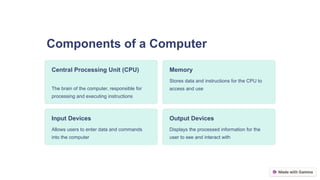
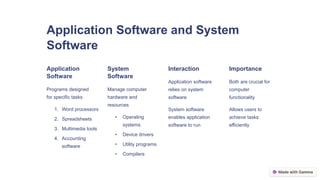
A computer is an electronic device that solves problems based on given instructions and facilitates calculations, data processing, and communication. It consists of hardware components like the CPU, memory, and input/output devices, and operates through software, which includes application and system software. Understanding computers is essential in today's digital world, and further resources are suggested for deeper exploration of the topic.