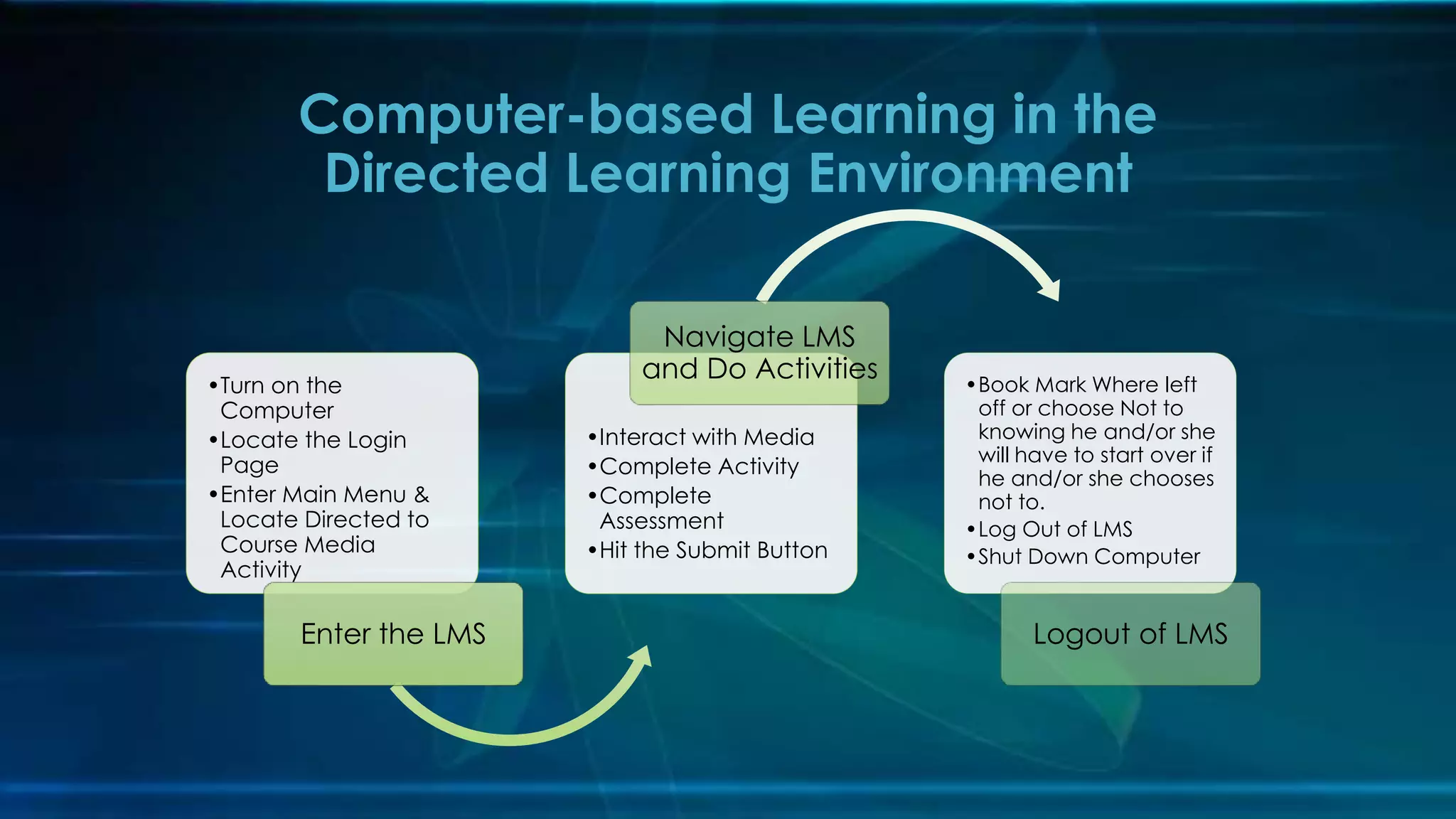
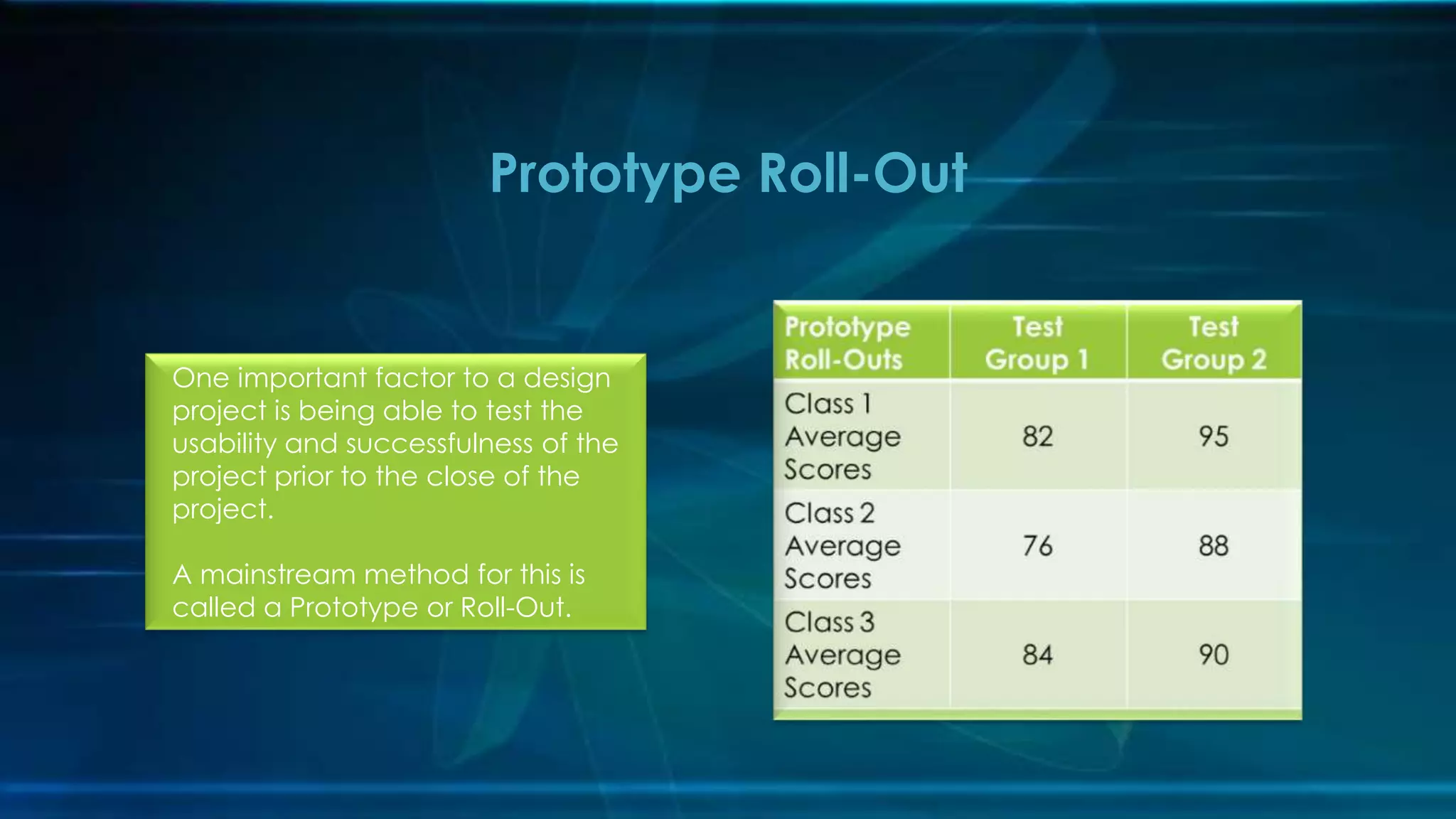
This document outlines standards and plans for developing a computer-based training module for new engineers. It includes sections on instructional strategies, media and evaluation plans, how the training will be organized in an online learning management system, how the content will be organized for the target learner audience of new engineers, and a prototype rollout plan. Key points are that the training will provide skills practice, assessments without grades until the end, and Spanish language alternatives to meet the needs of the target learner group.