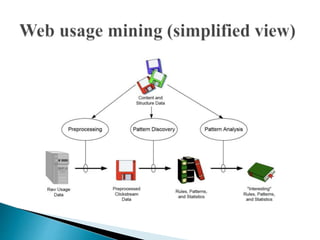
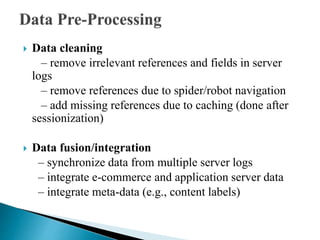
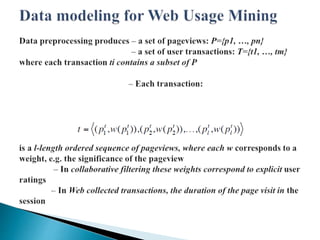
This document discusses web usage mining and related processes. It begins with an introduction to web usage mining and its goal of analyzing user behavioral patterns on websites. It then covers topics like data collection and pre-processing, including cleaning, fusion, transformation, and reduction. Specific pre-processing techniques are described, such as sessionization, pageview identification, and user identification. The document also discusses data modeling and discovery of patterns, including various pattern types like decision trees, paths, groups, and associations. Finally, it covers potential applications and conclusions about web usage mining.