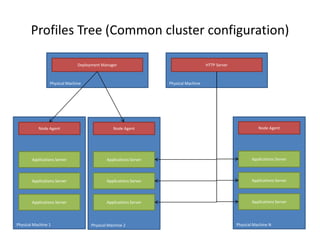
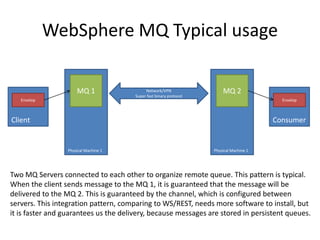
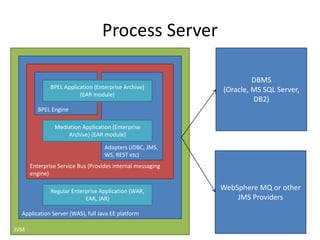
IBM WebSphere is an expensive but effective full stack technology for building scalable and productive business applications. It includes products like the WebSphere Application Server, HTTP Server, MQ, Process Server, Integration Designer, and Process Center. The WebSphere Application Server is the base for most WebSphere products and uses profiles to configure servers for different needs like deployment management, node management, and application hosting. WebSphere MQ provides messaging solutions and Integration Designer enables visual development of integrated business processes.