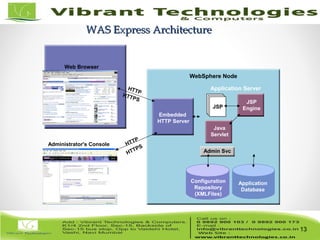
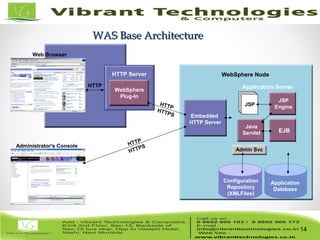
The document provides an in-depth overview of IBM's WebSphere software platform, including its various packaging options and architecture. It covers the management and performance monitoring of WebSphere, emphasizing tools like Tivoli Performance Viewer and the Performance Monitoring Servlet for analyzing performance data. Key details include the functionalities and limitations of each WebSphere edition, important for running Java 2 Enterprise Edition applications.