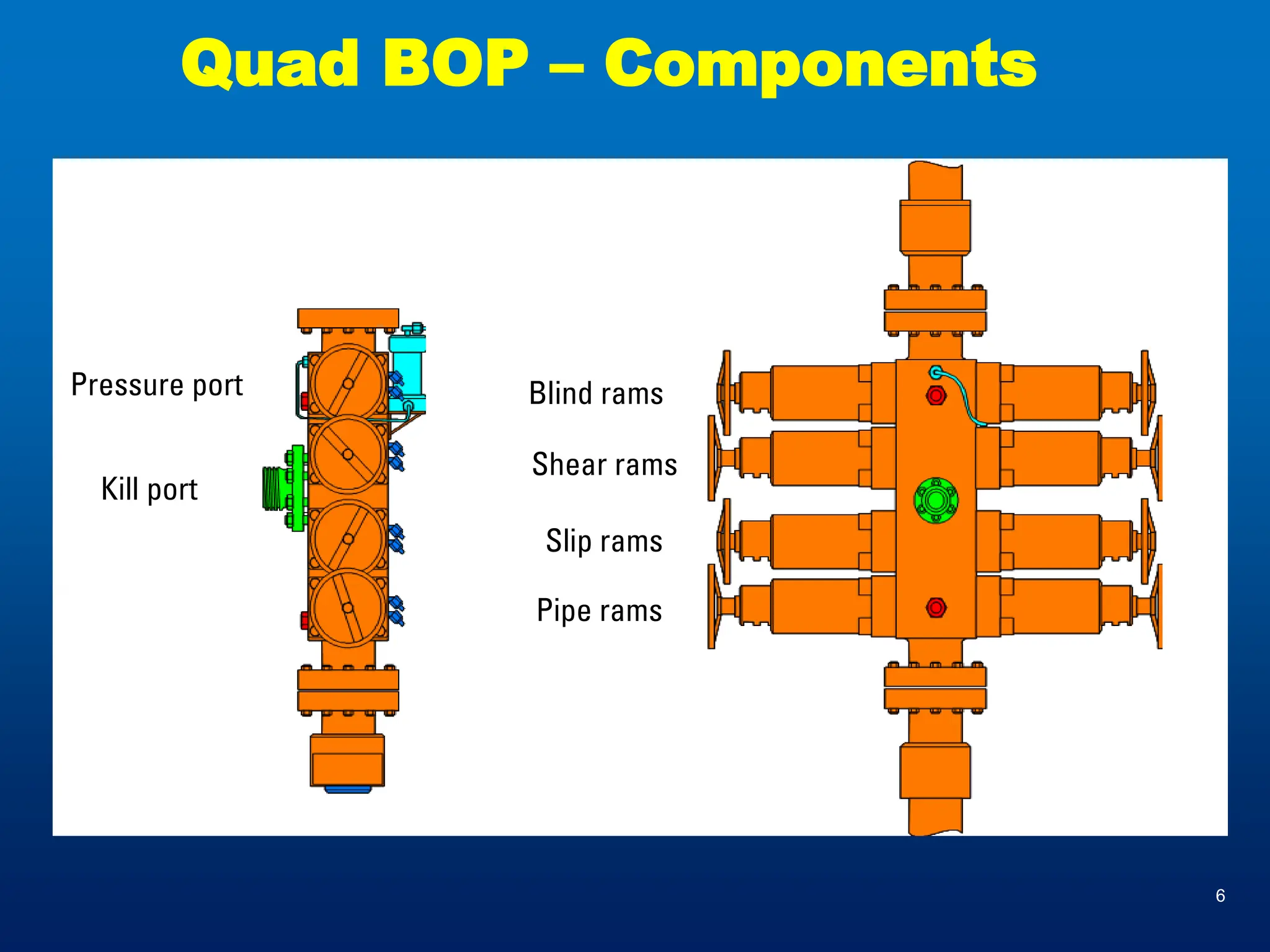
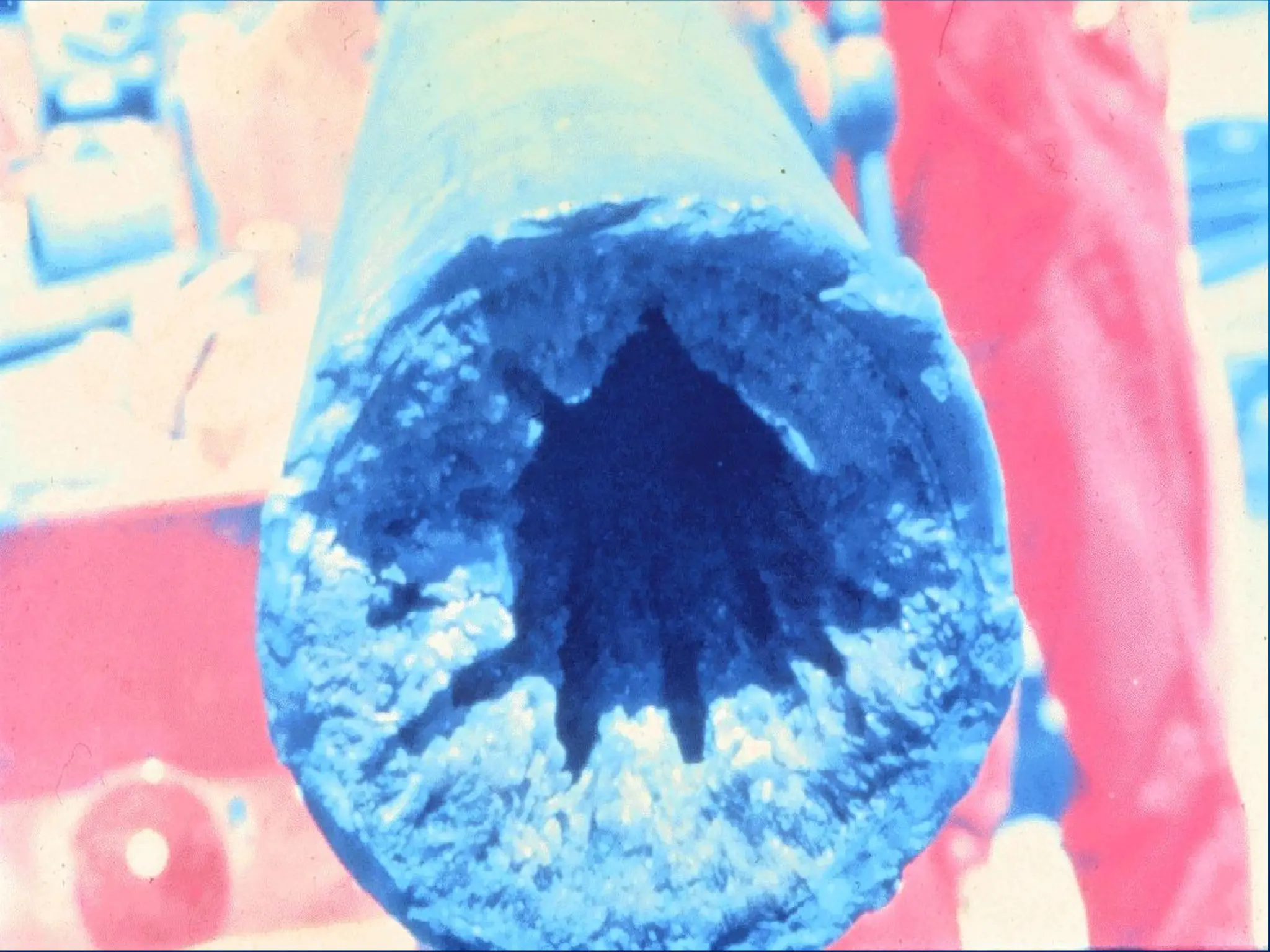
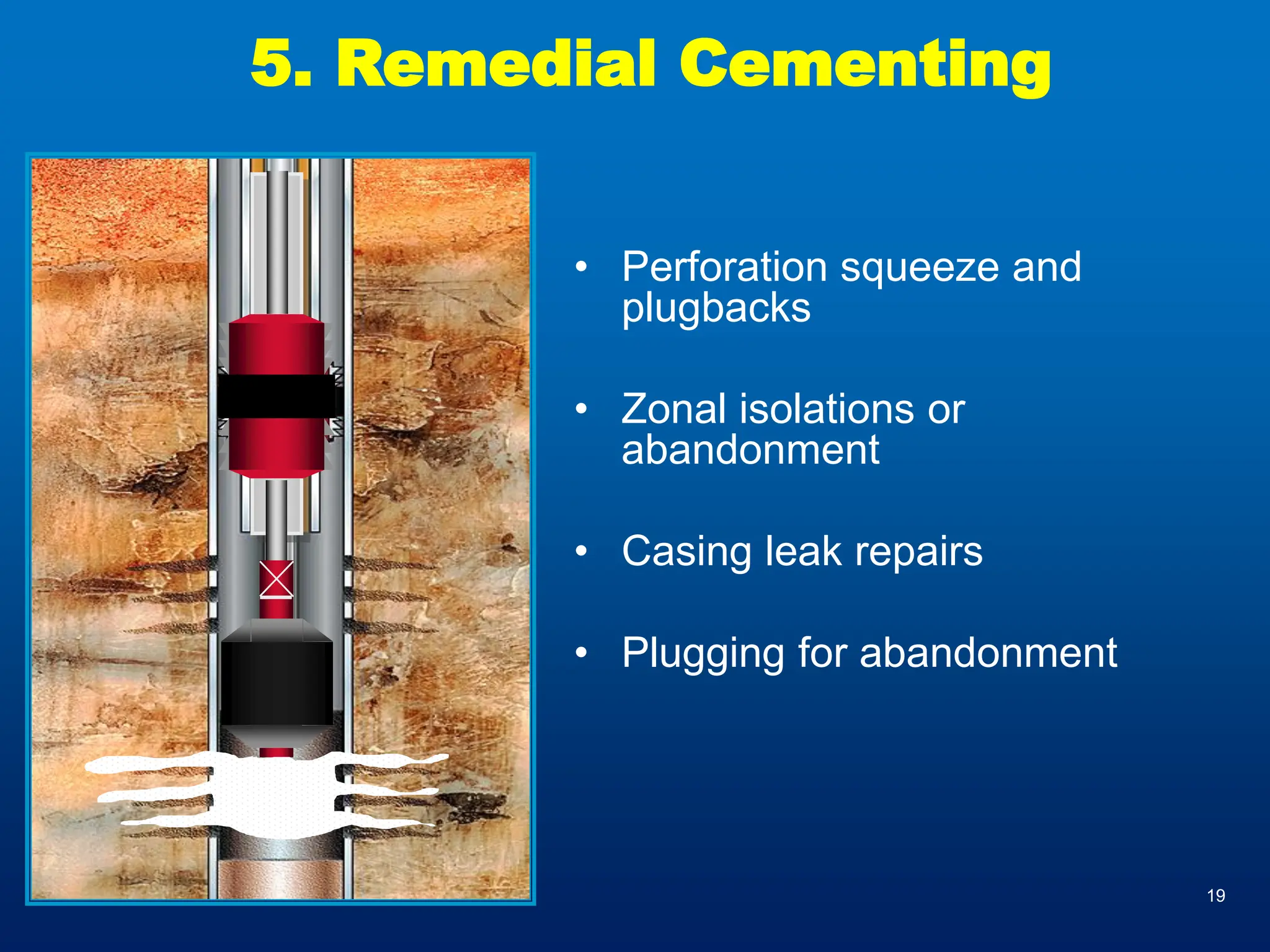
Coiled tubing (CT) is defined by its diameter ranging from 0.75 to 4 inches and reel lengths of 4,000 to 25,000 feet, evolving from its first fully functional unit in the 1960s. Key components include the reel, injector head, and control cabin, with applications ranging from sand washing and scale removal to drilling and wireline logging. Advantages include high efficiency and versatility, while disadvantages focus on fatigue life limits and pressure tensions.