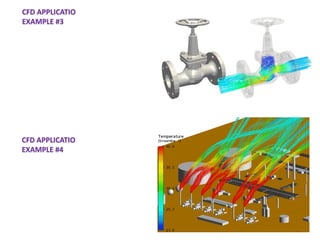
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a set of numerical methods used to simulate fluid flow and heat transfer. CFD involves three main steps: pre-processing (defining the problem, governing equations, and boundary conditions), processing (solving the governing equations), and post-processing (validating results). The document provides examples of applying CFD to ventilation problems in tunnels, non-uniform flame distribution in boilers, and discusses pre- and post-processing software used like GAMBIT, FLUENT, and ParaView.