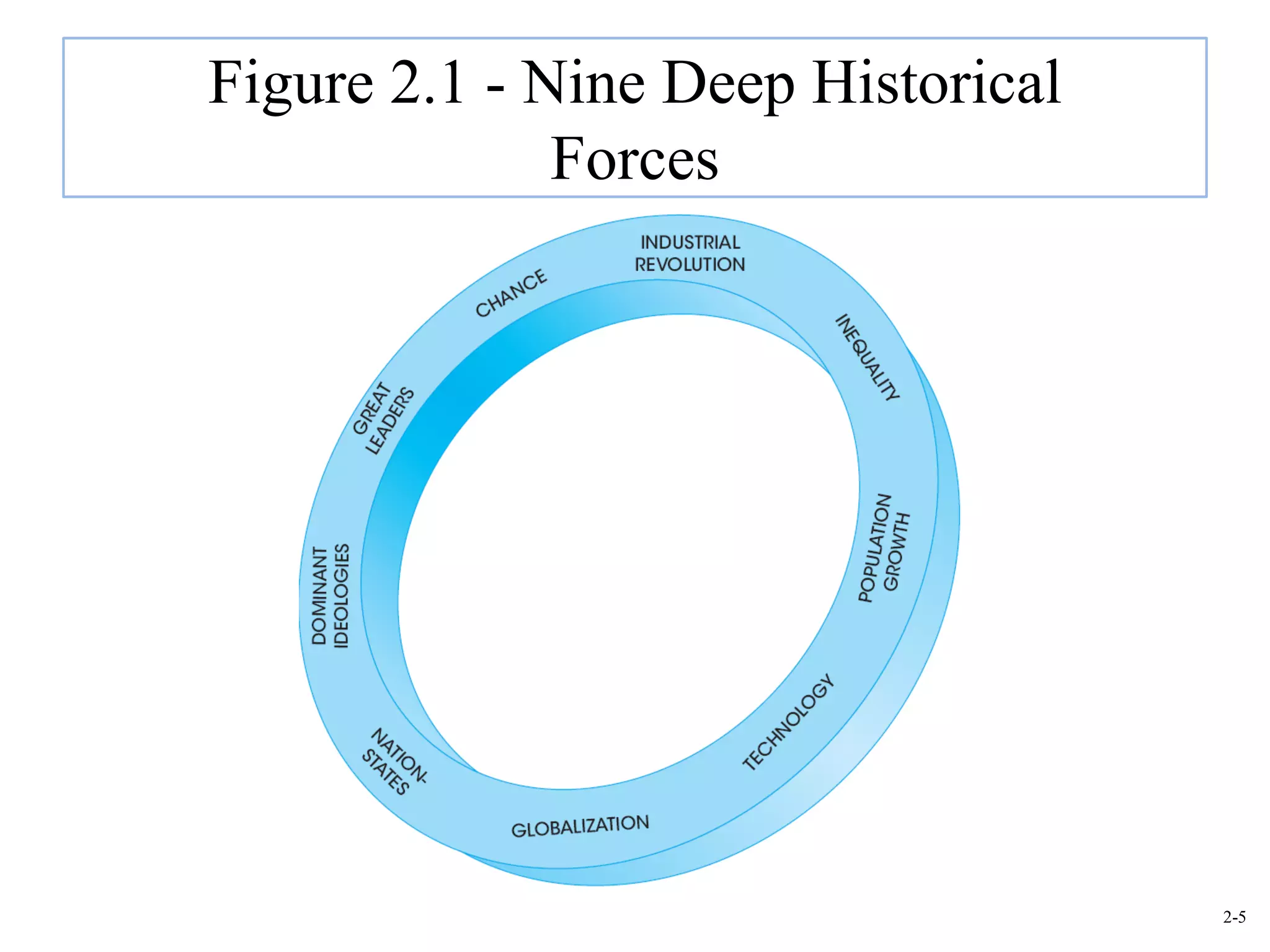
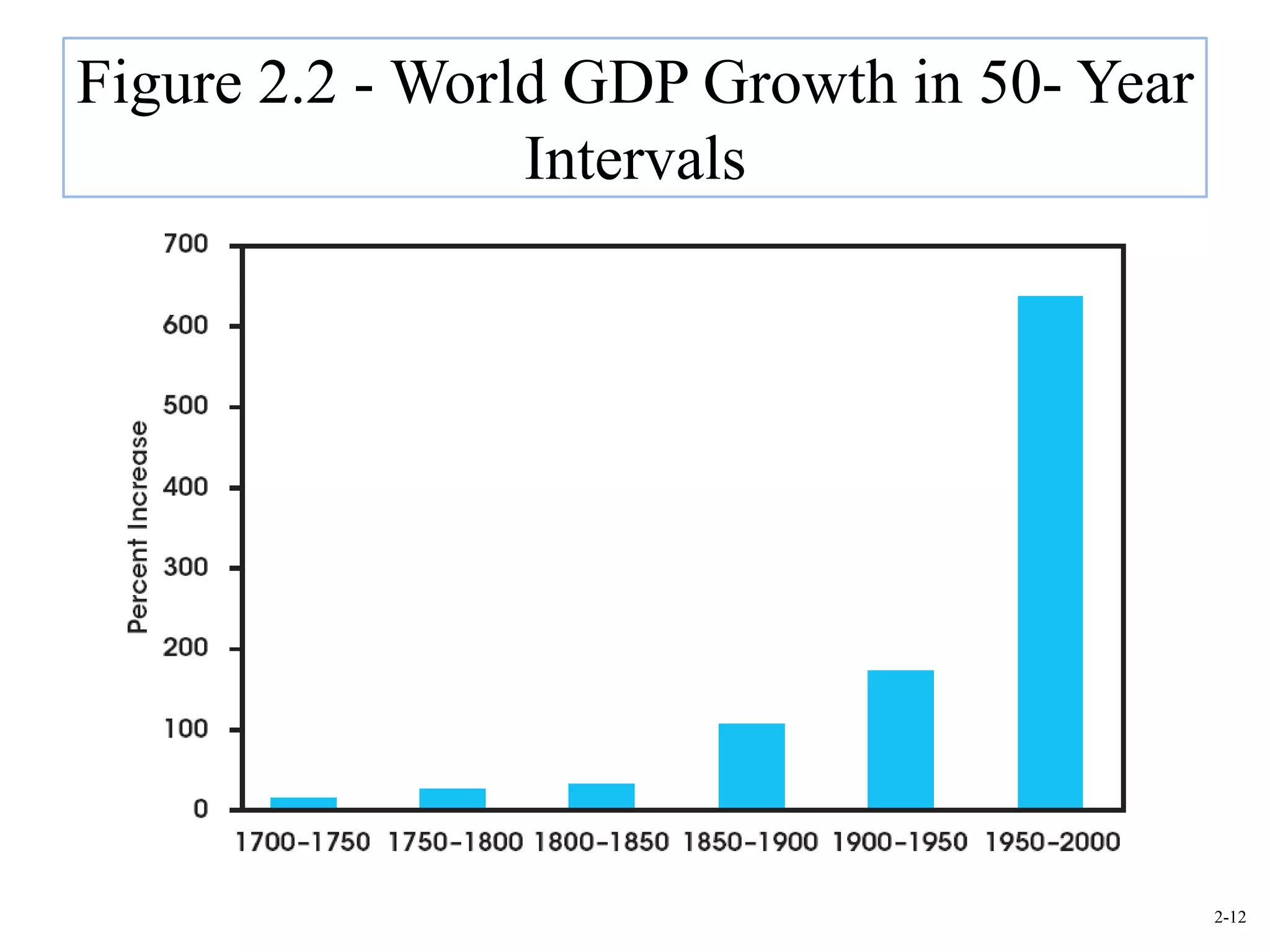
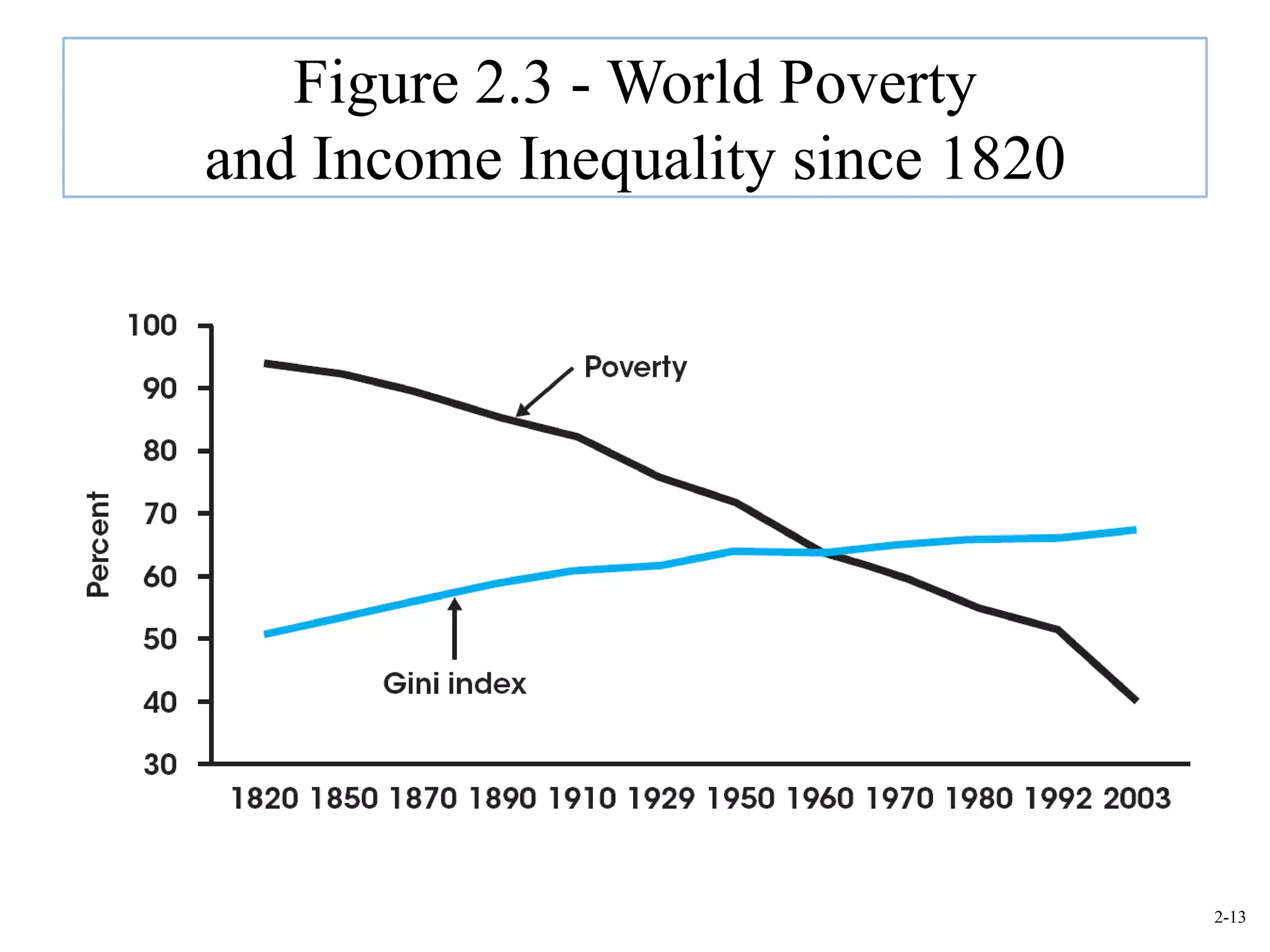
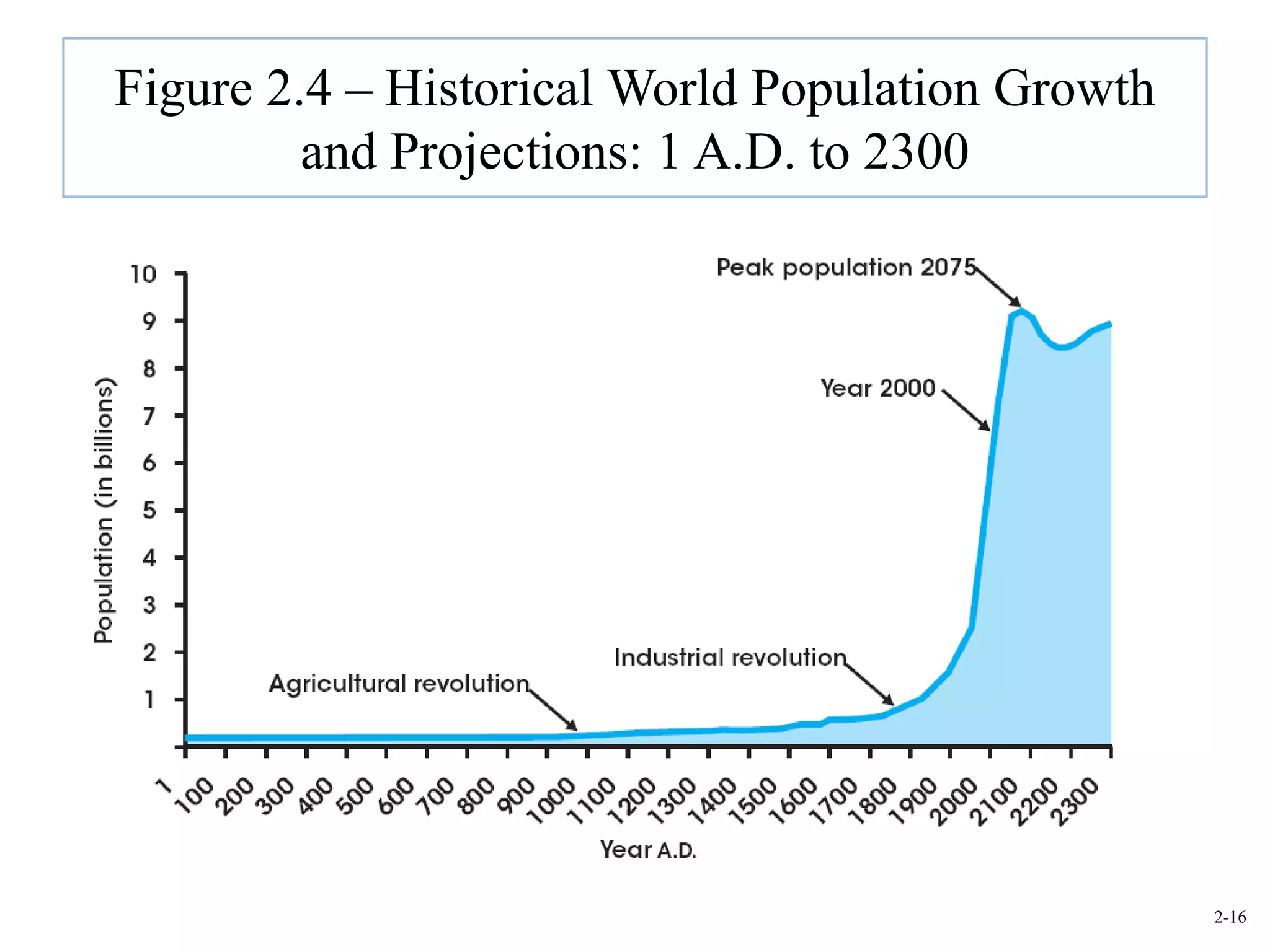
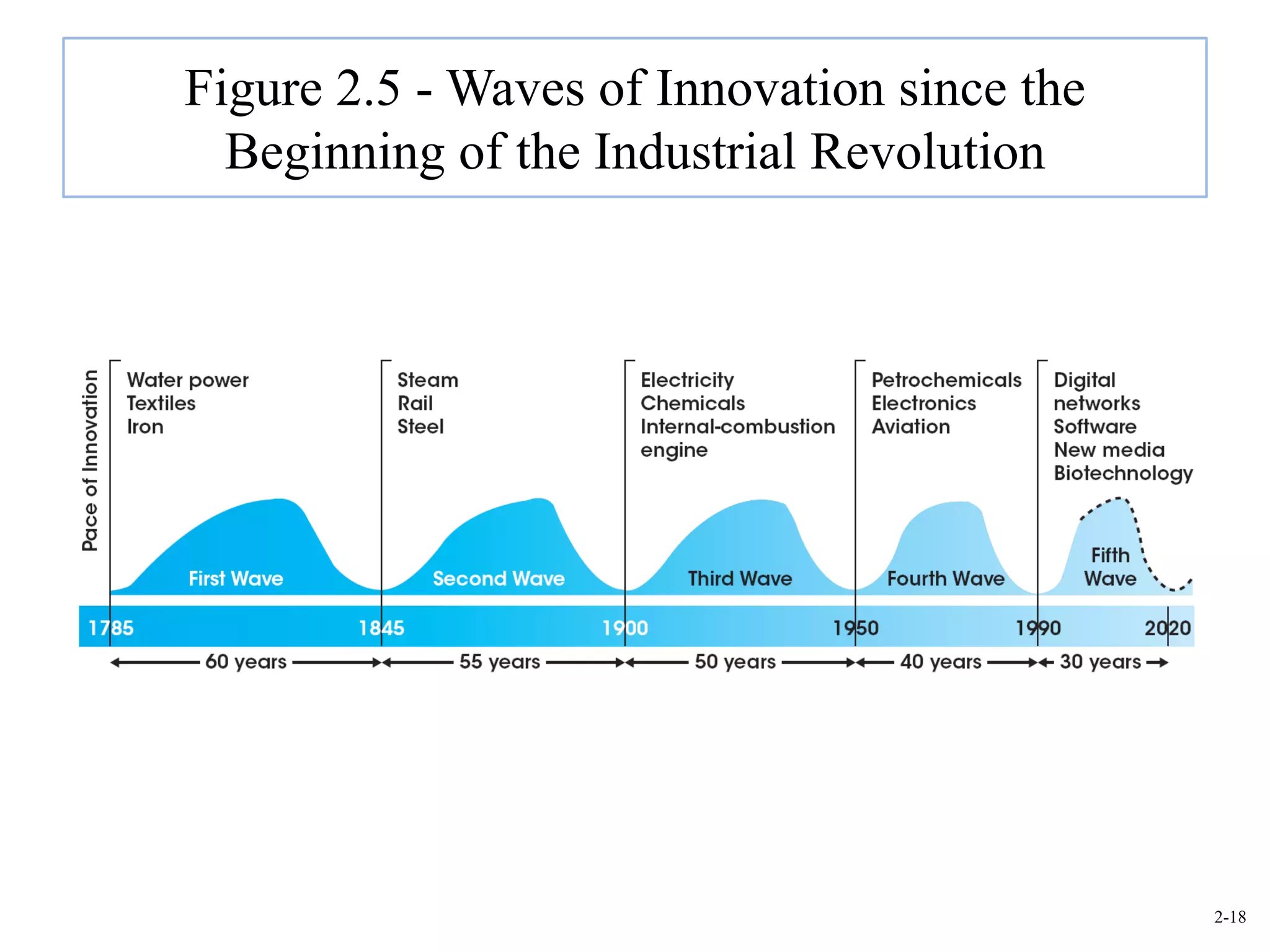
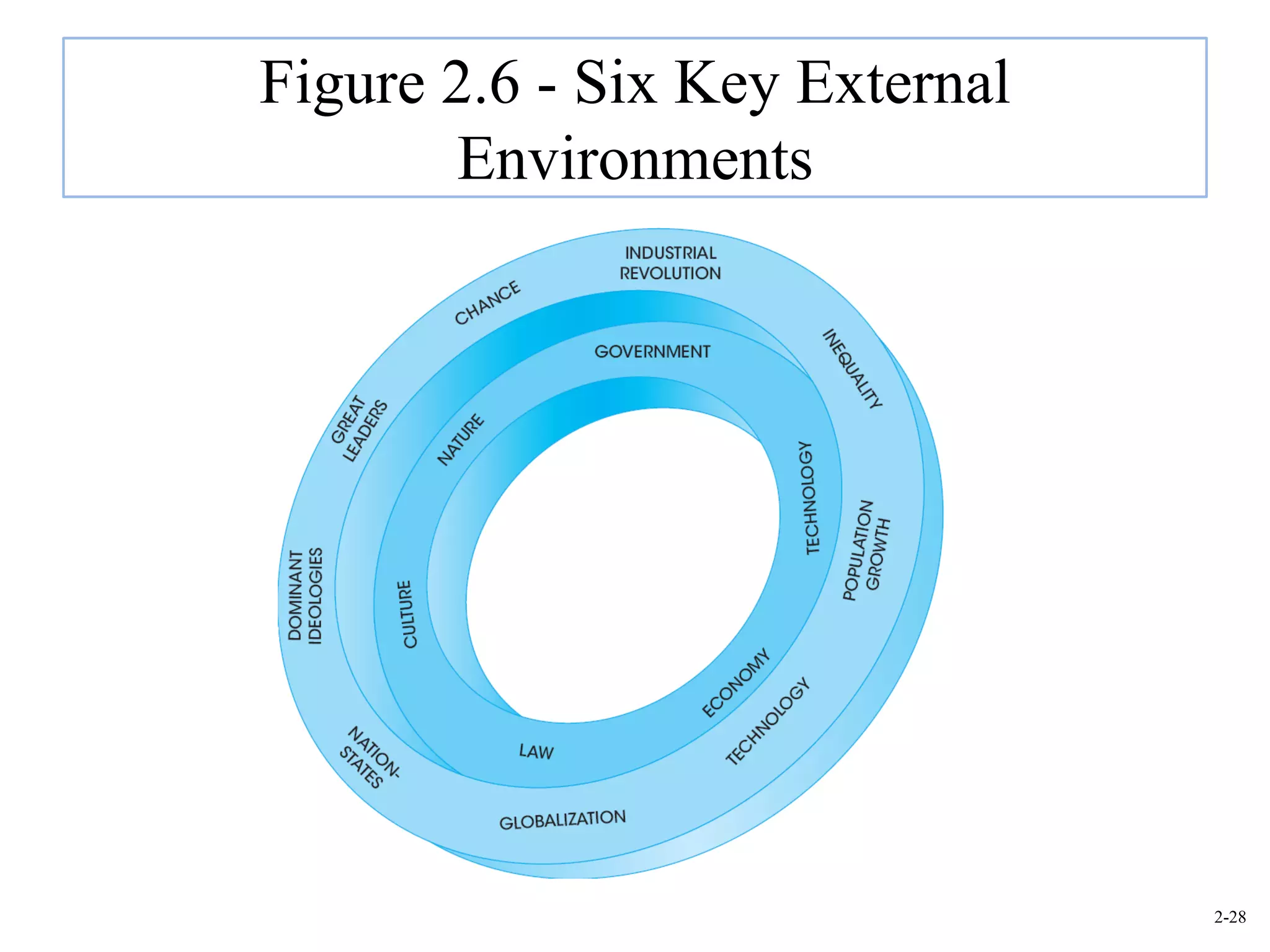
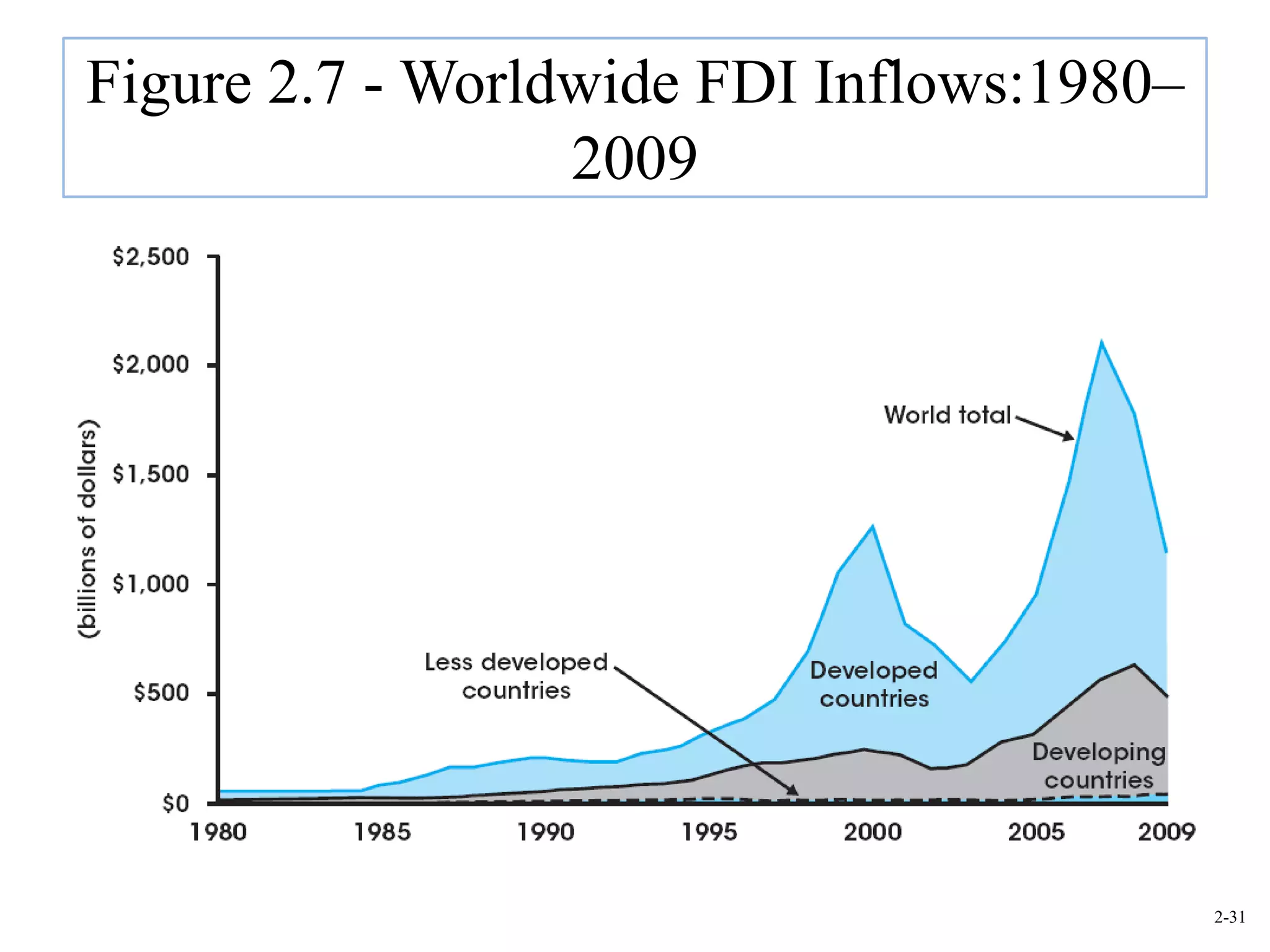
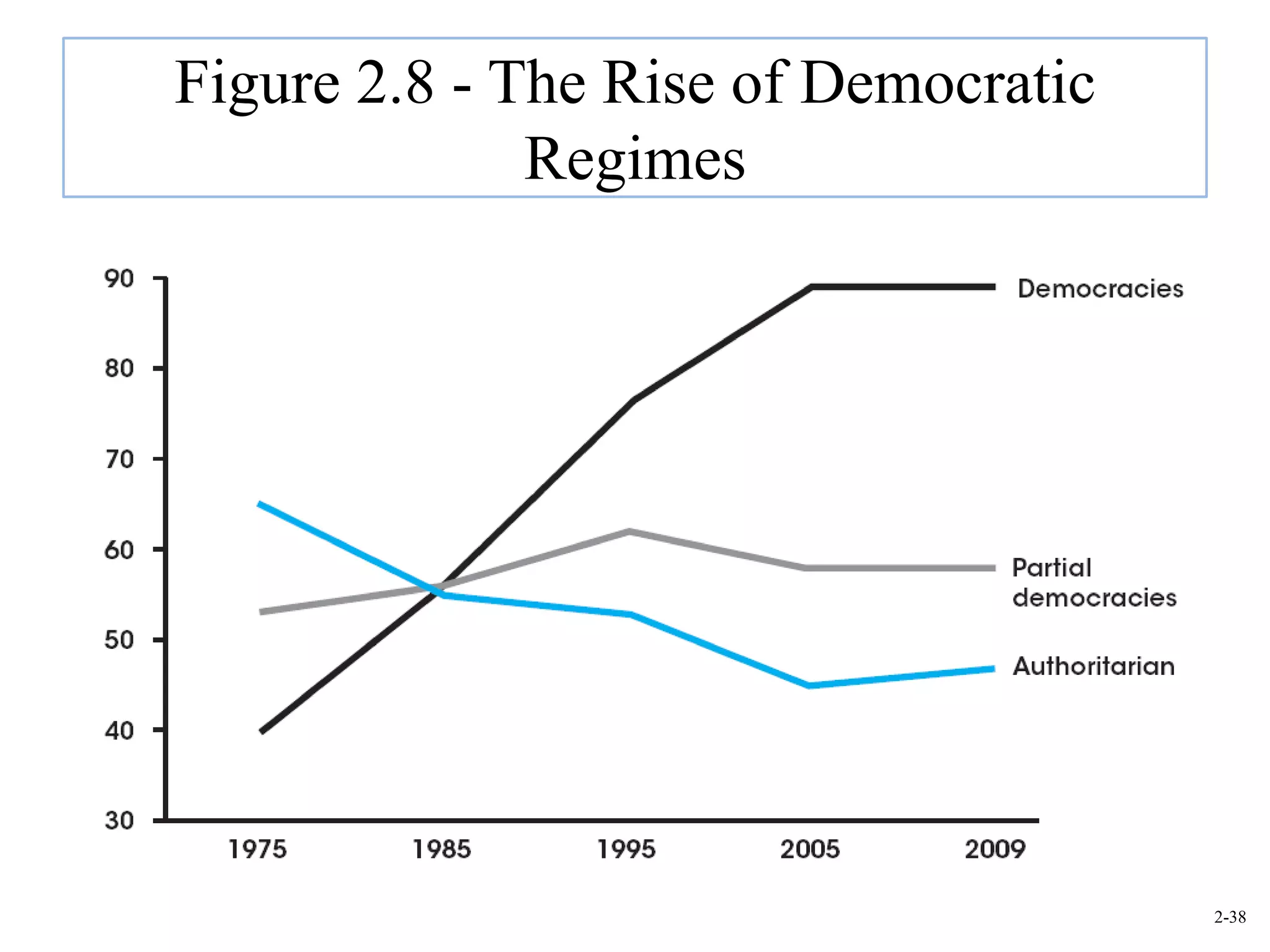
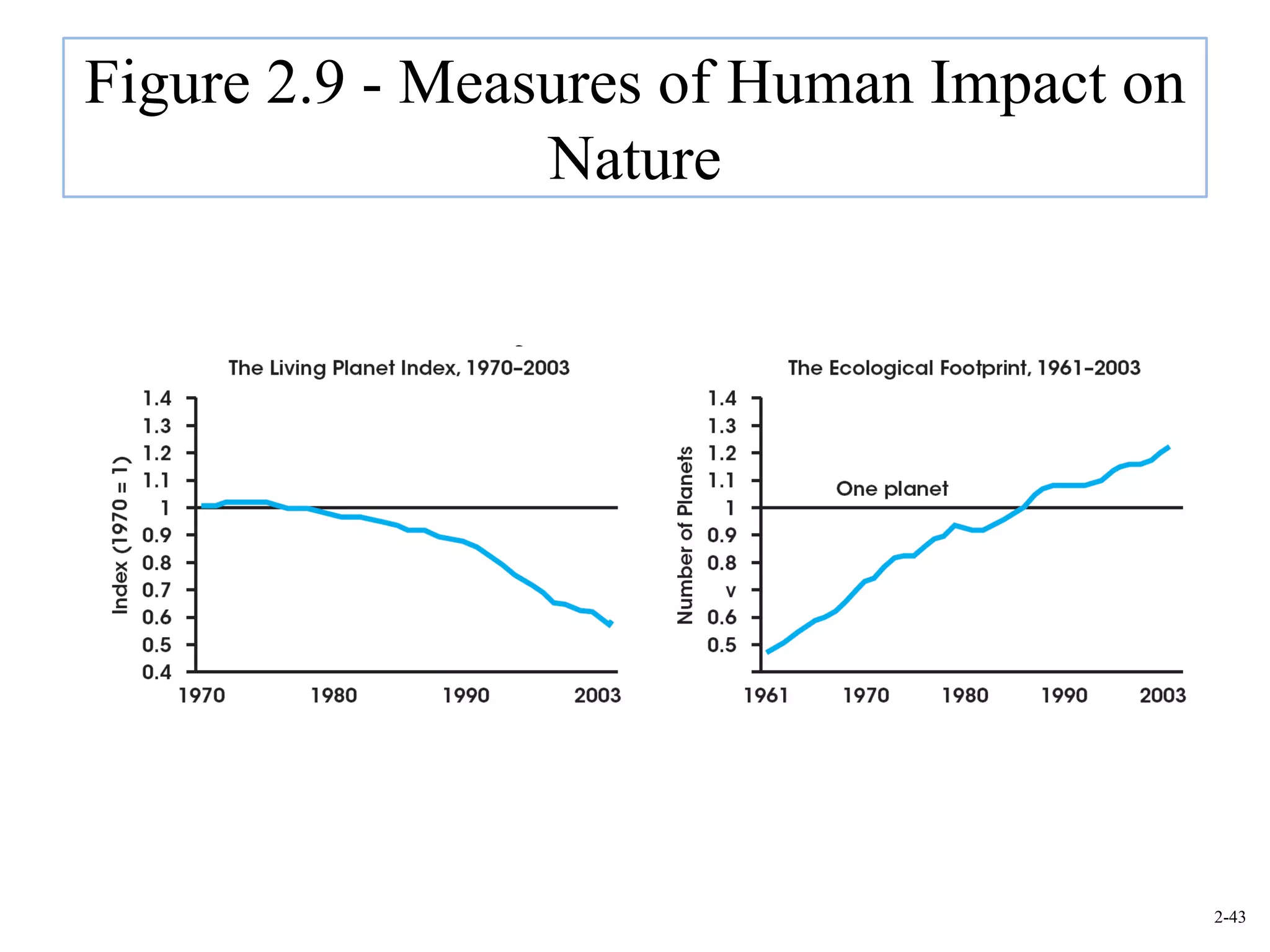
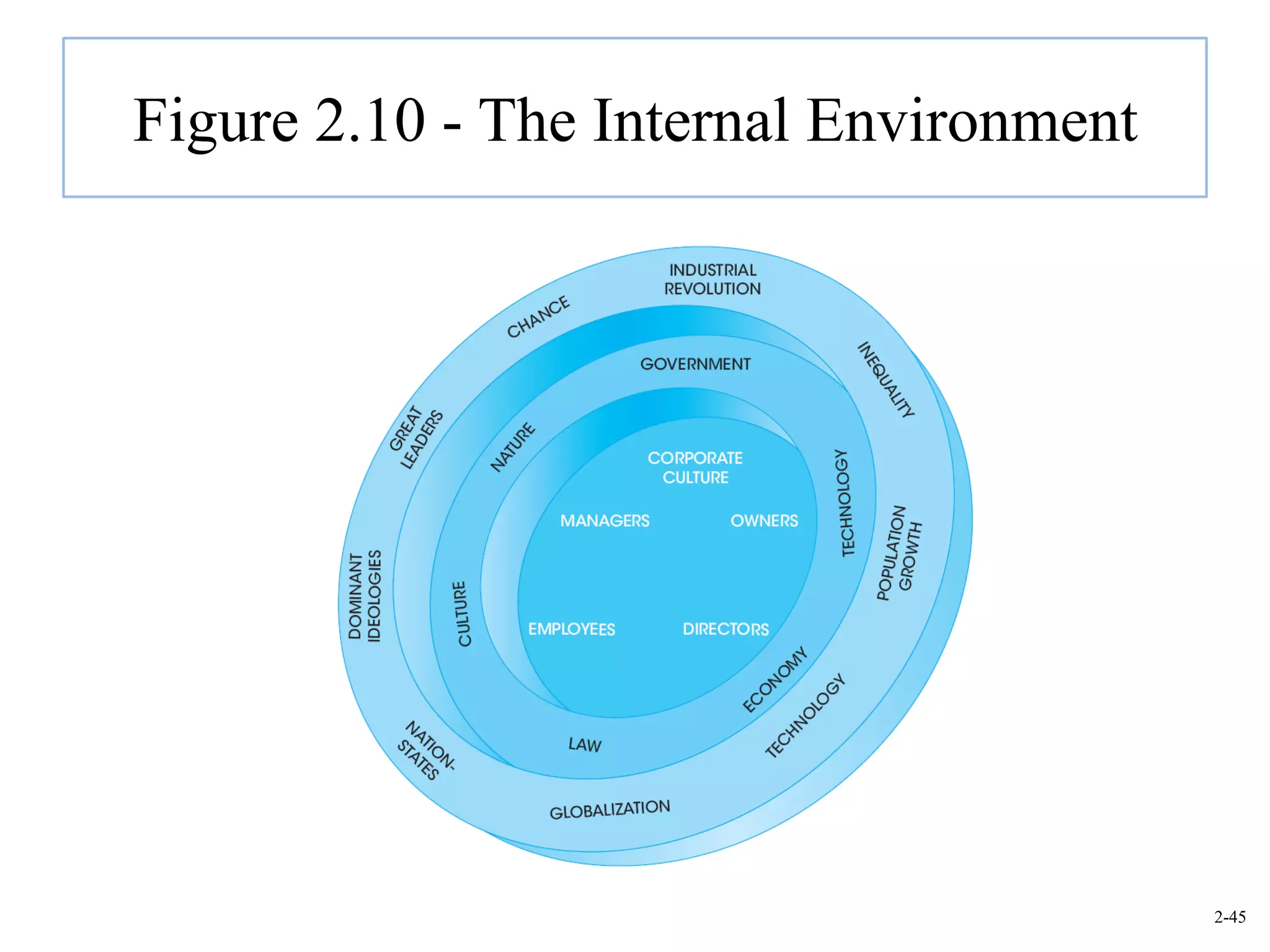
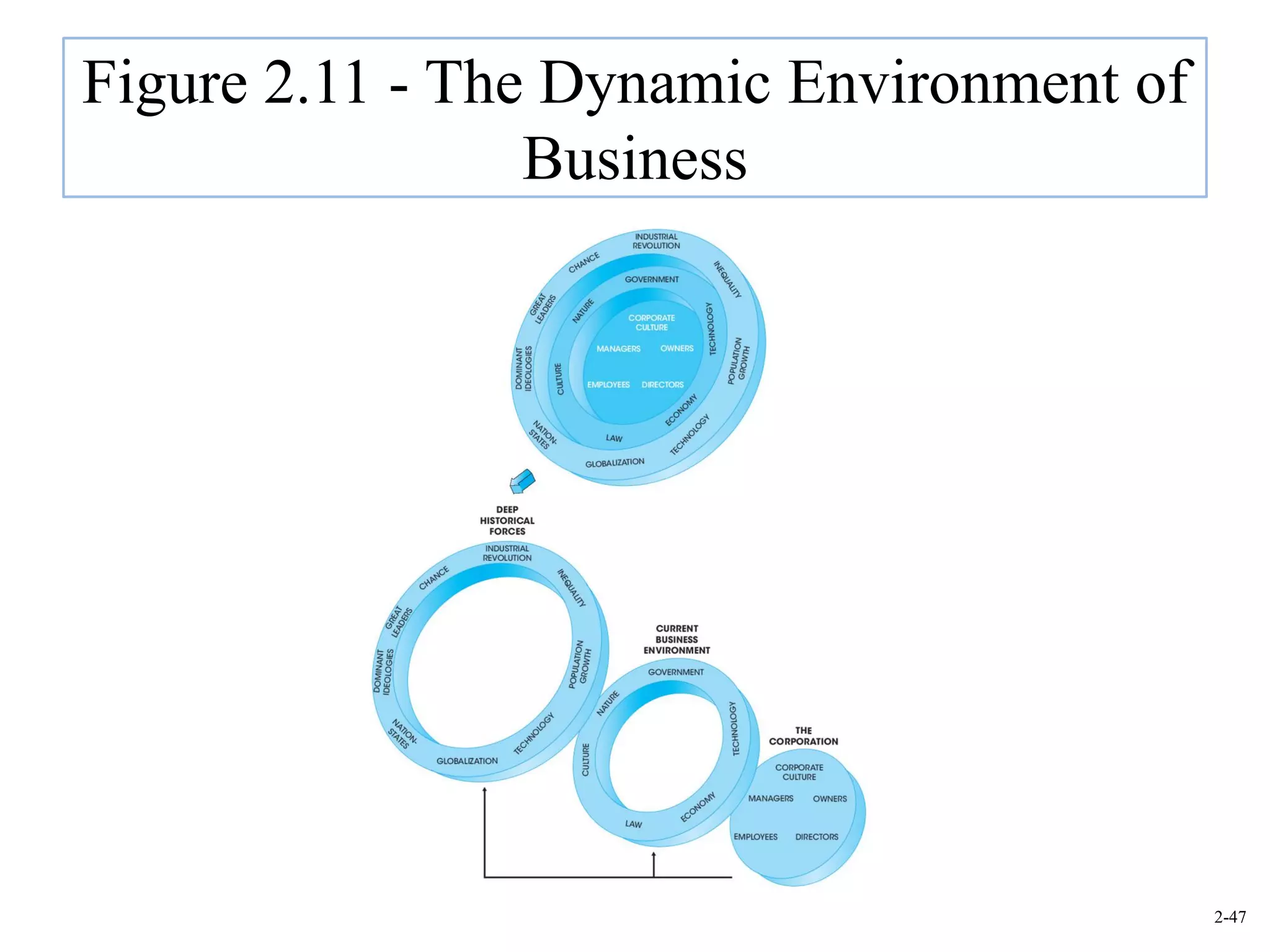
This document provides an overview of Royal Dutch Shell and discusses nine deep historical forces that have shaped the dynamic business environment: the Industrial Revolution, inequality, population growth, technology, globalization, nation-states, dominant ideologies, great leadership, and chance. It also examines key external environments including the economic, technological, and cultural environments that influence business operations.