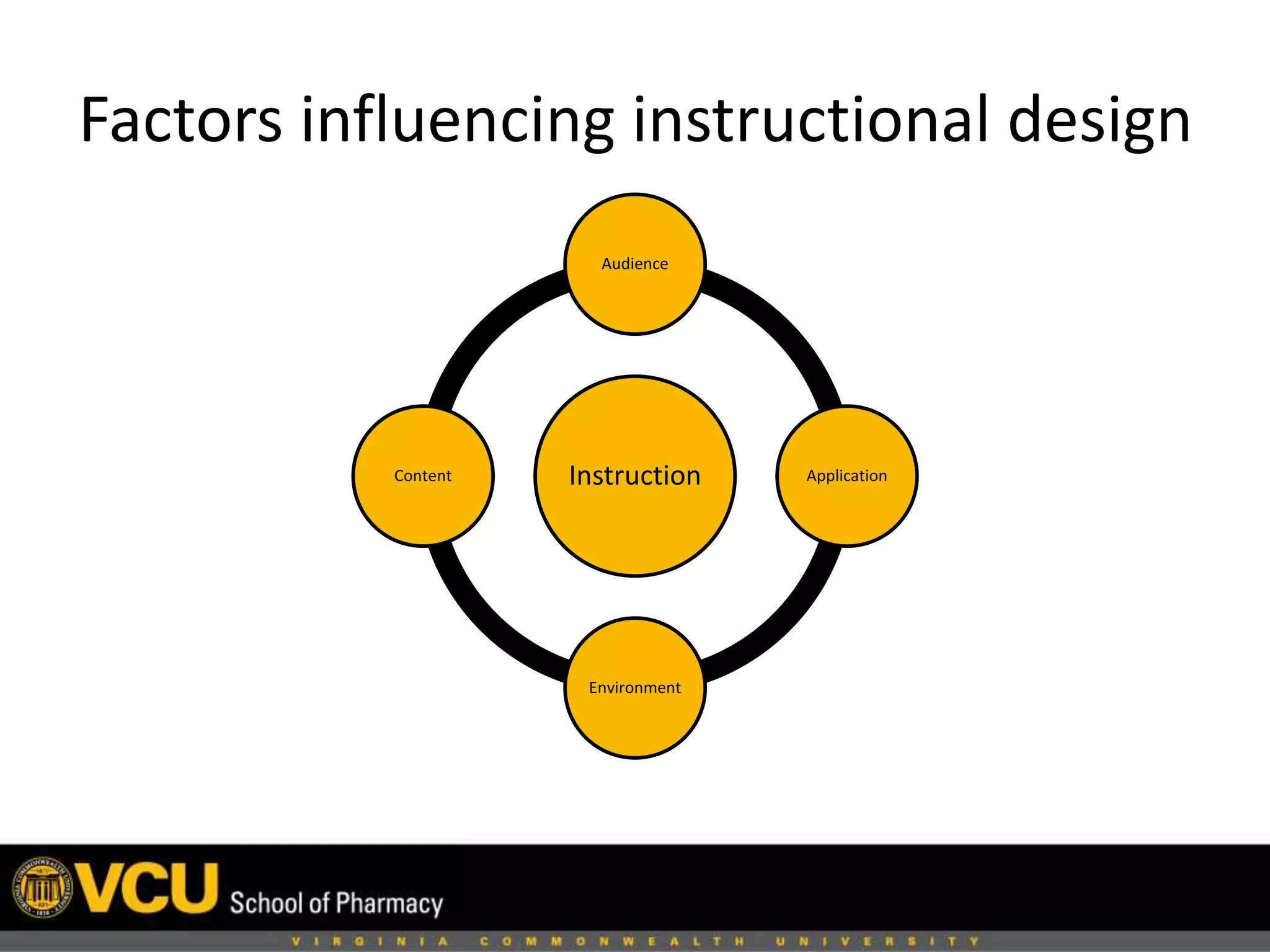
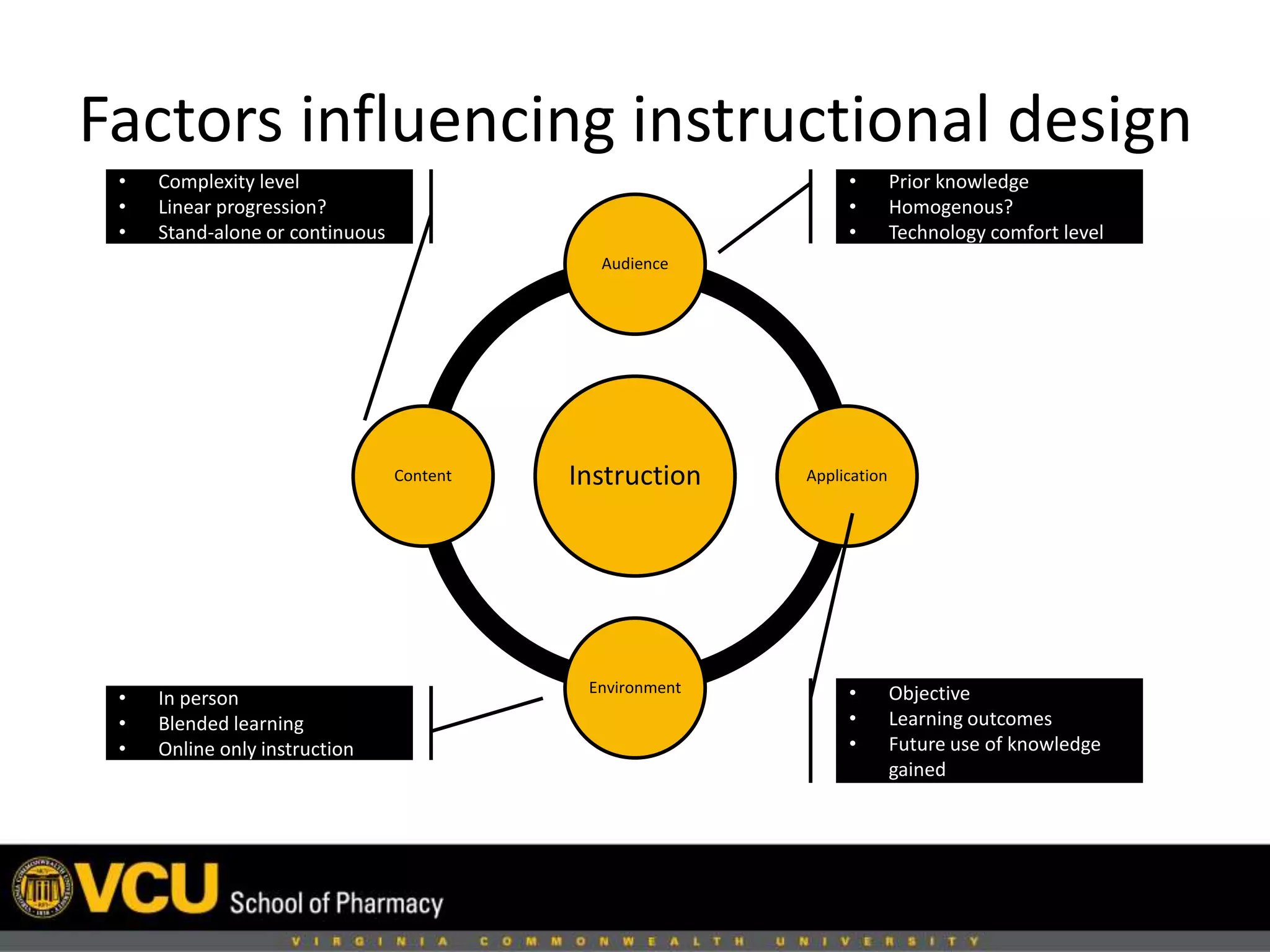
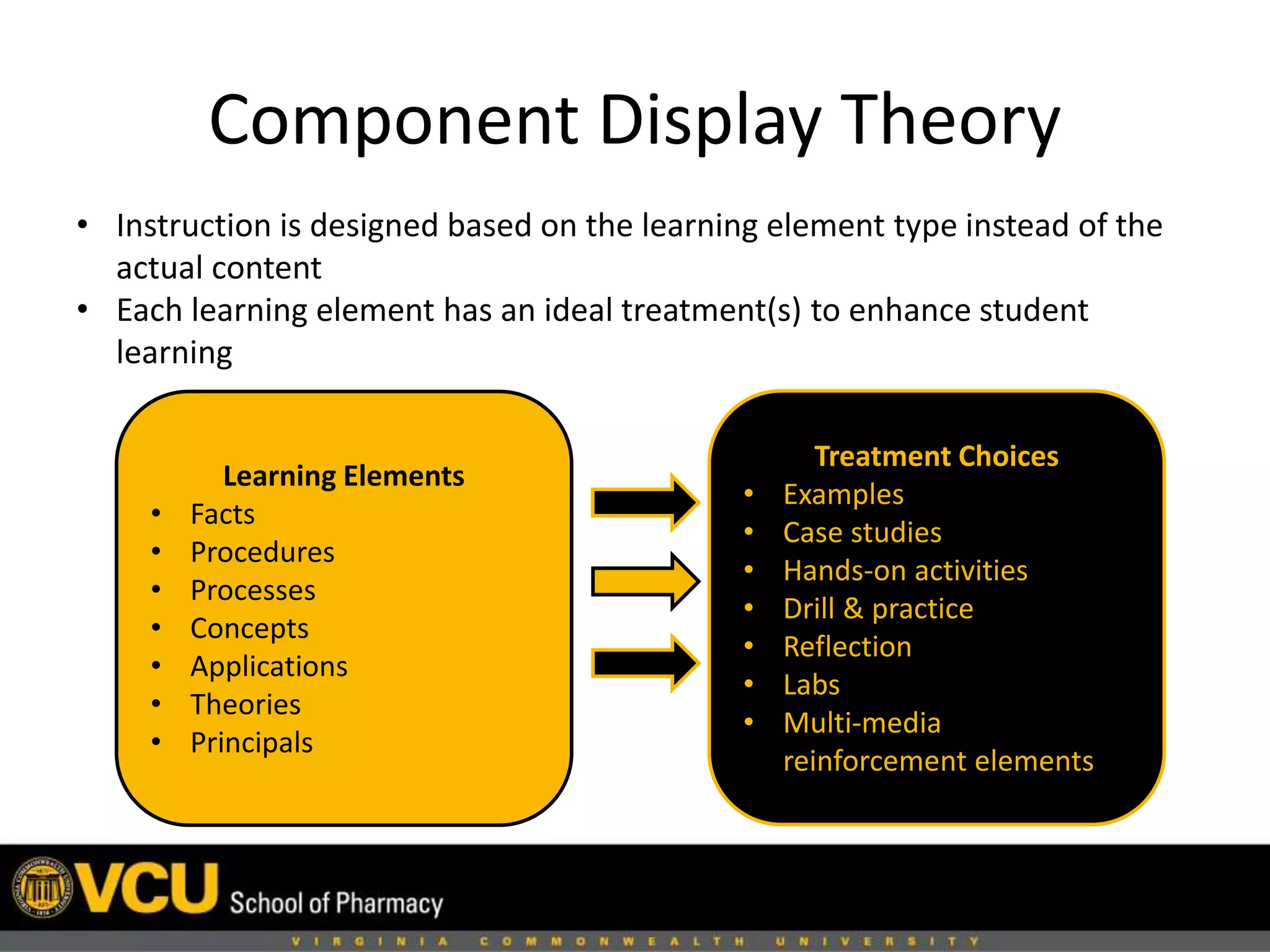
This document discusses factors to consider when designing a learning module, including the audience, content, environment, and application. It recommends keeping the objective and learning outcomes in mind, and only including pertinent content. The document also discusses component display theory for designing instruction based on learning element types. Modern design theory advises using a maximum of two sources of information. Meaningful assessment should take place after chunks of information and encourage learning rather than punish learners. Performance support materials can help learners succeed by providing easily accessible references.