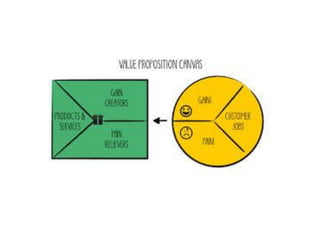
This document discusses aggregation and disaggregation marketing strategies. Aggregation involves treating all consumers the same, while disaggregation involves segmenting the market. Disaggregation is becoming more efficient due to information availability. It allows for targeted, personalized communication with consumer segments. While brands were traditionally the focus, disaggregation shifts the focus to consumers. This challenges existing brand-centric organizational structures. However, brands still provide value in communicating differentiated value propositions. Ultimately, companies must decide whether to focus on aggregation, disaggregation, or a balanced approach based on building strong customer relationships.