1. The document discusses three main types of economic systems - traditional, command, and market - and how they differ in who makes decisions about what/how to produce goods and who receives them.
2. Most modern economies are mixed, combining aspects of market and command systems, with private businesses producing goods and the government regulating certain industries.
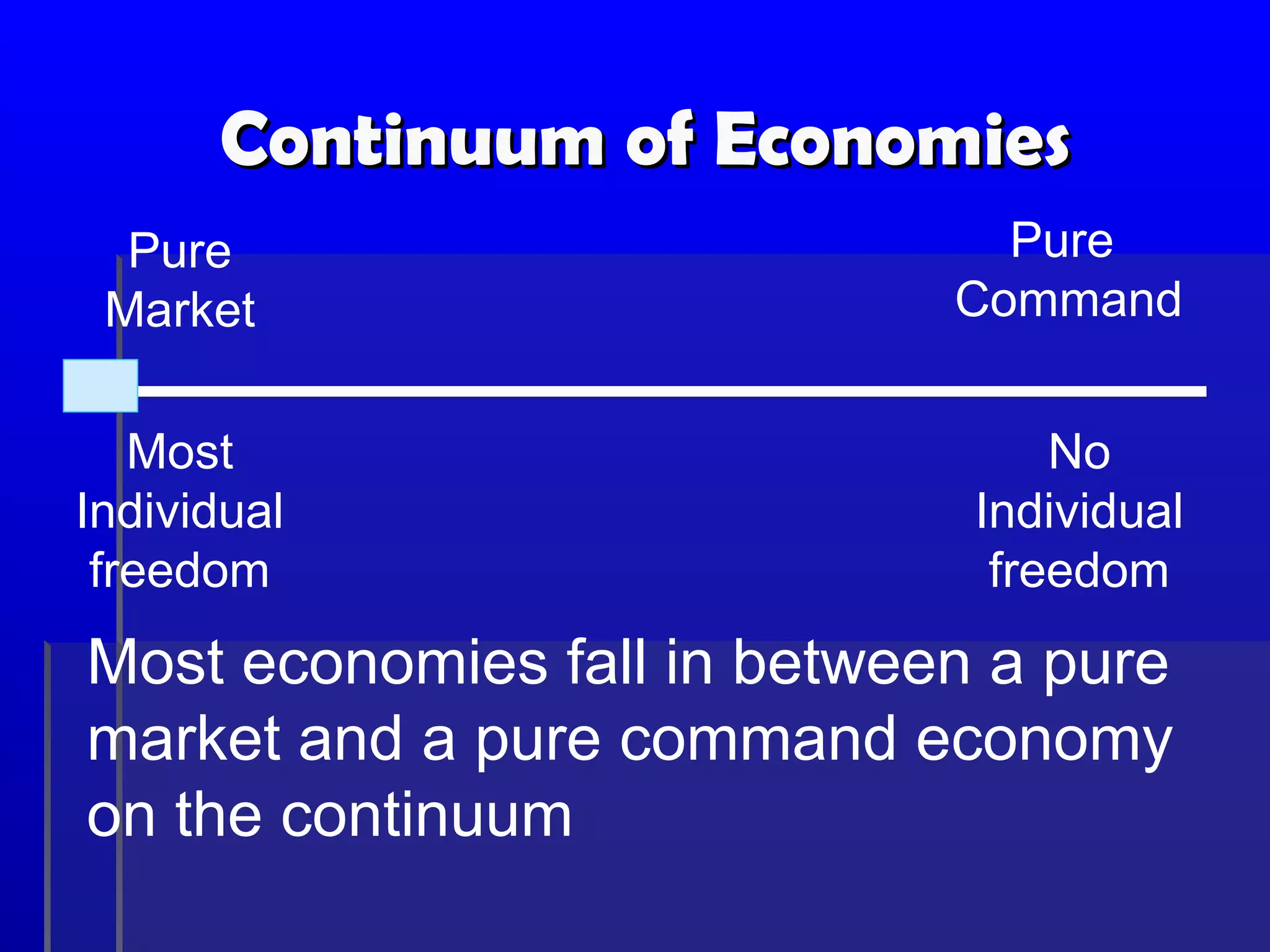
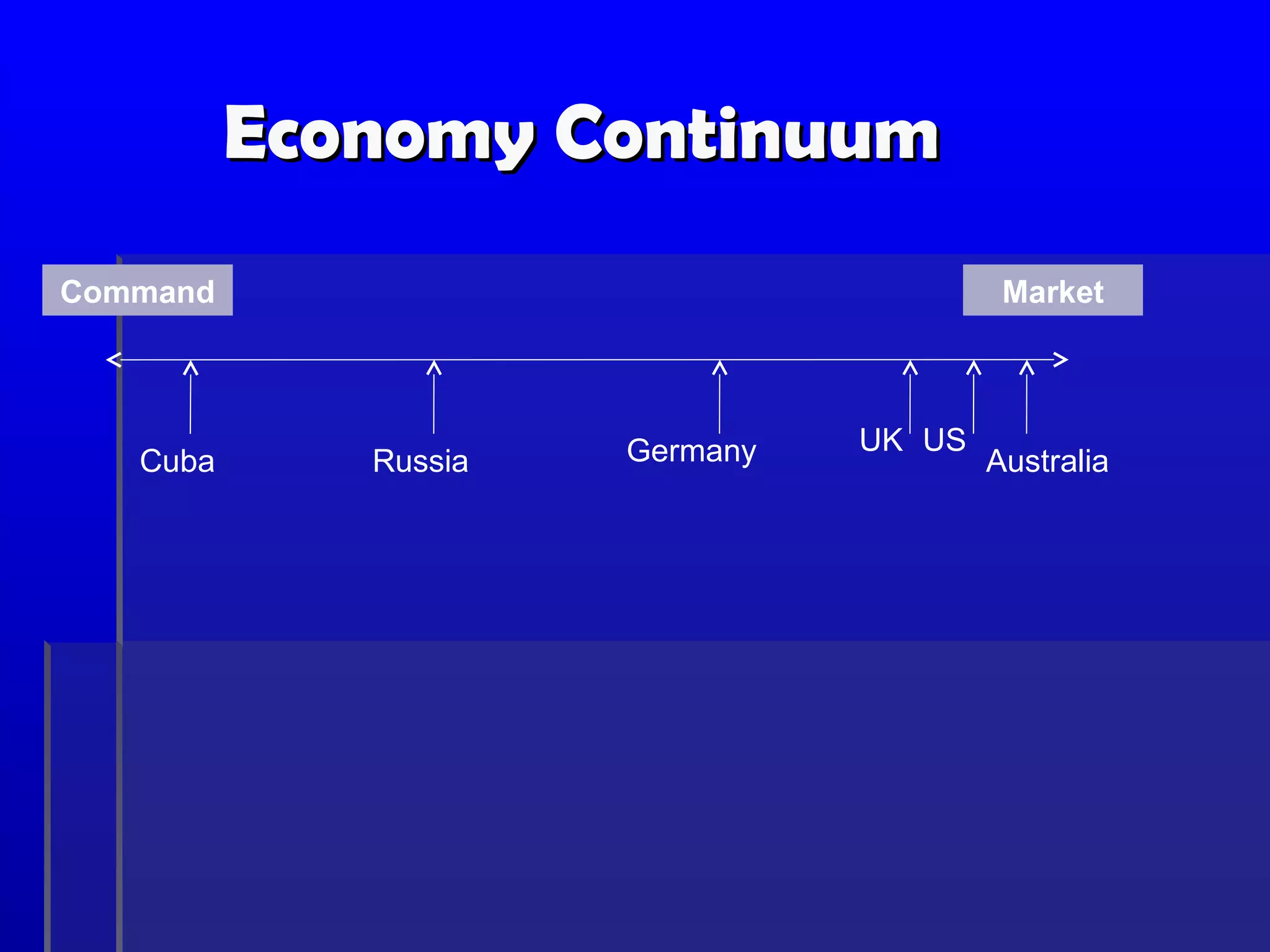
3. The continuum shows most economies fall between pure market and command systems, balancing individual freedom with some government intervention.