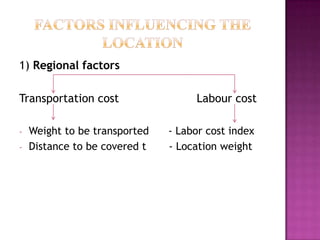
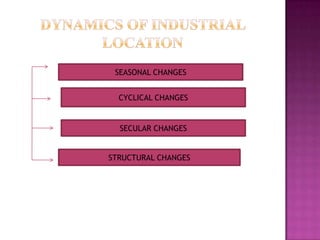
This document discusses factors that affect the ideal location of an industry. It notes that the aim of any industry is to earn profits, and profit depends on production and distribution costs. An ideal location can minimize these costs. The document then lists and explains various regional, secondary, raw material, and other factors that must be considered to properly locate an industry and maximize profits while minimizing costs.