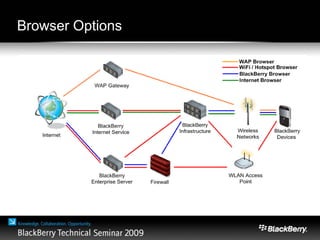
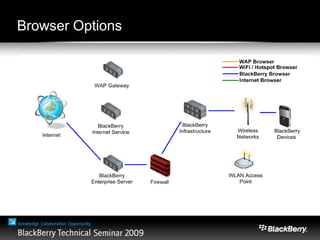
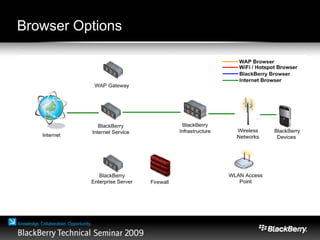
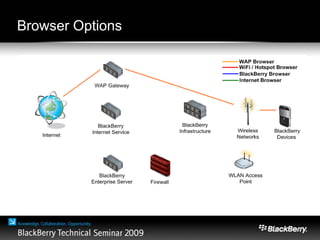
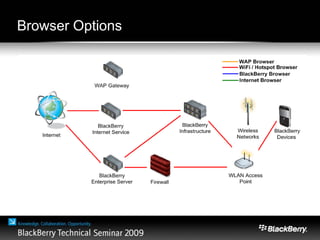
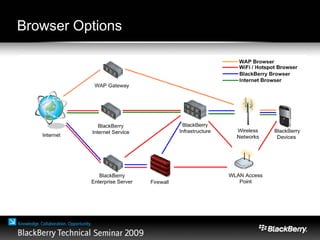
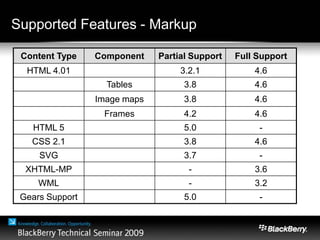
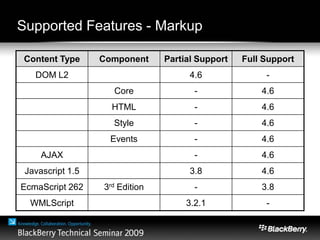
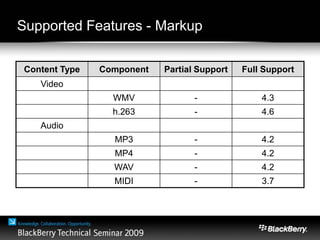
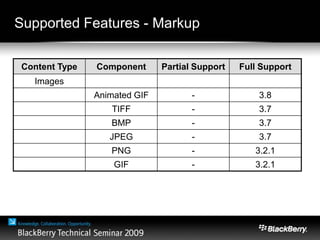
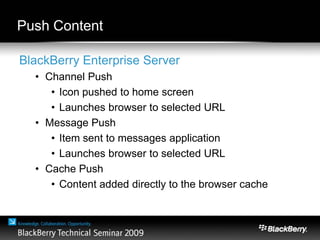
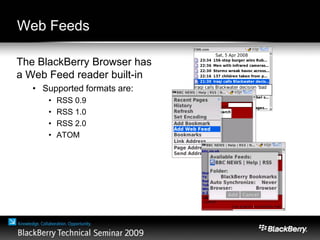
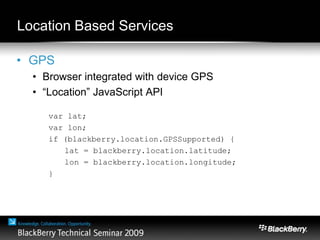
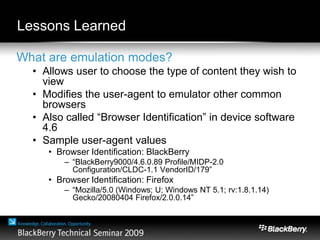
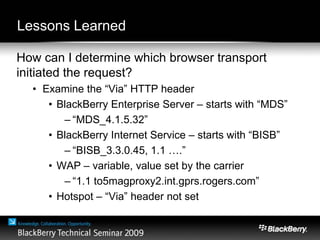
The document provides an overview of web development specifically for Blackberry smartphones, focusing on the advantages and challenges of creating web applications for mobile devices. It outlines various browser options, key features of the Blackberry environment, and design considerations to optimize web applications for smaller screens and variable network speeds. Additionally, it highlights the upcoming features in the Blackberry 5.0 browser and offers resources for developers, including tools and community support.